数据读取部分实现
文中采用了tensorflow的从文件直接读取数据的方式,逻辑流程如下,
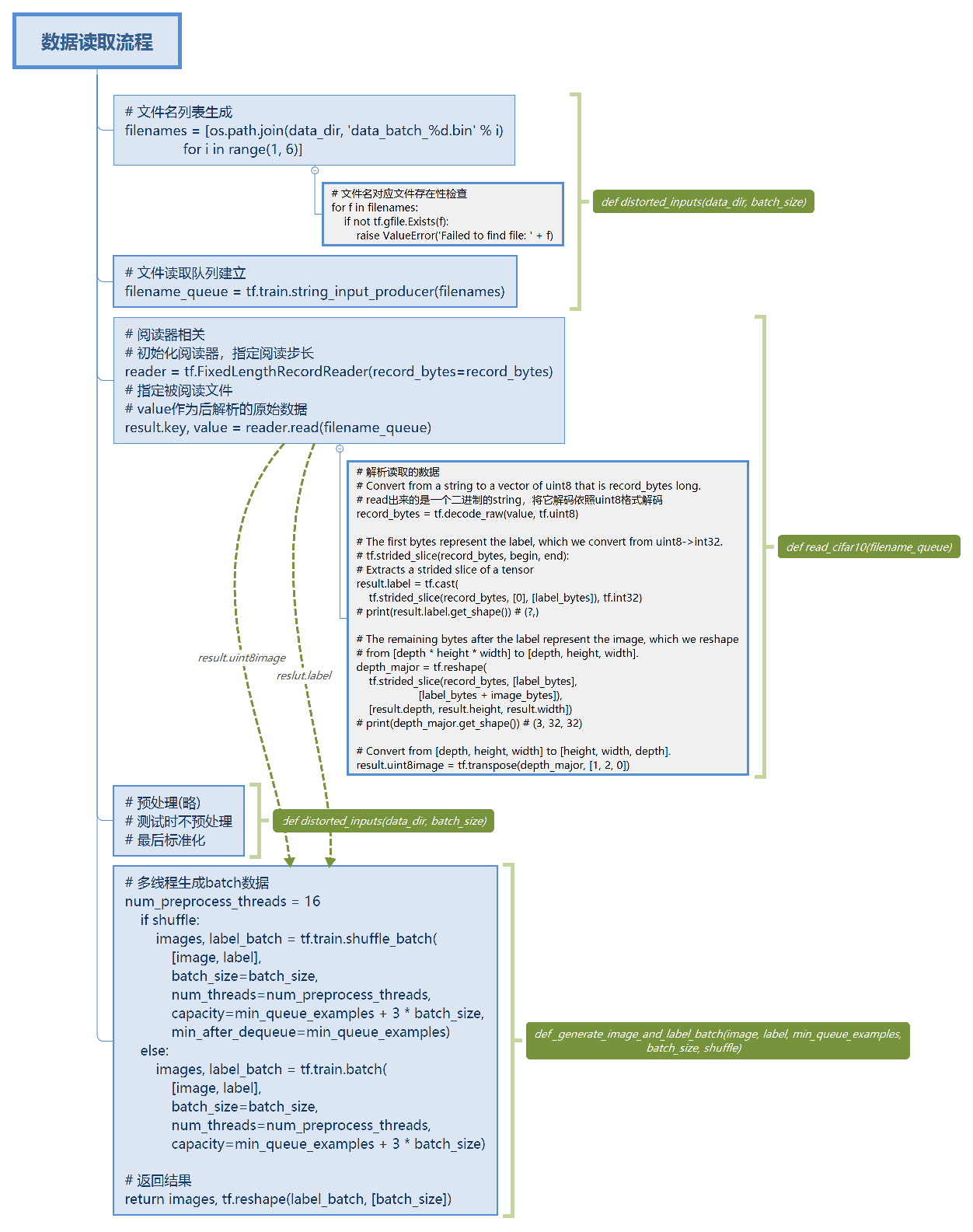
实现如下,
# Author : Hellcat
# Time : 2017/12/9
import os
import tensorflow as tf
IMAGE_SIZE = 24
NUM_CLASSES = 10
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = 50000
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = 10000
def read_cifar10(filename_queue):
"""Reads and parses examples from CIFAR10 data files.
Recommendation: if you want N-way read parallelism, call this function
N times. This will give you N independent Readers reading different
files & positions within those files, which will give better mixing of
examples.
Args:
filename_queue: A queue of strings with the filenames to read from.
Returns:
An object representing a single example, with the following fields:
height: number of rows in the result (32)
number of columns in the result (32)
depth: number of color channels in the result (3)
key: a scalar string Tensor describing the filename & record number
for this example.
label: an int32 Tensor with the label in the range 0..9.
uint8image: a [height, width, depth] uint8 Tensor with the image data
"""
class CIFAR10Record(object):
pass
result = CIFAR10Record()
# Dimensions of the images in the CIFAR-10 dataset.
label_bytes = 1 # 2 for CIFAR-100
result.height = 32
result.width = 32
result.depth = 3
image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth
record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes
# Read a record, getting filenames from the filename_queue.
# No header or footer in the CIFAR-10 format, so we leave header_bytes
# and footer_bytes at their default of 0.
# 初始化阅读器
reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes)
# 指定被阅读文件
result.key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
# Convert from a string to a vector of uint8 that is record_bytes long.
# read出来的是一个二进制的string,将它解码依照uint8格式解码
record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8)
# The first bytes represent the label, which we convert from uint8->int32.
# tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, begin, end):
# Extracts a strided slice of a tensor
result.label = tf.cast(
tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32)
# print(result.label.get_shape()) # (?,)
# The remaining bytes after the label represent the image, which we reshape
# from [depth * height * width] to [depth, height, width].
depth_major = tf.reshape(
tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes],
[label_bytes + image_bytes]),
[result.depth, result.height, result.width])
# print(depth_major.get_shape()) # (3, 32, 32)
# Convert from [depth, height, width] to [height, width, depth].
result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0])
return result
def distorted_inputs(data_dir, batch_size):
'''
读入&预处理图片
:param data_dir: bin文件位置
:param batch_size: 单批输出大小
:return:
'''
# 读取文件名
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i)
for i in range(1, 6)]
# 检查文件名对应的文件是否存在
for f in filenames:
if not tf.gfile.Exists(f):
raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f)
# 建立文件名队列
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
# 读取文件得到图片,转为tf.float32
read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue)
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32)
height = IMAGE_SIZE
width = IMAGE_SIZE
# 随机裁剪
distorted_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [height, width, 3])
# 随机翻转
distorted_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(distorted_image)
# 随机亮度
distorted_image = tf.image.random_brightness(distorted_image,max_delta=63)
# 随机对比度
distorted_image = tf.image.random_contrast(distorted_image,lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
# 标准化
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(distorted_image)
'''
tf.Tensor.set_shape() 方法(method)会更新(updates)一个 Tensor 对象的静态 shape ,
当静态 shape 信息不能够直接推导得出的时候,此方法常用来提供额外的 shape 信息。
它不改变此 tensor 动态 shape 的信息。
tf.reshape() 操作(operation)会以不同的动态 shape 创建一个新的 tensor。
tf.strided_slice()由于不会显示的计算tensor形状,所以其返回shape是?的,所以label
需要使用set_shape,而image在skice之后已经reshape了,所以其tensor是有静态shape的。
'''
# Set the shapes of tensors.
# float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
# Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties.
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4
min_queue_examples = int(NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN *
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue)
print ('Filling queue with %d CIFAR images before starting to train. '
'This will take a few minutes.' % min_queue_examples)
# Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples.
return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label,
min_queue_examples, batch_size,
shuffle=True)
def _generate_image_and_label_batch(image, label, min_queue_examples,
batch_size, shuffle):
'''
单batch数据生成
:param image: reader读取的值经过处理后的tensor
:param label: reader读取的值经过处理后的tensor
:param min_queue_examples: 最短队列长度
:param batch_size: batch尺寸
:param shuffle: 是否随机化
:return: batch的图片和标签
'''
num_preprocess_threads = 16
if shuffle:
images, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch(
[image, label],
batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=num_preprocess_threads,
capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size,
min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples)
else:
images, label_batch = tf.train.batch(
[image, label],
batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=num_preprocess_threads,
capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size)
# Display the training images in the visualizer.
tf.summary.image('images', images)
return images, tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size])
def inputs(eval_data, data_dir, batch_size):
"""Construct input for CIFAR evaluation using the Reader ops.
Args:
eval_data: bool, indicating if one should use the train or eval data set.
data_dir: Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.
batch_size: Number of images per batch.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
"""
# 建立文件名队列
if not eval_data:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i)
for i in range(1, 6)]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN
else:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_batch.bin')]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL
# 确认文件是否存在
for f in filenames:
if not tf.gfile.Exists(f):
raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f)
# 读取文件名队列
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
# 读取文件
read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue)
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32)
height = IMAGE_SIZE
width = IMAGE_SIZE
# 重置图片大小,简单裁剪或填充
resized_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image,
height, width)
# 标准化
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(resized_image)
# Set the shapes of tensors.
float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
# Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties.
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4
min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_per_epoch *
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue)
# Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples.
return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label,
min_queue_examples, batch_size,
shuffle=False)
TensorFlow使用总结
tensorflow直接从文件读取数据流程
1.建立文件名队列
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
2.阅读器初始化 & 单次读取规则设定
# 初始化阅读器 reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes) # 指定被阅读文件 result.key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
3.对单次读取的数据tensor进行处理
# Convert from a string to a vector of uint8 that is record_bytes long. # read出来的是一个二进制的string,将它解码依照uint8格式解码 record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) …… ……
由于读取来的tensor不具有静态shape,需要使用tensor.set_shape()指定shape(或者在处理中显示的赋予shape如使用reshape等函数),否则无法建立图
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
4.将最后的规则tensor传入batch生成池节点中,输出的张量可以直接feed进网络
images_train, labels_train = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=batch_size)
…… ……
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_train, labels_train])
_, loss_value = sess.run(
[train_op, loss],
feed_dict={image_holder:image_batch, label_holder:label_batch})
5.初始化队列(相关的线程控制器组件添加也在这里)
# 启动数据增强队列 tf.train.start_queue_runners()
附上线程控制组件使用示意,
import tensorflow as tf sess = tf.Session() coord = tf.train.coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) # 训练过程 coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)