这里的数组要点在于:
- 数组结构,array.array或者numpy.array
- 本篇的数组仅限一维,不过基础的C数组也是一维
一、分块讲解
源函数
/* Average values in an array */
double avg(double *a, int n) {
int i;
double total = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total += a[i];
}
return total / n;
}
封装函数
/* Call double avg(double *, int) */
static PyObject *py_avg(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) {
PyObject *bufobj;
Py_buffer view;
double result;
/* Get the passed Python object */
// 在一个C对象指针中储存一个Python对象(没有任何转换)。
// 因此,C程序接收传递的实际对象。对象的引用计数没有增加。
// 存储的指针不是空的
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "O", &bufobj)) {
return NULL;
}
/* Attempt to extract buffer information from it */
if (PyObject_GetBuffer(bufobj, &view,
PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_FORMAT) == -1) {
return NULL;
}
if (view.ndim != 1) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected a 1-dimensional array");
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return NULL;
}
/* Check the type of items in the array */
if (strcmp(view.format,"d") != 0) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected an array of doubles");
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return NULL;
}
/* Pass the raw buffer and size to the C function */
result = avg(view.buf, view.shape[0]);
/* Indicate we're done working with the buffer */
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return Py_BuildValue("d", result);
}
代码的关键点在于 PyBuffer_GetBuffer() 函数。 给定一个任意的Python对象,它会试着去获取底层内存信息,它简单的抛出一个异常并返回-1. 传给 PyBuffer_GetBuffer() 的特殊标志给出了所需的内存缓冲类型。 例如,PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS 表示是一个连续的内存区域。
if (PyObject_GetBuffer(bufobj, &view,
PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_FORMAT) == -1) {
return NULL;
}
对于数组、字节字符串和其他类似对象而言,一个 Py_buffer 结构体包含了所有底层内存的信息。 它包含一个指向内存地址、大小、元素大小、格式和其他细节的指针。下面是这个结构体的定义:
typedef struct bufferinfo {
void *buf; /* Pointer to buffer memory */
PyObject *obj; /* Python object that is the owner */
Py_ssize_t len; /* Total size in bytes */
Py_ssize_t itemsize; /* Size in bytes of a single item */
int readonly; /* Read-only access flag */
int ndim; /* Number of dimensions */
char *format; /* struct code of a single item */
Py_ssize_t *shape; /* Array containing dimensions */
Py_ssize_t *strides; /* Array containing strides */
Py_ssize_t *suboffsets; /* Array containing suboffsets */
} Py_buffer;
本节中,我们只关注接受一个双精度浮点数数组作为参数。 要检查元素是否是一个双精度浮点数,只需验证 format 属性是不是字符串”d”. 这个也是 struct 模块用来编码二进制数据的。 通常来讲,format 可以是任何兼容 struct 模块的格式化字符串, 并且如果数组包含了C结构的话它可以包含多个值。
/* Check the type of items in the array */
if (strcmp(view.format,"d") != 0) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected an array of doubles");
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return NULL;
}
一旦我们已经确定了底层的缓存区信息,那只需要简单的将它传给C函数,然后会被当做是一个普通的C数组了。 实际上,我们不必担心是怎样的数组类型或者它是被什么库创建出来的。 这也是为什么这个函数能兼容 array 模块也能兼容 numpy 模块中的数组了。
在返回最终结果之前,底层的缓冲区视图必须使用 PyBuffer_Release() 释放掉。 之所以要这一步是为了能正确的管理对象的引用计数。
库信息修改
/* Module method table */
static PyMethodDef SampleMethods[] = {
{"gcd", py_gcd, METH_VARARGS, "Greatest common divisor"},
{"in_mandel", py_in_mandel, METH_VARARGS, "Mandelbrot test"},
{"divide", py_divide, METH_VARARGS, "Integer division"},
{"avg", py_avg, METH_VARARGS, "Average values in an array"},
{ NULL, NULL, 0, NULL}
};
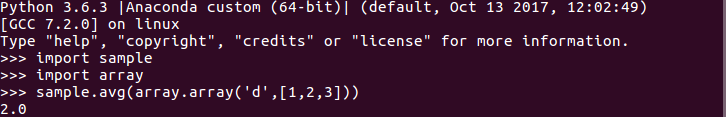
测试
python setup.py install
二、全程序展示
pysample.c全文如下,其他部分并未修改,参见上节即可
#include "Python.h"
#include "sample.h"
/* int gcd(int, int) */
static PyObject *py_gcd(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) {
int x, y, result;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args,"ii", &x, &y)) {
return NULL;
}
result = gcd(x,y);
return Py_BuildValue("i", result);
}
/* int in_mandel(double, double, int) */
static PyObject *py_in_mandel(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) {
double x0, y0;
int n;
int result;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "ddi", &x0, &y0, &n)) {
return NULL;
}
result = in_mandel(x0,y0,n);
return Py_BuildValue("i", result);
}
/* int divide(int, int, int *) */
static PyObject *py_divide(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) {
int a, b, quotient, remainder;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "ii", &a, &b)) {
return NULL;
}
quotient = divide(a,b, &remainder);
return Py_BuildValue("(ii)", quotient, remainder);
}
/* Call double avg(double *, int) */
static PyObject *py_avg(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) {
PyObject *bufobj;
Py_buffer view;
double result;
/* Get the passed Python object */
// 在一个C对象指针中储存一个Python对象(没有任何转换)。
// 因此,C程序接收传递的实际对象。对象的引用计数没有增加。
// 存储的指针不是空的
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "O", &bufobj)) {
return NULL;
}
/* Attempt to extract buffer information from it */
if (PyObject_GetBuffer(bufobj, &view,
PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_FORMAT) == -1) {
return NULL;
}
if (view.ndim != 1) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected a 1-dimensional array");
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return NULL;
}
/* Check the type of items in the array */
if (strcmp(view.format,"d") != 0) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected an array of doubles");
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return NULL;
}
/* Pass the raw buffer and size to the C function */
result = avg(view.buf, view.shape[0]);
/* Indicate we're done working with the buffer */
PyBuffer_Release(&view);
return Py_BuildValue("d", result);
}
/* Module method table */
static PyMethodDef SampleMethods[] = {
{"gcd", py_gcd, METH_VARARGS, "Greatest common divisor"},
{"in_mandel", py_in_mandel, METH_VARARGS, "Mandelbrot test"},
{"divide", py_divide, METH_VARARGS, "Integer division"},
{"avg", py_avg, METH_VARARGS, "Average values in an array"},
{ NULL, NULL, 0, NULL}
};
/* Module structure */
static struct PyModuleDef samplemodule = {
PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,
"sample", /* name of module */
"A sample module", /* Doc string (may be NULL) */
-1, /* Size of per-interpreter state or -1 */
SampleMethods /* Method table */
};
/* Module initialization function */
PyMODINIT_FUNC
PyInit_sample(void) {
return PyModule_Create(&samplemodule);
}