spring中的配置文件有两种:
- 以XML结尾的spring配置文件
- 以properties结尾的属性配置文件
在spring中有两种方式加载这两种文件:
- 通过注解+java配置的方式
- 通过XML的方式
详细配置且看下文:
一、加载spring配置文件*.xml
假设有一个关于数据源的配置文件spring-database.xml,它的配置内容如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> 9 10 <!-- 配置数据源 --> 11 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> 12 <property name="driverClassName" value="org.postgresql.Driver" /> 13 <property name="url" value="jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5433/postgres" /> 14 <property name="username" value="postgres" /> 15 <property name="password" value="postgres" /> 16 </bean> 17 </beans>
1⃣️通过注解+java配置方式
第一步:通过注解+配置方式时需要创建一个配置类AppConfig.java
1 @ComponentScan(basePackages= {"com.hyc.config"}) 2 @ImportResource({"classpath:spring-database.xml"}) 3 public class AppConfig { 4 5 }
上面的配置中:
1⃣️使用注解@ImportResource引入配置文件,可以是多个;
2⃣️通过注解@ComponentScan定义spring扫描的包(因为下面有个bean的类我定义在这个包下,所以这里加上这个扫描路径)
第二步:写一个获取数据库连接的类
1 package com.hyc.config; 2 /* 3 * 通过注解+配置的方式加载spring配置文件 4 */ 5 6 import java.sql.Connection; 7 import java.sql.SQLException; 8 9 import javax.sql.DataSource; 10 11 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 12 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 13 14 @Component("dbba") 15 public class DatasourceByAnnotation { 16 17 @Autowired 18 DataSource dataSource = null; 19 20 // 获取数据库连接 21 public Connection getConnection() { 22 Connection conn = null; 23 try { 24 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); 25 if (null != conn) { 26 System.out.println("获取数据库连接成功"); 27 } else { 28 System.out.println("获取数据库连接失败"); 29 } 30 } catch (SQLException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 34 return conn; 35 } 36 }
上面代码中加粗部分:
- 此类所在的包,需要告知spring在哪个包下扫描,如果配置文件类和这个类在同意包下,则不需要配置
- @Component注解:定义此bean的名称,这样可以通过getBean方法获取到
第三步:编写测试方法
1 public class GetDatasourceByConfigTest { 2 3 @Test 4 public void testGetByConfig() { 5 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); 6 DatasourceByAnnotation dba = (DatasourceByAnnotation) context.getBean("dbba"); 7 dba.getConnection(); 8 } 9 }
这里就是使用注解+java配置方式获取bean,调用其方法,测试结果:
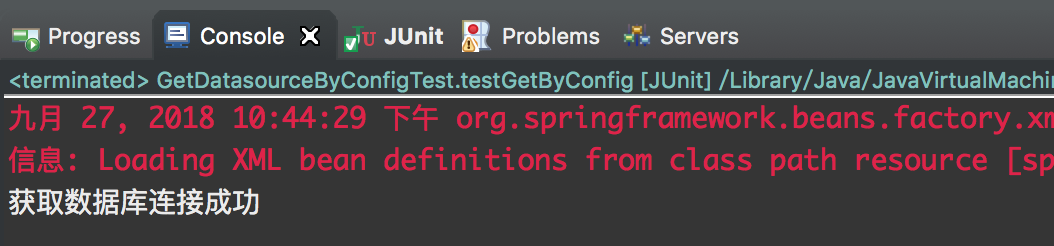
配置成功,有些书上说这个地方获取DataSource时可以使用自动注解,我试了一下是不可以的,其实按理说也是不行的,因为DataSource是第三方包中的类,我们无法对它进行修改,如果使用自动注解获取,必定要给他增加@Component注解进行定义,所以这种方式只能通过配置获取。
2⃣️通过XML方式
使用XML的方式,假设我要在spring-bean.xml中引入spring-database.xml文件,只需要在spring-bean.xml中加入一句代码即可:
<import resource="spring-database.xml"/>
这样就可以当作spring-bean.xml文件进行使用了,其实这种方式主要是为了将不同业务的配置通过文件区分开来,不要是spring-bean.xml文件变得很庞大复杂,具体实现不做介绍。
二、加载属性配置文件*.properties
依然是数据源的配置文件,只不过这次将其写在属性配置文件db.properties中,配置如下:
1 db.driver=org.postgresql.Driver 2 db.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5433/postgres 3 db.username=postgresql 4 db.pwd=postgresql
1⃣️通过注解+java配置方式
第一步:通过注解+配置方式时需要创建一个配置类AppConfig.java
1 @Configuration 2 @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:db.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true) 3 public class AppConfig { 4 5 }
上面的配置中:
- 使用注解@PropertySource引入配置文件,可以是多个;
- 通过注解@Configuration不能缺失,否则将找不到这个配置
第二步:测试
1 @Test 2 public void testGetPropByConfig() { 3 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); 4 String url = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("db.url"); 5 System.out.println(url); 6 }
获取属性文件中的数据库连接URL,看能不能获取到,测试结果如下:
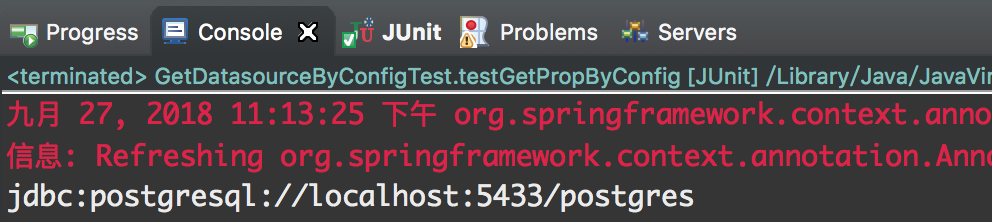
可见获取成功。
上面的测试中是通过环境来获取对应的配置属性,但如果这样在spring中是没有解析属性占位符的能力,spring推荐使用一个属性文件解析类PropertySourcePlaceholderConfigurer,使用它就意味允许spring解析对应的属性文件,并通过占位符去引用对应的配置。
修改上述的配置类为如下:
1 @Configuration 2 @ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.hyc.config" }) 3 @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:db.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true) 4 public class AppConfig { 5 6 /** 7 * 定义一个PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类的bean,它的作用是为了让spring能解析占位符 8 * @return 9 */ 10 @Bean 11 public PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer propertyPlaceholderConfigurer() { 12 return new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(); 13 } 14 15 }
有了上面的配置,就可以通过占位符引用属性值了,如下:
1 @Component("dsb") 2 public class DataSourceBean { 3 4 @Value("${db.driver}") 5 private String driver = null; 6 7 @Value("${db.url}") 8 private String url = null; 9 10 @Value("${db.username}") 11 private String userName = null; 12 13 @Value("${db.pwd}") 14 private String pwd = null; 15 16 public void getDataSourceUrl() { 17 System.out.println(url); 18 } 19 20 }
编写测试类:
1 @Test 2 public void testGetPropByConfig1() { 3 @SuppressWarnings("resource") 4 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); 5 DataSourceBean ds = (DataSourceBean) context.getBean("dsb"); 6 ds.getDataSourceUrl(); 7 }
这样就能获取到了
2⃣️通过XML方式
XML方式的配置如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> 9 10 <!-- 配置单个属性文件 --> 11 <context:property-placeholder 12 ignore-resource-not-found="false" location="classpath*:db.properties" /> 13 <!-- 配置多个属性文件 --> 14 <bean 15 class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> 16 <property name="locations"> 17 <array> 18 <value>classpath:db.properties</value> 19 <value>classpath:log4j.properties</value> 20 </array> 21 </property> 22 <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="false"></property> 23 </bean> 24 </beans>
如上,可以配置多个,也可以配置一个,这样以来,就能在spring的配置文件中通过占位符引用属性了。