代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理
代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-cookbook
解决问题:使用“词袋”嵌入来进行垃圾短信的预测(使用逻辑回归算法)
缺点:不考虑相关单词顺序特征,长文本的处理困难
步骤如下:
step1:导入需要的包
step2:准备数据集
step3:选择参数(每个文本保留多少单词数,最低词频是多少)
step4:构建词袋
step5:分割数据集
step6:构建图
step7:训练
step8:测试
step1:导入需要的包
import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import os import numpy as np import csv import string import requests import io from zipfile import ZipFile from tensorflow.contrib import learn from tensorflow.python.framework import ops ops.reset_default_graph() # Start a graph session sess = tf.Session()
step2:准备数据集
# Check if data was downloaded, otherwise download it and save for future use save_file_name = os.path.join('temp','temp_spam_data.csv') if os.path.isfile(save_file_name): text_data = [] with open(save_file_name, 'r') as temp_output_file: reader = csv.reader(temp_output_file) for row in reader: text_data.append(row) else: zip_url = 'http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00228/smsspamcollection.zip' r = requests.get(zip_url) z = ZipFile(io.BytesIO(r.content)) file = z.read('SMSSpamCollection') # Format Data text_data = file.decode() text_data = text_data.encode('ascii',errors='ignore') text_data = text_data.decode().split(' ') text_data = [x.split(' ') for x in text_data if len(x)>=1] # And write to csv with open(save_file_name, 'w') as temp_output_file: writer = csv.writer(temp_output_file) writer.writerows(text_data) texts = [x[1] for x in text_data] target = [x[0] for x in text_data] # Relabel 'spam' as 1, 'ham' as 0 target = [1 if x=='spam' else 0 for x in target] # Normalize text,为减少无意义的词汇,对文本进行规则化处理 # Lower case texts = [x.lower() for x in texts] # Remove punctuation texts = [''.join(c for c in x if c not in string.punctuation) for x in texts] # Remove numbers texts = [''.join(c for c in x if c not in '0123456789') for x in texts] # Trim extra whitespace texts = [' '.join(x.split()) for x in texts]
step3:选择参数
# Plot histogram of text lengths文本数据中的单词数的直方图 text_lengths = [len(x.split()) for x in texts] text_lengths = [x for x in text_lengths if x < 50] plt.hist(text_lengths, bins=25) plt.title('Histogram of # of Words in Texts')
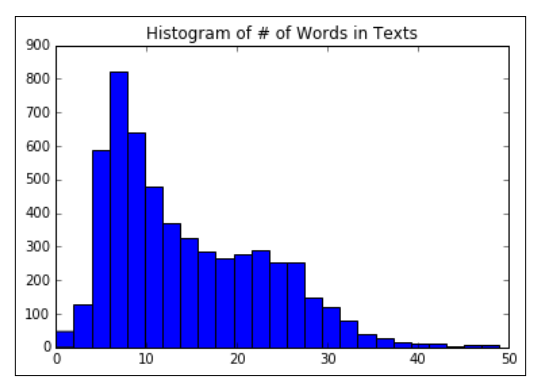
step4:构建词袋
# Choose max text word length at 25,也可以设为30或者40 sentence_size = 25 min_word_freq = 3 # Setup vocabulary processor vocab_processor = learn.preprocessing.VocabularyProcessor(sentence_size, min_frequency=min_word_freq) # Have to fit transform to get length of unique words. vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts) embedding_size = len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_)
step5:分割数据集
# Split up data set into train/test train_indices = np.random.choice(len(texts), round(len(texts)*0.8), replace=False) test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(texts))) - set(train_indices))) texts_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in train_indices] texts_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in test_indices] target_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in train_indices] target_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in test_indices]
step6:构建图
step6.1:构建出文本的向量
# Setup Index Matrix for one-hot-encoding,使用该矩阵为每个单词查找稀疏向量 identity_mat = tf.diag(tf.ones(shape=[embedding_size])) # Create variables for logistic regression A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[embedding_size,1])) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1])) # Initialize placeholders x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[sentence_size], dtype=tf.int32) y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Text-Vocab Embedding,使用tf的嵌入查找函数来映射句子中的单词为单位矩阵的one-hot向量,再进行求和 # tf.nn.embedding_lookup(y,x)x为索引,找出y中对应索引的值 x_embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(identity_mat, x_data) x_col_sums = tf.reduce_sum(x_embed, 0) # Declare model operations x_col_sums_2D = tf.expand_dims(x_col_sums, 0)
疑问:如何利用词袋将文本变成向量?
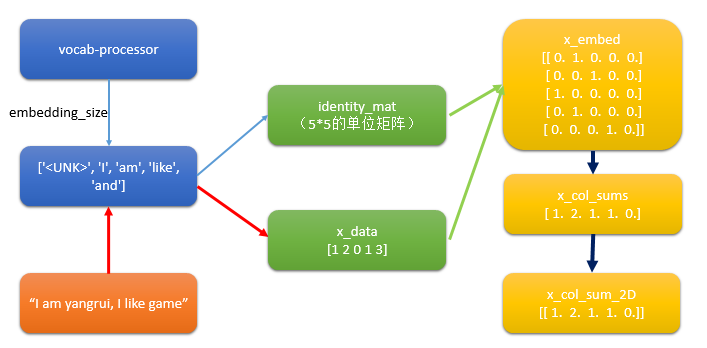
step6.2 构建图
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_col_sums_2D, A), b) # Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(model_output, y_target)) # Prediction operation prediction = tf.sigmoid(model_output) # Declare optimizer my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001) train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
step7:训练
# Intitialize Variables init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess.run(init) # Start Logistic Regression print('Starting Training Over {} Sentences.'.format(len(texts_train))) loss_vec = [] train_acc_all = [] train_acc_avg = [] for ix, t in enumerate(vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts_train)): y_data = [[target_train[ix]]] sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: t, y_target: y_data}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: t, y_target: y_data}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) if (ix+1)%10==0: print('Training Observation #' + str(ix+1) + ': Loss = ' + str(temp_loss)) # Keep trailing average of past 50 observations accuracy # Get prediction of single observation [[temp_pred]] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data:t, y_target:y_data}) # Get True/False if prediction is accurate train_acc_temp = target_train[ix]==np.round(temp_pred) train_acc_all.append(train_acc_temp) if len(train_acc_all) >= 50: train_acc_avg.append(np.mean(train_acc_all[-50:]))
step8:测试
# Get test set accuracy print('Getting Test Set Accuracy For {} Sentences.'.format(len(texts_test))) test_acc_all = [] for ix, t in enumerate(vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts_test)): y_data = [[target_test[ix]]] if (ix+1)%50==0: print('Test Observation #' + str(ix+1)) # Keep trailing average of past 50 observations accuracy # Get prediction of single observation [[temp_pred]] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data:t, y_target:y_data}) # Get True/False if prediction is accurate test_acc_temp = target_test[ix]==np.round(temp_pred) test_acc_all.append(test_acc_temp) print(' Overall Test Accuracy: {}'.format(np.mean(test_acc_all))) # Plot training accuracy over time plt.plot(range(len(train_acc_avg)), train_acc_avg, 'k-', label='Train Accuracy') plt.title('Avg Training Acc Over Past 50 Generations') plt.xlabel('Generation') plt.ylabel('Training Accuracy') plt.show()