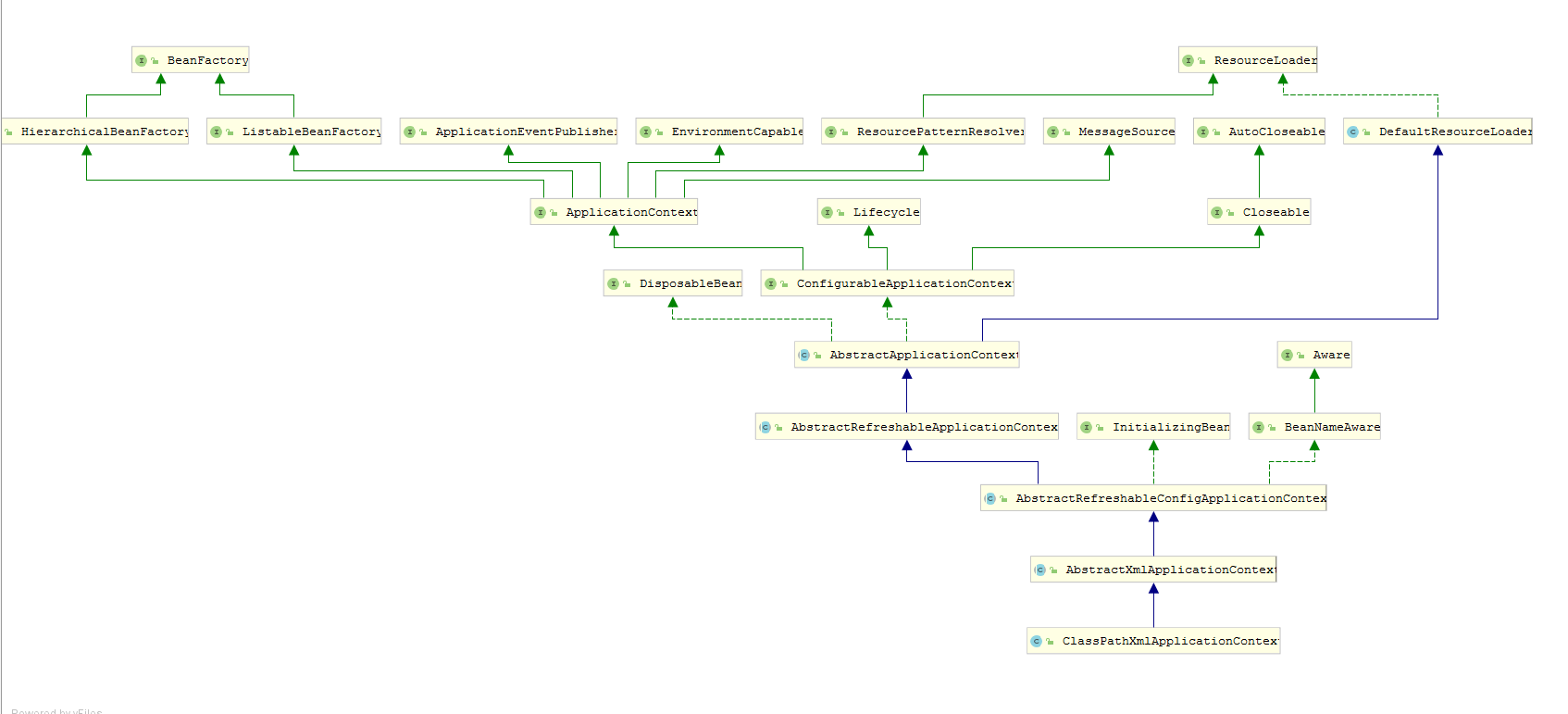
springboot启动时,默认配置文件会加载到 beanfactory
以下简单代码看配置文件的加载过程
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"}); context.start(); System.out.println(" app run "); System.in.read(); // 按任意键退出 } }
进入ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
//继承parent的applicationContext super(parent);
//将xml放入当前容器 this.setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) {
//初始化beanfactory. this.refresh(); } }
主要是refresh方法,从中可以看出applicationcontext与beanfactory的关系
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) { this.prepareRefresh();
//获取新的Bean工厂, 加载Xml资源并解析,根据解析结果组装BeanDefinitions ,然后初始化BeanFactory的过程 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory(); this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
//beanfactory准备工作完成后的后置处理工作 this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//执行postprocessor方法 this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册beanpostprocessor(bean的后置处理器)在创建bean前后等执行 this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化message组件,(做国际化,消息绑定解析) this.initMessageSource();
//初始化事件派发器 this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//子类重写这个方法,容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑如创建tomcat, this.onRefresh();
//注册应用监听。就是注册实现了ApplicationListener接口的监听器bean,这些监听器是注册到ApplicationEventMulticaster中的
this.registerListeners();
//注册非懒加载的单例bean
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//
/完成context的刷新。主要是调用LifecycleProcessor的onRefresh()方法,并且发布事件(ContextRefreshedEvent)
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) { if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) { this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9); } this.destroyBeans(); this.cancelRefresh(var9); throw var9; } finally { this.resetCommonCaches(); } } }
进入 obtainFreshBeanFactory初始化beanFactory方法有个refreshbeanfactory 方法
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (this.hasBeanFactory()) { this.destroyBeans(); this.closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId()); this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//组装组装BeanDefinitions this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException var5) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5); } }
组装BeanDefinitions
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); this.initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); } protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) { reader.setValidating(this.validating); } protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = this.getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } //与上面setConfigLocations(“”)对应
String[] configLocations = this.getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
解析xml使用了DocumentBuilder
此处仿写了 读取文件的方法,放到resource根目录,在项目中获取数据的方法:
name=testDemo
Stirng filename = "test.properties";
this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(filename); Properties contextConfig = new Properties(); try { contextConfig.load(is); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(null != is){ try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }