A. Level Statistics
签到。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/10 22:41:10
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 100 + 5;
int n;
int p[N], c[N];
void run() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> p[i] >> c[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(p[i] < p[i - 1] || c[i] < c[i - 1]) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
if(p[i] < c[i]) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
if(p[i] - p[i - 1] < c[i] - c[i - 1]) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
}
cout << "YES" << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
B. Middle Class
贪心。排序后求出前缀和直接搞即可。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/10 22:48:39
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, x;
int a[N];
ll sum[N];
void run() {
cin >> n >> x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
reverse(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(1ll * x * i <= sum[i]) ans = i;
}
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
C. Circle of Monsters
题意:
现有(n)只怪兽围成环,每个怪兽有两个属性(a_i,b_i),(a_i)为其生命值,(b_i)为怪兽死亡后对下一个怪兽造成的伤害。
现在你每次可以打一发子弹使得一个怪兽生命减(1),问最少需要打多少子弹,使得所有怪兽都死亡。
思路:
如果是一条链的话,那直接从第一个怪兽开始打,所需要的最少子弹数都是不变的。
但题目中是一个环,我们可以直接枚举起点,然后就会在某个地方断开变为一条链。因为链的情况答案不会发生改变,提前通过前缀和计算即可。
详见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/11 0:04:38
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 6e5 + 5;
int n;
ll a[N], b[N], sum[N];
void run() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
a[i + n] = a[i], b[i + n] = b[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + max(0ll, a[i] - b[i - 1]);
ll ans = 1e18;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ll res = a[i] + sum[i + n - 1] - sum[i];
ans = min(ans, res);
}
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
D. Minimum Euler Cycle
就类似于这样走就行:
(1,2,1,3,cdots,1,n,2,3,2,4,cdots,2,n,3,4,cdots,n-1,n,1)
即可。
随便求一下就行。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/15 8:39:21
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
ll n, l, r;
ll f[N];
void init() {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = f[i - 1] + 2 * (n - i);
}
}
int calc(ll i) {
if(i == f[n] + 1) return 1;
int t = lower_bound(f + 1, f + n + 1, i) - f - 1;
i -= f[t];
if(i & 1) return t + 1;
else return i / 2 + t + 1;
}
void run() {
cin >> n >> l >> r;
init();
for(ll i = l; i <= r; i++) {
cout << calc(i) << "
"[i == r];
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
E. Divisor Paths
题意:
给出整数(D,Dleq 10^{16}),现在由(D)的所有因子按照如下规则构造一张图:
- 对于两个因子(u,v),若(u|v且v/u=p,p)为一个素数,那么(u,v)之间存在一条边;
- 边((u,v))的边权为整除(u)但不整除(v)的因子个数。
类似于下图:
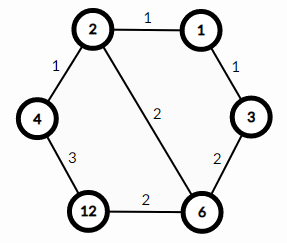
现在给出多组询问,对于每组询问((u,v)),回答从(u)到(v)最短路径有多少条。
思路:
这种数学题,我们一点一点来剖析其性质。
- 对于一条边((u,v),u<v),其边权为(d(v)-d(u)),其中(d(i))为(i)的因子个数。
那么对于一条路径而言,长度只于起点和终点两点有关。
我们现在要从(x)走到(y,x>y),路径长度为(d(x)-d(y))。
- 我们可以将该图形抽象为(k)维网格图,每次只能在某一维度走一步,每一维代表一个素因子。
据此我们可以得出从(x)到(y)的最优的走法:(x
ightarrow gcd(x,y)
ightarrow y)或者(x
ightarrow lcm(x,y)
ightarrow y)。
接下来就证明第一种走法比第二种走法更优。
我们记(g=gcd(x,y),l=lcm(x,y)),那么两种的贡献分别为:(d(x)+d(y)-d(g)-d(g),d(l)+d(l)-d(x)-d(y)),我们将两者相减:
这里我们应该还是比较容易发现等式是小于等于(0)的,感觉就是证明(d(a)+d(b)-1leq d(ab)=d(a)cdot d(b),a,b)互质。
所以我们就证明了最优走法。
也有另外一种证明方法:因为是网格图,假设为二维网格图,我们要从(xy
ightarrow (x-1)(y+1)),那么有两种走法,通过简单比较就会发现肯定先往小的走再往大的走更优,然后就没了。
我们事先在(O(sqrt{n}))的时间复杂度内找到所有(D)的素因子,然后对于每个询问直接搞就行。
代码如下:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/15 18:59:20
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#include <numeric>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5, MOD = 998244353;
int qpow(ll a, ll b) {
ll res = 1;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) res = res * a % MOD;
a = a * a % MOD;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void run() {
ll D; cin >> D;
vector <ll> primes;
for(ll i = 2; i * i <= D; i++) if(D % i == 0) {
primes.push_back(i);
while(D % i == 0) D /= i;
}
if(D > 1) primes.push_back(D);
vector <ll> fac(100), inv(100);
fac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < 100; i++) fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % MOD;
inv[99] = qpow(fac[99], MOD - 2);
for(int i = 98; i >= 0; i--) inv[i] = inv[i + 1] * (i + 1) % MOD;
auto calc = [&](ll x, ll y) {
vector <ll> v;
for(auto it : primes) if(x % it == 0) {
int cnt = 0;
while(x % it == 0) {
if(y % it == 0) {
x /= it, y /= it;
} else {
x /= it;
++cnt;
}
}
v.push_back(cnt);
}
ll res = fac[accumulate(all(v), 0)];
for(auto it : v) res = res * inv[it] % MOD;
return res;
};
int q; cin >> q;
while(q--) {
ll a, b; cin >> a >> b;
ll g = __gcd(a, b);
ll ans = calc(a, g) * calc(b, g) % MOD;
cout << ans << '
';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
F. Strange Function
题意:
给出序列(a_{1,2,...,n}),现在定义(f(a))表示选择所有(i),满足(a_i>max{a_j},j<i)的(a_i)出来,得到一个递增的序列(b)。
现在可以删除某些位置上的数花费(p_i)的代价(可以为负)。
现在给出(b),问最少要多少代价,使得(f(a)=b)。
思路:
定义(dp_{i,j})表示现在位于(a)序列第(i)位,(b)序列第(j)位的最小代价,我们考虑下一个位置(a_{i+1}:)
- 假设(a_{i+1}leq b_j),我们可以删除或者不删除,此时(dp_{i+1,j}=dp_{i,j}+min(0,p_{i+1}));
- 假设(a_{i+1}>b_j),此时又分两种情况:
- 若(a_{i+1}=b_{j+1}),那么此时可选可不选,所以就有(dp_{i+1,j}=dp_{i,j}+p_{i+1},dp_{i+1,j+1}=dp_{i,j});
- 若(a_{i+1} ot ={b_{j+1}}),此时我们必须删除,那么(dp_{i+1,j}=dp_{i,j}+p_{i+1})。
我们相当于有三种转移,因为(b)数组是连续的,并且我们观察到转移时只有一种情况是(j)向(j+1)转移的。
我们可以用线段树维护所有(dp_{i-1,j})的值,然后我们将(b)分为几个区间,分别按照转移方程进行区间/单点修改即可。
很巧妙的一个题,主要利用了转移方程(j)不变以及(b)单调的性质,因此我们可以沿用之前的状态并且分区间进行区间修改。
细节见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/15 20:23:48
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m;
int a[N], p[N], b[N];
ll minv[N << 2], lz[N << 2];
void tag(int o, ll v) {
minv[o] += v, lz[o] += v;
}
void push_up(int o) {
minv[o] = min(minv[o << 1], minv[o << 1|1]);
}
void push_down(int o, int l, int r) {
if(lz[o] != 0) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
tag(o << 1, lz[o]);
tag(o << 1|1, lz[o]);
lz[o] = 0;
}
}
void build(int o, int l, int r) {
lz[o] = 0;
if(l == r) {
if(l == 0) minv[o] = 0;
else minv[o] = 1e18;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(o << 1, l, mid), build(o << 1|1, mid + 1, r);
push_up(o);
}
void update(int o, int l, int r, int L, int R, ll v) {
if(L > R) return;
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
tag(o, v); return;
}
push_down(o, l, r);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(L <= mid) update(o << 1, l, mid, L, R, v);
if(R > mid) update(o << 1|1, mid + 1, r, L, R, v);
push_up(o);
}
void modify(int o, int l, int r, int p, ll v) {
if(l == r) {
minv[o] = min(minv[o], v);
return;
}
push_down(o, l, r);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(p <= mid) modify(o << 1, l, mid, p, v);
else modify(o << 1|1, mid + 1, r, p, v);
push_up(o);
}
ll query(int o, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
return minv[o];
}
push_down(o, l, r);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
ll res = 1e18;
if(L <= mid) res = query(o << 1, l, mid, L, R);
if(R > mid) res = min(res, query(o << 1|1, mid + 1, r, L, R));
return res;
}
void run() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> p[i];
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] == b[j]) ++j;
if(i == n && j <= m) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
}
build(1, 0, m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t = lower_bound(b + 1, b + m + 1, a[i + 1]) - b;
if (p[i + 1] < 0) update(1, 0, m, t, m, p[i + 1]);
if (b[t] == a[i + 1]) {
ll v = query(1, 0, m, t - 1, t - 1);
modify(1, 0, m, t, v);
}
update(1, 0, m, 0, t - 1, p[i + 1]);
}
ll ans = query(1, 0, m, m, m);
cout << "YES" << '
';
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
G. Substring Search
题意:
给出(s)串和(t)串,现在问对于(s)的每个长度为(m)的子串,是否有(s'=t)。字符串相等定义为:
- 对于(1leq ileq len,s_i=t_i或p_{s_i}=t_i);
其中(p)为(1)到(26)的排列。
对所有的(1leq ileq n-m+1)都要输出答案。
思路:
将字符串相等形式化即可表示为:
那么稍微变一下即为:
后面这一部分我们直接将其打开是一个关于(t_j)的四次多项式,系数是关于(i+j)位置的一个表达式。
那么我们直接将多项式拆开算,提前算出来系数,然后对于每一项求卷积即可。
关键在于形式化的表述,这一步挺巧妙的,平方的话是使得其结果非负,那么如果为(0)的话,就说明这个等式即保证了每一项都至少有一个成立。
代码略。