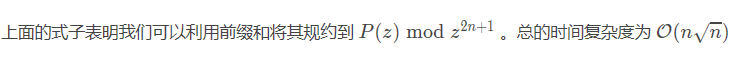Contest Info
| Solved | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 / 12 | O | O | O | - | - | O | - | Ø | - | Ø | O | Ø |
- O 在比赛中通过
- Ø 赛后通过
- ! 尝试了但是失败了
- - 没有尝试
Solutions:
A. Add More Zero
签到。
Code
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
#define hhh cerr<<"hhh"<<endl
#define see(x) cerr<<(#x)<<'='<<(x)<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pr;
inline int read() {int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9'))c=getchar();if(c=='-')f=-1,c=getchar();while(c>='0'&&c<='9')x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();return f*x;}
const int maxn = 3e5+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
typedef long double ld;
int main() {
int cas=0;
int m;
while(cin>>m) {
printf("Case #%d: %d
", ++cas, int(m*(ld(log(2))/log(10))));
}
}
B. Balala Power!
大数比较。
Code
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
#define hhh cerr<<"hhh"<<endl
#define see(x) cerr<<(#x)<<'='<<(x)<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pr;
inline int read() {int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9'))c=getchar();if(c=='-')f=-1,c=getchar();while(c>='0'&&c<='9')x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();return f*x;}
const int maxn = 1e5+1111;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
struct P{
int a[maxn], id;
int & operator [] (int x) { return a[x]; }
friend bool operator < (const P &a, const P &b) {
for(int i=maxn-1; i>=0; --i) {
if(a.a[i]<b.a[i]) return 1;
else if(a.a[i]>b.a[i]) return 0;
}
return 0;
}
void init(int i) { memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); id=i; }
ll cal(int x) {
ll res=0, t=1;
for(int i=0; i<maxn; ++i) {
(res+=x*a[i]*t)%=mod;
t=t*26%mod;
}
return res;
}
}cnt[26];
int n;
int f[26];
string s;
int main() {
int cas=0;
while(cin>>n) {
for(int i=0; i<26; ++i) cnt[i].init(i);
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) {
cin>>s;
int len=s.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; ++i) {
if(i==0&&len>=1) f[s[i]-'a']=1;
cnt[s[i]-'a'][len-1-i]++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<26; ++i) {
for(int j=0; j<maxn; ++j) {
if(cnt[i][j]>=26) {
cnt[i][j+1]+=cnt[i][j]/26;
cnt[i][j]%=26;
}
}
}
sort(cnt,cnt+26);
int p=0; ll ans=0;
for(int i=0; i<26; ++i) {
if(!f[cnt[i].id]&&!p) { p=1; continue; }
ans=(ans+cnt[i].cal(1+i-p))%mod;
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld
", ++cas, ans);
}
}
C. Colorful Tree
和这个题很像,可以用桶做到(O(n)),核心是利用了子数具有可减性。
F. Function
题意:
给定关于(0...n-1)和(0...m-1)的两个排列(a,b)。
定义函数(f)为(0...n-1
ightarrow 0...m-1)的一个映射。
计算不同的(f)个数满足(f(i)=b_{f(a_i)})。
思路:
这类题可以将问题转化为图上环的问题。
首先将(a,b)抽象为有向图,而(f)就相当于要在两张图中连边,并且满足(i
ightarrow a_i
ightarrow
f(a_i)
ightarrow b') 最终能够到达(f(i))。
那么问题就是图上的路径问题,发现步数很小,我们可以写作几个矩阵的乘积,每个矩阵((i,j))表示(i
ightarrow j)的可行性。
矩阵写出来就类似于这样子:
通过右乘(B^{-1})可以得到:
现在已知(A,B^{-1}),求满足条件的(F)个数。
假设(B^{-1})选定((x_1,y_1),A)选定((x_2,y_2)),那么就要满足((x_2,x_1),(y_2,y_1))都在(F)矩阵中合法。
注意到题目要求映射关系,也就是说(F)矩阵中每一行只有一个数,列没有限制,即第二维的取值没有限制。
注意现在所有的((x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2))都是已知的,现在相当于要(x_2)与(x_1),(y_2)与(y_1)进行匹配。我们只看(x)的话会在一个环上跑,即(x_2,x_1,x_i,...,x_2),同理(y)也会在一个环上跑(注意刚刚说的图论的问题)。因为列没有要求,我们对于选择的一个(x_2),都可以任意选择一个(y_i)作为起点,但是因为要满足(x)成环,(y)在跑过若干圈之后也要成环,这样才是一组合法的方案。
也就是说对于每个(x)的环,可以任选一个(y)的环,但要满足长度的整除关系。
细节见代码:
Code
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
#define hhh cerr<<"hhh"<<endl
#define see(x) cerr<<(#x)<<'='<<(x)<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pr;
inline int read() {int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9'))c=getchar();if(c=='-')f=-1,c=getchar();while(c>='0'&&c<='9')x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();return f*x;}
const int maxn = 3e5+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
int n, m;
int a[maxn], b[maxn];
ll fac[maxn], inv[maxn];
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll qpow(ll a,ll k){ll s=1;while(k){if(k&1)s=s*a%mod;a=a*a%mod;k>>=1;}return s;}
ll comb(int n, int m) {
if(n<m||m<0||n<0) return 0;
return fac[n]*inv[m]%mod*inv[n-m]%mod;
}
int vis[maxn], sz;
int c[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int *a) {
vis[x]=1; sz++;
if(!vis[a[x]]) dfs(a[x],a);
}
int main() {
int cas=0;
fac[0]=fac[1]=inv[0]=inv[1]=1;
for(int i=2; i<maxn; ++i) fac[i]=i*fac[i-1]%mod;
for(int i=2; i<maxn; ++i) inv[i]=(mod-mod/i)*inv[mod%i]%mod;
for(int i=2; i<maxn; ++i) inv[i]=inv[i]*inv[i-1]%mod;
while(cin>>n>>m) {
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i) c[i]=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) a[i]=read();
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) b[read()]=i;
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) vis[i]=0;
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) if(!vis[i]) {
sz=0, dfs(i,b);
c[sz]+=sz;
}
for(int i=n; i; --i) {
for(int j=i+i; j<=n; j+=i) {
c[j]+=c[i];
}
}
ll ans=1;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) vis[i]=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) if(!vis[i]) {
sz=0, dfs(i,a);
ans=ans*c[sz]%mod;
}
printf("Case #%d: ", ++cas);
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
}
H. Hints of sd0061
题意:
给定一个随机序列(a),然后现在有(m)组询问,每组询问询问序列第(b_i)大,满足(b_i+b_jleq b_k,b_i
ot ={b_j},b_i<b_k,b_j<b_k)。
思路:
求序列第(k)大,利用kth_element可以(O(n))得到,注意到(b)有条件限制,我们可以认为(b)是以斐波纳契数列那样进行增长,所以可以直接暴力kth_element,这里我们反着来进行操作即可,因为斐波纳契数列前面的项较小的比较多,所以将kth_element更多地应用在前面比较好。
注意到(b_i=n,i=1,2,...m),所以代码中有个细节,就是kth_element的区间范围问题,我们每次对于一个左闭右开区间进行排序,如果第(k)项为右端点会直接返回不进行操作。这样就能保证复杂度。
代码如下:
Code
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
#define hhh cerr<<"hhh"<<endl
#define see(x) cerr<<(#x)<<'='<<(x)<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned int ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pr;
inline int read() {int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9'))c=getchar();if(c=='-')f=-1,c=getchar();while(c>='0'&&c<='9')x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();return f*x;}
const int maxn = 1e7+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
int n, m;
ll A, B, C, x, y, z;
ll a[maxn];
struct node {
int val;
int p;
bool operator < (const node& A) const {
return val < A.val;
}
}b[105];
ll ans[maxn];
ll rng61() {
ll t;
x = x ^ (x << 16);
x = x ^ (x >> 5);
x = x ^ (x << 1);
t = x;
x = y;
y = z;
z = (t ^ x) ^ y;
return z;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int cas=0;
while(cin>>n>>m>>A>>B>>C) {
x=A, y=B, z=C;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
a[i]=rng61();
}
cout<<"Case #"<<++cas<<':';
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) {
cin>>b[i].val;
b[i].p = i;
}
sort(b, b+m);
int r=n;
for(int i=m-1; i>=0; --i) {
nth_element(a,a+b[i].val,a+r);
ans[b[i].p]=a[b[i].val];
r=b[i].val;
}
for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) cout<<' '<<ans[i];
cout<<'
';
}
}
J. Journey with Knapsack
题意:
求
思路:
这个乘积我们可以分子、分母单独计算。
对于分子(prod_{i=1}^n1-x^{i(a_i+1)}),因为有(a_i>a_{i-1}),所以至多(sqrt{2n})项有用,否则在模意义下为(1)。
对于分母,可以发现很类似于拆分数的生成函数。
接下来推式子:
注意上面我们都在模意义下进行,我们可以直接将(prod_{i=1}^{2n}frac{1}{1-x^i})变为(P(x))的原因是在模意义下后面的数都会变为(1),没有意义。
最后后面那一部分我们可以维护前缀和(O(1))进行计算贡献。
更详细的推导可以见官方题解:
细节见代码吧:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/6/5 20:43:13
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
//p[n]=p[n-1]+p[n-2]-p[n-5]-p[n-7]...
//广义五边形数 P[i]
void init_p(int n, int* p) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = 0;
}
auto P = [&] (int i) {
return MP(i * (3 * i - 1) / 2, i * (3 * i + 1) / 2);
};
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1;; j++) {
pii val = P(j);
if (val.fi > i) break;
int t = p[i - val.fi];
if (val.se <= i) {
t += p[i - val.se];
if (t >= MOD) t -= MOD;
}
if (!(j & 1)) p[i] = (p[i] + MOD - t) % MOD;
else p[i] = (p[i] + t) % MOD;
}
}
}
int n, m, _;
int f[N];
void add(int& x, int y) {
x += y;
if (x >= MOD) x -= MOD;
}
void dec(int& x, int y) {
x -= y;
if (x < 0) x += MOD;
}
void run() {
init_p(2 * n, f);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x; cin >> x;
ll t = 1ll * i * (x + 1);
if (t > 2 * n) continue;
for (int j = 2 * n; j >= t; j--) {
dec(f[j], f[j - t]);
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
add(sum, f[i - n - 1]);
dec(f[i], sum);
}
cout << "Case #" << ++_ << ": ";
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x; cin >> x;
add(ans, f[2 * n - x]);
}
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while (cin >> n >> m) run();
return 0;
}
K. KazaQ's Socks
直接找规律即可。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/5/29 13:43:59
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
ll n, k;
int _;
void run() {
++_;
cout << "Case #" << _ << ": ";
if (k <= n) {
cout << k << '
';
return;
}
k -= n;
ll t = (k + n - 2) / (n - 1);
if (t & 1) {
cout << (k - 1) % (n - 1) + 1 << '
';
} else {
if (k % (n - 1) == 0) {
cout << n << '
';
} else {
cout << (k - 1) % (n - 1) + 1 << '
';
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while (cin >> n >> k) run();
return 0;
}
L. Limited Permutation
题意:
现有排列(p),对于每个位置给定区间([l_i,r_i]),意即(i)这个位置的数为该区间最小值。
现在问满足这个限制条件的排列个数为多少。
思路:
考虑构造出排列的笛卡尔树,在该树中任意一个子树结点的权值都大于当前结点。
之后统计一下树上的拓扑序计数即可,详情可见传送门。
注意一下细节,就是树不“完全”的情况我们要判一下。
细节见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/6/2 11:46:41
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e6 + 5, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int fac[N], inv[N];
void init() {
fac[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
fac[i] = 1ll * fac[i - 1] * i % MOD;
}
inv[0] = inv[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
inv[i] = 1ll * inv[MOD % i] * (MOD - MOD / i) % MOD;
}
}
int n, _;
struct seg {
int l, r;
}a[N];
void run() {
++_;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].l;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].r;
}
vector <vector<pii>> L(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
L[a[i].l].push_back(MP(a[i].r, i));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sort(all(L[i]));
}
cout << "Case #" << _ << ": ";
int ans = fac[n];
function <int(int, int)> dfs;
bool f = false;
dfs = [&](int l, int r) {
if (l > r) return 0;
int t = sz(L[l]) - 1;
if (t < 0) {
f = true;
return 0;
}
pii now = L[l][t];
L[l].pop_back();
int nr = now.fi, m = now.se;
if (nr != r) {
f = true;
return 0;
}
int sz = 1 + dfs(l, m - 1) + dfs(m + 1, r);
ans = 1ll * ans * inv[sz] % MOD;
return sz;
};
dfs(1, n);
if (f) ans = 0;
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
init();
while (cin >> n) {
run();
}
return 0;
}