一、以下是我要解析的一个二叉树的模型形状。本文实现了以下方式的遍历:
1、用递归的方法实现了前序、中序、后序的遍历;
2、利用队列的方法实现层次遍历;
3、用堆栈的方法实现前序、中序、后序的遍历。
。
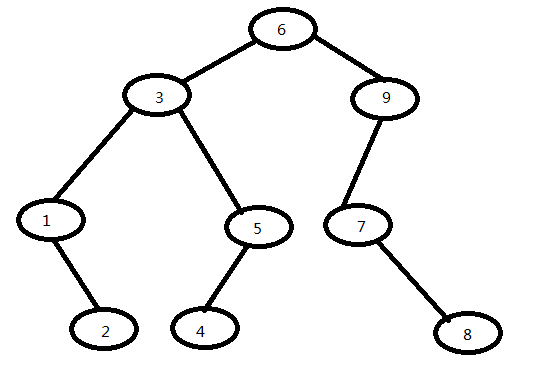
二、遍历
1、首先创建节点类

public class Node { private int data; private Node leftNode; private Node rightNode; public Node(int data, Node leftNode, Node rightNode){ this.data = data; this.leftNode = leftNode; this.rightNode = rightNode; } public int getData() { return data; } public void setData(int data) { this.data = data; } public Node getLeftNode() { return leftNode; } public void setLeftNode(Node leftNode) { this.leftNode = leftNode; } public Node getRightNode() { return rightNode; } public void setRightNode(Node rightNode) { this.rightNode = rightNode; } }
2、递归方式实现前序、中序、后续遍历

public class BinaryTree { /** * @author yaobo * 二叉树的先序中序后序排序 */ public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错 Node J = new Node(8, null, null); Node H = new Node(4, null, null); Node G = new Node(2, null, null); Node F = new Node(7, null, J); Node E = new Node(5, H, null); Node D = new Node(1, null, G); Node C = new Node(9, F, null); Node B = new Node(3, D, E); Node A = new Node(6, B, C); return A; //返回根节点 } public void printNode(Node node){ System.out.print(node.getData()); } public void theFirstTraversal(Node root) { //先序遍历 printNode(root); if (root.getLeftNode() != null) { //使用递归进行遍历左孩子 theFirstTraversal(root.getLeftNode()); } if (root.getRightNode() != null) { //递归遍历右孩子 theFirstTraversal(root.getRightNode()); } } public void theInOrderTraversal(Node root) { //中序遍历 if (root.getLeftNode() != null) { theInOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode()); } printNode(root); if (root.getRightNode() != null) { theInOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode()); } } public void thePostOrderTraversal(Node root) { //后序遍历 if (root.getLeftNode() != null) { thePostOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode()); } if(root.getRightNode() != null) { thePostOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode()); } printNode(root); } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); Node root = tree.init(); System.out.println("先序遍历"); tree.theFirstTraversal(root); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("中序遍历"); tree.theInOrderTraversal(root); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("后序遍历"); tree.thePostOrderTraversal(root); System.out.println(""); } }
3、借助队列实现层次遍历

//层次遍历 public void theLeverTraversal(Node root) { if (root == null) { return; } //新建一个队列,LinkedList实现了Quene接口,可以直接当作队列来用 LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); Node current; //当前节点 queue.offer(root);//根节点入队列 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { current = queue.poll(); //取出队列的头节点 System.out.print(current.val + " ");//输出队列的头节点的值 if (current.left != null) { queue.offer(current.left); //如果当前节点的左节点不为空,则左节点入队列 } if (current.right != null) { queue.offer(current.right); //如果当前节点的右节点不为空,则右节点入队列 } } }
4、堆栈方式实现前序、中序、后续遍历

public class BinaryTree1 { public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错 Node J = new Node(8, null, null); Node H = new Node(4, null, null); Node G = new Node(2, null, null); Node F = new Node(7, null, J); Node E = new Node(5, H, null); Node D = new Node(1, null, G); Node C = new Node(9, F, null); Node B = new Node(3, D, E); Node A = new Node(6, B, C); return A; //返回根节点 } public void printNode(Node node){ System.out.print(node.getData()); } public void theFirstTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //先序遍历 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Node node = root; while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) { //将所有左孩子压栈 if (node != null) { //压栈之前先访问 printNode(node); stack.push(node); node = node.getLeftNode(); } else { node = stack.pop(); node = node.getRightNode(); } } } public void theInOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //中序遍历 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Node node = root; while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) { if (node != null) { stack.push(node); //直接压栈 node = node.getLeftNode(); } else { node = stack.pop(); //出栈并访问 printNode(node); node = node.getRightNode(); } } } public void thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //后序遍历 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Stack<Node> output = new Stack<Node>();//构造一个中间栈来存储逆后序遍历的结果 Node node = root; while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) { if (node != null) { output.push(node); stack.push(node); node = node.getRightNode(); } else { node = stack.pop(); node = node.getLeftNode(); } } System.out.println(output.size()); while (output.size() > 0) { printNode(output.pop()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree1 tree = new BinaryTree1(); Node root = tree.init(); System.out.println("先序遍历"); tree.theFirstTraversal_Stack(root); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("中序遍历"); tree.theInOrderTraversal_Stack(root); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("后序遍历"); tree.thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(root); System.out.println(""); } }
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
参考链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yaobolove/p/6213936.html
二叉树遍历(前序、中序、后序、层次、深度优先、广度优先遍历):https://blog.csdn.net/yimingsilence/article/details/54783208
