先来看一段简单的代码,稍微有点并发知识的都可以知道打印出结果必然是一个小于20000的值
package com.example.test.cas; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-09 * @description */ public class LockDemo { private volatile int i; public void add(){ i++; } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { LockDemo lockDemo = new LockDemo(); for (int i = 0; i <2 ; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ for (int j = 0; j <10000 ; j++) { lockDemo.add(); } }).start(); } System.in.read(); System.out.println(lockDemo.i); } }
改进一下,使用jdk给我们提供的原子操作类,达到了我们预想的结果
package com.example.test.cas; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ public class AtomicTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 自增 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { new Thread(() -> { for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) { atomicInteger.incrementAndGet(); } }).start(); } Thread.sleep(2000L); System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); } }
下面就来探究下jdk为我们提供的原子操作类的原理,基于java native方法实现一个自己原子操作类
package com.example.test.cas; import sun.misc.Unsafe; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-09 * @description */ public class LockCASDemo { private volatile int i; private static Unsafe unsafe; private static long offset; static{ try { Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); theUnsafe.setAccessible(true); unsafe = (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null); offset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(LockCASDemo.class.getDeclaredField("i")); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void add(){ int curent; int value; do{ curent = unsafe.getIntVolatile(this,offset); value = curent+1; }while (!unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this,offset,curent,value)); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { LockCASDemo lockDemo = new LockCASDemo(); for (int i = 0; i <2 ; i++) { new Thread(() ->{ for (int j = 0; j <10000 ; j++) { lockDemo.add(); } }).start(); } System.in.read(); System.out.println(lockDemo.i); } }
实现这样一个类的要点有:1、基于反射机制获取UnSafe对象2、利用UnSafe对象获取属性偏移量,然后调用compareAndSwapInt方法,比较和替换是硬件同步原语,处理器提供了基于内存操作的原子性保证。
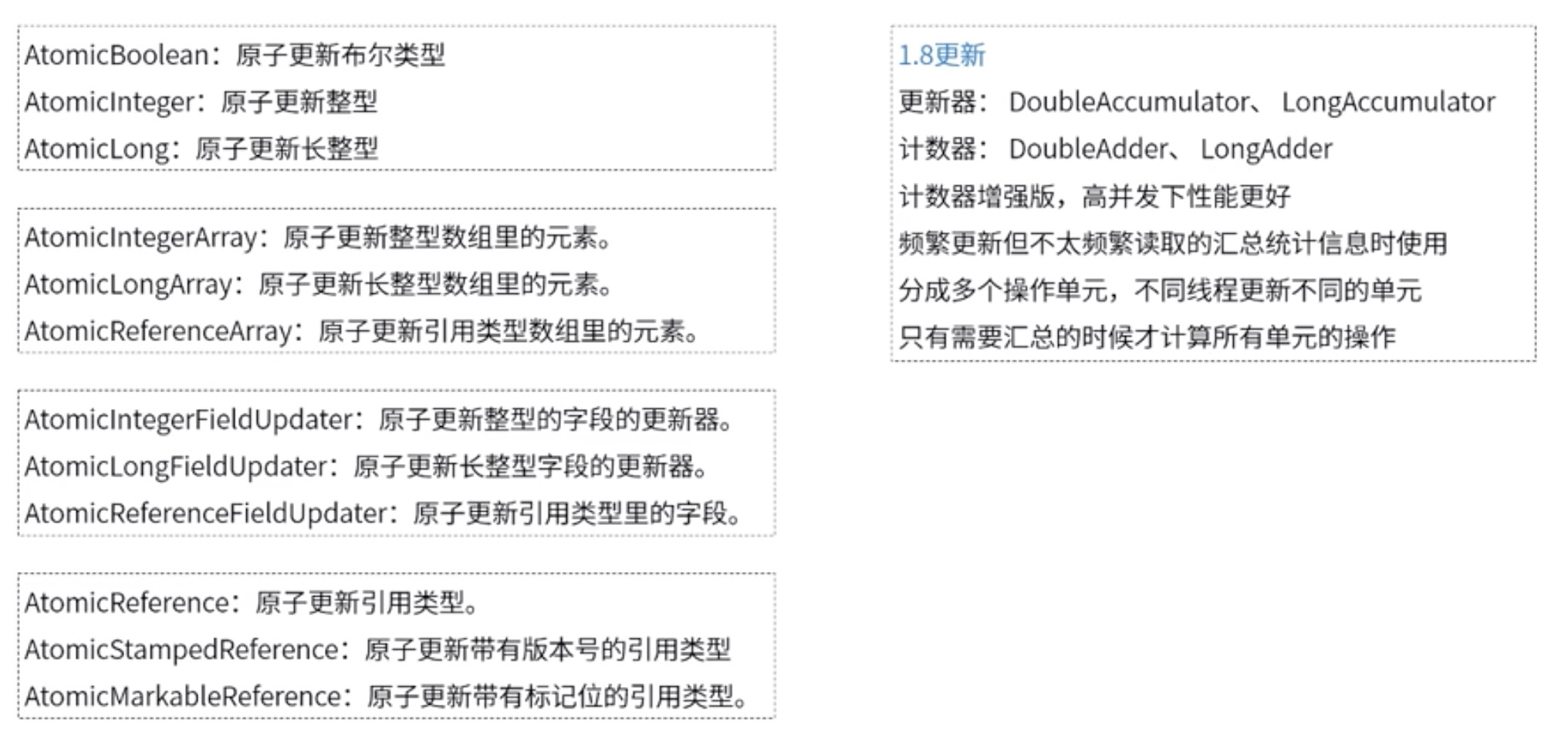
以上的代码未免麻烦,因此jdk为我们封装了一些原子操作类来简化使用,打开这些原子操作类的源代码,可以发现其内部实现就是循环+调用native方法(比较替换),常用的原子操作类如下:
cas存在的三个问题
1、循环+cas,自旋的实现让cpu处于高频运行状态,争抢cpu执行时间,如果并发太高,部分线程长时间执行不成功,带来很大的cpu消耗
2、只能针对单个变量实现原子操作
3、出现ABA问题
针对第一个问题,jdk1.8为我们提供了增强版的计数器,内部利用分而治之的思想来减少线程间的cpu争抢,提高并发效率,具体可以看下面的测试
package com.example.test.cas; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description asd */ public class LongAdderDemo { private long count = 0; // 同步代码块的方式 public void testSync() throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { new Thread(() -> { long starttime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (System.currentTimeMillis() - starttime < 2000) { // 运行两秒 synchronized (this) { ++count; } } long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("SyncThread spend:" + (endtime - starttime) + "ms" + " v" + count); }).start(); } } // Atomic方式 private AtomicLong acount = new AtomicLong(0L); public void testAtomic() throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { new Thread(() -> { long starttime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (System.currentTimeMillis() - starttime < 2000) { // 运行两秒 acount.incrementAndGet(); // acount++; } long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("AtomicThread spend:" + (endtime - starttime) + "ms" + " v-" + acount.incrementAndGet()); }).start(); } } // LongAdder 方式 private LongAdder lacount = new LongAdder(); public void testLongAdder() throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { new Thread(() -> { long starttime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (System.currentTimeMillis() - starttime < 2000) { // 运行两秒 lacount.increment(); } long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("LongAdderThread spend:" + (endtime - starttime) + "ms" + " v-" + lacount.sum()); }).start(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { LongAdderDemo demo = new LongAdderDemo(); demo.testSync(); demo.testAtomic(); demo.testLongAdder(); } }
三种方式在同样的时间内,自增的数值如下,可以看到LongAdder的效率更高一些
SyncThread spend:2000ms v23074332 SyncThread spend:2000ms v23094924 AtomicThread spend:2000ms v-38137398 AtomicThread spend:2000ms v-38152694 SyncThread spend:2011ms v23094924 AtomicThread spend:2000ms v-38416095 LongAdderThread spend:2000ms v-40097562 LongAdderThread spend:2000ms v-40606405 LongAdderThread spend:2001ms v-40917467 Process finished with exit code 0
针对第二个问题,我们只能通过加锁或者其它手段其处理,这里不做展开
针对第三个问题,我们先模拟出以下的场景来展示这个问题
package com.example.test.cas.aba; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ public class Node { public final String item; public Node next; public Node(String item) { this.item = item; } @Override public String toString() { return "item内容:" + this.item; } }
package com.example.test.cas.aba; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ // 实现一个 栈(后进先出) public class Stack { // top cas无锁修改 AtomicReference<Node> top = new AtomicReference<Node>(); public void push(Node node) { // 入栈 Node oldTop; do { oldTop = top.get(); node.next = oldTop; } while (!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, node)); // CAS 替换栈顶 } // 为了演示ABA效果, 增加一个CAS操作的延时 public Node pop(int time) throws InterruptedException { // 出栈 -- 取出栈顶 Node newTop; Node oldTop; do { oldTop = top.get(); if (oldTop == null) { return null; } newTop = oldTop.next; if (time != 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 休眠前拿到的数据" + oldTop.item); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(time); // 休眠指定的时间 } } while (!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, newTop)); return oldTop; } }
package com.example.test.cas.aba; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Stack stack = new Stack(); stack.push(new Node("B")); stack.push(new Node("A")); Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(3)); // 再继续拿,就会有问题了,理想情况stack出数据应该是 A->C->D->B,实际上ABA问题导致A-B->null System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); thread1.start(); Thread.sleep(300); // 让线程1先启动 Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { Node A = null; try { A = stack.pop(0); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + A); stack.push(new Node("D")); stack.push(new Node("C")); stack.push(A); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); thread2.start(); } }
在上面的例子中我们想实现一个栈,单线程情况下是没有任何问题的,但是在并发场景下就会出现丢数据的问题,运行结果:
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 睡一下,预期拿到的数据A Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:A Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:A Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:B Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:null Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:null Process finished with exit code 0
好在jdk为我们考虑了这个问题,提供了AtomicStampedReference和AtomicMarkableReference,前者基于时间戳,后者基于标记位来对同样的数据做区分,从未避免了ABA问题
package com.example.test.cas.aba; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ public class ConcurrentStack { AtomicStampedReference<Node> top = new AtomicStampedReference<Node>(null,0); public void push(Node node){ Node oldTop; int v; do{ v=top.getStamp(); oldTop = top.getReference(); node.next = oldTop; } while(!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, node,v,v+1)); // }while(!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, node,top.getStamp(),top.getStamp()+1)); } public Node pop(int time){ Node newTop; Node oldTop; int v; do{ v=top.getStamp(); oldTop = top.getReference(); if(oldTop == null){ return null; } newTop = oldTop.next; try { if (time != 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 睡一下,预期拿到的数据" + oldTop.item); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(time); // 休眠指定的时间 } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } while(!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, newTop,v,v+1)); // }while(!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, newTop,top.getStamp(),top.getStamp())); return oldTop; } public void get(){ Node node = top.getReference(); while(node!=null){ System.out.println(node.item); node = node.next; } } }
package com.example.test.cas.aba; /** * @author hehang on 2019-10-14 * @description */ public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentStack stack = new ConcurrentStack(); stack.push(new Node("B")); stack.push(new Node("A")); Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(3)); // #再继续拿,就会有问题了,理想情况stack出数据应该是 A->C->D->B,实际上ABA问题导致A-B->null System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + stack.pop(0)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); thread1.start(); Thread.sleep(300); // 让线程1先启动 Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { Node A = null; try { A = stack.pop(0); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 拿到数据:" + A); stack.push(new Node("D")); stack.push(new Node("C")); stack.push(A); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); thread2.start(); } }
结果如下:
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 睡一下,预期拿到的数据A Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:A Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 睡一下,预期拿到的数据A Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:A Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:C Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:D Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 拿到数据:item内容:B Process finished with exit code 0