第3章 分组
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/table.csv',index_col='ID')
df.head()
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1101 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| 1102 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
192 |
73 |
32.5 |
B+ |
| 1103 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_2 |
186 |
82 |
87.2 |
B+ |
| 1104 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
167 |
81 |
80.4 |
B- |
| 1105 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_4 |
159 |
64 |
84.8 |
B+ |
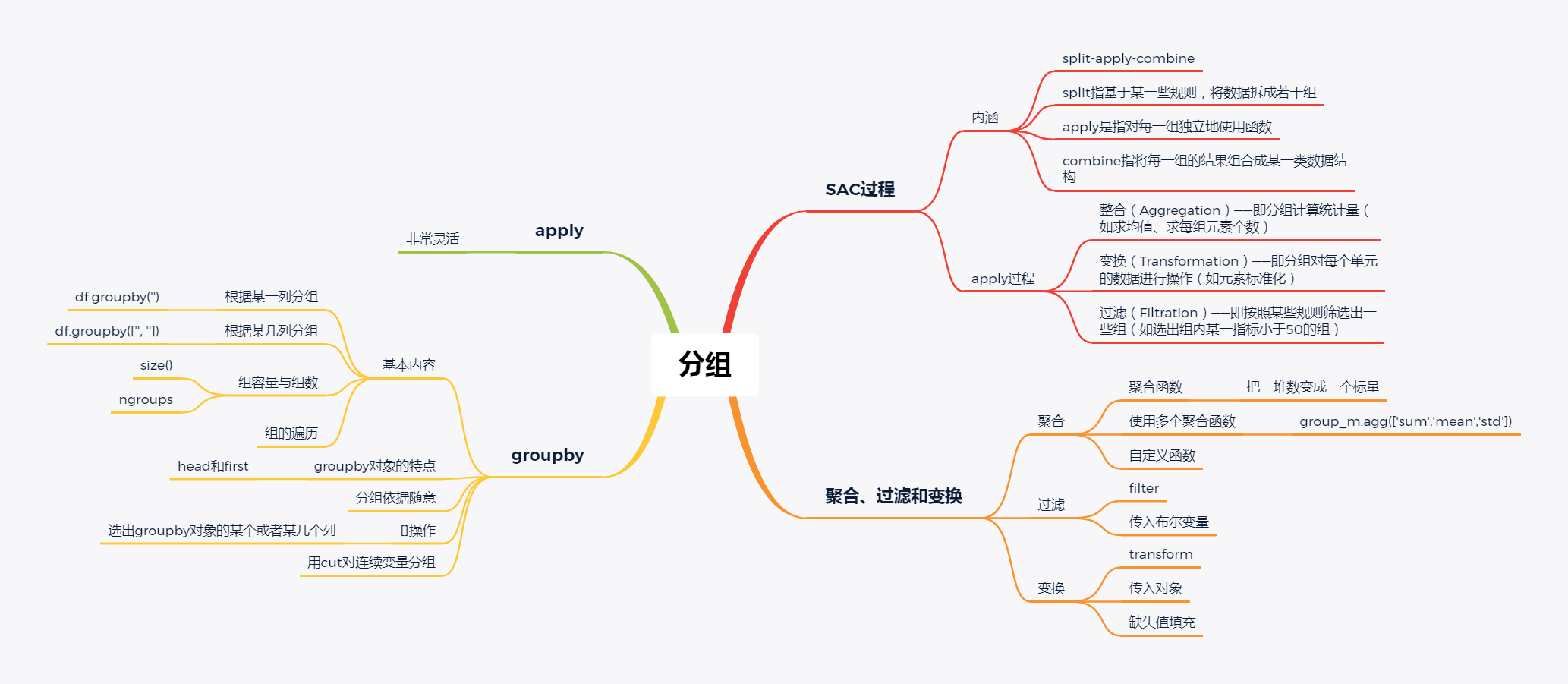
一、SAC过程
1. 内涵
SAC指的是分组操作中的split-apply-combine过程
其中split指基于某一些规则,将数据拆成若干组,apply是指对每一组独立地使用函数,combine指将每一组的结果组合成某一类数据结构
2. apply过程
在该过程中,我们实际往往会遇到四类问题:
整合(Aggregation)——即分组计算统计量(如求均值、求每组元素个数)
过滤(Filtration)——即按照某些规则筛选出一些组(如选出组内某一指标小于50的组)
综合问题——即前面提及的三种问题的混合
二、groupby函数
1. 分组函数的基本内容:
(a)根据某一列分组
grouped_single = df.groupby('School')
经过groupby后会生成一个groupby对象,该对象本身不会返回任何东西,只有当相应的方法被调用才会起作用
例如取出某一个组:
grouped_single.get_group('S_1').head()
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1101 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| 1102 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
192 |
73 |
32.5 |
B+ |
| 1103 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_2 |
186 |
82 |
87.2 |
B+ |
| 1104 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
167 |
81 |
80.4 |
B- |
| 1105 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_4 |
159 |
64 |
84.8 |
B+ |
(b)根据某几列分组
grouped_mul = df.groupby(['School','Class'])
grouped_mul.get_group(('S_2','C_4'))
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2401 |
S_2 |
C_4 |
F |
street_2 |
192 |
62 |
45.3 |
A |
| 2402 |
S_2 |
C_4 |
M |
street_7 |
166 |
82 |
48.7 |
B |
| 2403 |
S_2 |
C_4 |
F |
street_6 |
158 |
60 |
59.7 |
B+ |
| 2404 |
S_2 |
C_4 |
F |
street_2 |
160 |
84 |
67.7 |
B |
| 2405 |
S_2 |
C_4 |
F |
street_6 |
193 |
54 |
47.6 |
B |
(c)组容量与组数
grouped_single.size()
School
S_1 15
S_2 20
dtype: int64
grouped_mul.size()
School Class
S_1 C_1 5
C_2 5
C_3 5
S_2 C_1 5
C_2 5
C_3 5
C_4 5
dtype: int64
grouped_single.ngroups
2
grouped_mul.ngroups
7
(d)组的遍历
for name,group in grouped_single:
print(name)
display(group.head())
S_1
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1101 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| 1102 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
192 |
73 |
32.5 |
B+ |
| 1103 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_2 |
186 |
82 |
87.2 |
B+ |
| 1104 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
167 |
81 |
80.4 |
B- |
| 1105 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_4 |
159 |
64 |
84.8 |
B+ |
S_2
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2101 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_7 |
174 |
84 |
83.3 |
C |
| 2102 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
F |
street_6 |
161 |
61 |
50.6 |
B+ |
| 2103 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_4 |
157 |
61 |
52.5 |
B- |
| 2104 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
F |
street_5 |
159 |
97 |
72.2 |
B+ |
| 2105 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_4 |
170 |
81 |
34.2 |
A |
(e)level参数(用于多级索引)和axis参数
df.set_index(['Gender','School']).groupby(level=1,axis=0).get_group('S_1').head()
|
|
Class |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| Gender |
School |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M |
S_1 |
C_1 |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| F |
S_1 |
C_1 |
street_2 |
192 |
73 |
32.5 |
B+ |
| M |
S_1 |
C_1 |
street_2 |
186 |
82 |
87.2 |
B+ |
| F |
S_1 |
C_1 |
street_2 |
167 |
81 |
80.4 |
B- |
| S_1 |
C_1 |
street_4 |
159 |
64 |
84.8 |
B+ |
2. groupby对象的特点
(a)查看所有可调用的方法
由此可见,groupby对象可以使用相当多的函数,灵活程度很高
print([attr for attr in dir(grouped_single) if not attr.startswith('_')])
['Address', 'Class', 'Gender', 'Height', 'Math', 'Physics', 'School', 'Weight', 'agg', 'aggregate', 'all', 'any', 'apply', 'backfill', 'bfill', 'boxplot', 'corr', 'corrwith', 'count', 'cov', 'cumcount', 'cummax', 'cummin', 'cumprod', 'cumsum', 'describe', 'diff', 'dtypes', 'expanding', 'ffill', 'fillna', 'filter', 'first', 'get_group', 'groups', 'head', 'hist', 'idxmax', 'idxmin', 'indices', 'last', 'mad', 'max', 'mean', 'median', 'min', 'ndim', 'ngroup', 'ngroups', 'nth', 'nunique', 'ohlc', 'pad', 'pct_change', 'pipe', 'plot', 'prod', 'quantile', 'rank', 'resample', 'rolling', 'sem', 'shift', 'size', 'skew', 'std', 'sum', 'tail', 'take', 'transform', 'tshift', 'var']
(b)分组对象的head和first
对分组对象使用head函数,返回的是每个组的前几行,而不是数据集前几行
grouped_single.head(2)
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1101 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| 1102 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
F |
street_2 |
192 |
73 |
32.5 |
B+ |
| 2101 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_7 |
174 |
84 |
83.3 |
C |
| 2102 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
F |
street_6 |
161 |
61 |
50.6 |
B+ |
first显示的是以分组为索引的每组的第一个分组信息
grouped_single.first()
|
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| School |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_1 |
173 |
63 |
34.0 |
A+ |
| S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_7 |
174 |
84 |
83.3 |
C |
(c)分组依据
对于groupby函数而言,分组的依据是非常自由的,只要是与数据框长度相同的列表即可,同时支持函数型分组
df.groupby(np.random.choice(['a','b','c'],df.shape[0])).get_group('a').head()
#相当于将np.random.choice(['a','b','c'],df.shape[0])当做新的一列进行分组
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1103 |
S_1 |
C_1 |
M |
street_2 |
186 |
82 |
87.2 |
B+ |
| 1201 |
S_1 |
C_2 |
M |
street_5 |
188 |
68 |
97.0 |
A- |
| 1203 |
S_1 |
C_2 |
M |
street_6 |
160 |
53 |
58.8 |
A+ |
| 1204 |
S_1 |
C_2 |
F |
street_5 |
162 |
63 |
33.8 |
B |
| 2101 |
S_2 |
C_1 |
M |
street_7 |
174 |
84 |
83.3 |
C |
从原理上说,我们可以看到利用函数时,传入的对象就是索引,因此根据这一特性可以做一些复杂的操作
df[:5].groupby(lambda x:print(x)).head(0)
1101
1102
1103
1104
1105
|
School |
Class |
Gender |
Address |
Height |
Weight |
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
根据奇偶行分组
df.groupby(lambda x:'奇数行' if not df.index.get_loc(x)%2==1 else '偶数行').groups
{'偶数行': Int64Index([1102, 1104, 1201, 1203, 1205, 1302, 1304, 2101, 2103, 2105, 2202,
2204, 2301, 2303, 2305, 2402, 2404],
dtype='int64', name='ID'),
'奇数行': Int64Index([1101, 1103, 1105, 1202, 1204, 1301, 1303, 1305, 2102, 2104, 2201,
2203, 2205, 2302, 2304, 2401, 2403, 2405],
dtype='int64', name='ID')}
如果是多层索引,那么lambda表达式中的输入就是元组,下面实现的功能为查看两所学校中男女生分别均分是否及格
注意:此处只是演示groupby的用法,实际操作不会这样写
math_score = df.set_index(['Gender','School'])['Math'].sort_index()
grouped_score = df.set_index(['Gender','School']).sort_index().
groupby(lambda x:(x,'均分及格' if math_score[x].mean()>=60 else '均分不及格'))
for name,_ in grouped_score:print(name)
(('F', 'S_1'), '均分及格')
(('F', 'S_2'), '均分及格')
(('M', 'S_1'), '均分及格')
(('M', 'S_2'), '均分不及格')
(d)groupby的[]操作
可以用[]选出groupby对象的某个或者某几个列,上面的均分比较可以如下简洁地写出:
df.groupby(['Gender','School'])['Math'].mean()>=60
Gender School
F S_1 True
S_2 True
M S_1 True
S_2 False
Name: Math, dtype: bool
用列表可选出多个属性列:
df.groupby(['Gender','School'])[['Math','Height']].mean()
|
|
Math |
Height |
| Gender |
School |
|
|
| F |
S_1 |
64.100000 |
173.125000 |
| S_2 |
66.427273 |
173.727273 |
| M |
S_1 |
63.342857 |
178.714286 |
| S_2 |
51.155556 |
172.000000 |
(e)连续型变量分组
例如利用cut函数对数学成绩分组:
bins = [0,40,60,80,90,100]
cuts = pd.cut(df['Math'],bins=bins) #可选label添加自定义标签
df.groupby(cuts)['Math'].count()
Math
(0, 40] 7
(40, 60] 10
(60, 80] 9
(80, 90] 7
(90, 100] 2
Name: Math, dtype: int64
三、聚合、过滤和变换
1. 聚合(Aggregation)
(a)常用聚合函数
所谓聚合就是把一堆数,变成一个标量,因此mean/sum/size/count/std/var/sem/describe/first/last/nth/min/max都是聚合函数
为了熟悉操作,不妨验证标准误sem函数,它的计算公式是:(frac{组内标准差}{sqrt{组容量}}),下面进行验证:
group_m = grouped_single['Math']
group_m.std().values/np.sqrt(group_m.count().values)== group_m.sem().values
array([ True, True])
(b)同时使用多个聚合函数
group_m.agg(['sum','mean','std'])
|
sum |
mean |
std |
| School |
|
|
|
| S_1 |
956.2 |
63.746667 |
23.077474 |
| S_2 |
1191.1 |
59.555000 |
17.589305 |
利用元组进行重命名
group_m.agg([('rename_sum','sum'),('rename_mean','mean')])
|
rename_sum |
rename_mean |
| School |
|
|
| S_1 |
956.2 |
63.746667 |
| S_2 |
1191.1 |
59.555000 |
指定哪些函数作用哪些列
grouped_mul.agg({'Math':['mean','max'],'Height':'var'})
|
|
Math |
Height |
|
|
mean |
max |
var |
| School |
Class |
|
|
|
| S_1 |
C_1 |
63.78 |
87.2 |
183.3 |
| C_2 |
64.30 |
97.0 |
132.8 |
| C_3 |
63.16 |
87.7 |
179.2 |
| S_2 |
C_1 |
58.56 |
83.3 |
54.7 |
| C_2 |
62.80 |
85.4 |
256.0 |
| C_3 |
63.06 |
95.5 |
205.7 |
| C_4 |
53.80 |
67.7 |
300.2 |
(c)使用自定义函数
grouped_single['Math'].agg(lambda x:print(x.head(),'间隔'))
#可以发现,agg函数的传入是分组逐列进行的,有了这个特性就可以做许多事情
1101 34.0
1102 32.5
1103 87.2
1104 80.4
1105 84.8
Name: Math, dtype: float64 间隔
2101 83.3
2102 50.6
2103 52.5
2104 72.2
2105 34.2
Name: Math, dtype: float64 间隔
School
S_1 None
S_2 None
Name: Math, dtype: object
官方没有提供极差计算的函数,但通过agg可以容易地实现组内极差计算
grouped_single['Math'].agg(lambda x:x.max()-x.min())
School
S_1 65.5
S_2 62.8
Name: Math, dtype: float64
(d)利用NamedAgg函数进行多个聚合
注意:不支持lambda函数,但是可以使用外置的def函数
def R1(x):
return x.max()-x.min()
def R2(x):
return x.max()-x.median()
grouped_single['Math'].agg(min_score1=pd.NamedAgg(column='col1', aggfunc=R1),
max_score1=pd.NamedAgg(column='col2', aggfunc='max'),
range_score2=pd.NamedAgg(column='col3', aggfunc=R2)).head()
|
min_score1 |
max_score1 |
range_score2 |
| School |
|
|
|
| S_1 |
65.5 |
97.0 |
33.5 |
| S_2 |
62.8 |
95.5 |
39.4 |
(e)带参数的聚合函数
判断是否组内数学分数至少有一个值在50-52之间:
def f(s,low,high):
return s.between(low,high).max()
grouped_single['Math'].agg(f,50,52)
School
S_1 False
S_2 True
Name: Math, dtype: bool
如果需要使用多个函数,并且其中至少有一个带参数,则使用wrap技巧:
def f_test(s,low,high):
return s.between(low,high).max()
def agg_f(f_mul,name,*args):
def wrapper(x):
return f_mul(x,*args)
wrapper.__name__ = name
return wrapper
grouped_single['Math'].agg([agg_f(f_test,'func_name',50,52),'mean'])
|
func_name |
mean |
| School |
|
|
| S_1 |
False |
63.746667 |
| S_2 |
True |
59.555000 |
2. 过滤(Filteration)
filter函数是用来筛选某些组的(务必记住结果是组的全体),因此传入的值应当是布尔标量
grouped_single[['Math','Physics']].filter(lambda x:(x['Math']>32).all()).head()
|
Math |
Physics |
| ID |
|
|
| 2101 |
83.3 |
C |
| 2102 |
50.6 |
B+ |
| 2103 |
52.5 |
B- |
| 2104 |
72.2 |
B+ |
| 2105 |
34.2 |
A |
(a)传入对象
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:x-x.min()).head()
|
Math |
Height |
| ID |
|
|
| 1101 |
2.5 |
14 |
| 1102 |
1.0 |
33 |
| 1103 |
55.7 |
27 |
| 1104 |
48.9 |
8 |
| 1105 |
53.3 |
0 |
如果返回了标量值,那么组内的所有元素会被广播为这个值
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:x.mean()).head()
|
Math |
Height |
| ID |
|
|
| 1101 |
63.746667 |
175.733333 |
| 1102 |
63.746667 |
175.733333 |
| 1103 |
63.746667 |
175.733333 |
| 1104 |
63.746667 |
175.733333 |
| 1105 |
63.746667 |
175.733333 |
(b)利用变换方法进行组内标准化
grouped_single[['Math','Height']].transform(lambda x:(x-x.mean())/x.std()).head()
|
Math |
Height |
| ID |
|
|
| 1101 |
-1.288991 |
-0.214991 |
| 1102 |
-1.353990 |
1.279460 |
| 1103 |
1.016287 |
0.807528 |
| 1104 |
0.721627 |
-0.686923 |
| 1105 |
0.912289 |
-1.316166 |
(c)利用变换方法进行组内缺失值的均值填充
df_nan = df[['Math','School']].copy().reset_index()
df_nan.loc[np.random.randint(0,df.shape[0],25),['Math']]=np.nan
df_nan.head()
|
ID |
Math |
School |
| 0 |
1101 |
34.0 |
S_1 |
| 1 |
1102 |
32.5 |
S_1 |
| 2 |
1103 |
87.2 |
S_1 |
| 3 |
1104 |
80.4 |
S_1 |
| 4 |
1105 |
84.8 |
S_1 |
df_nan.groupby('School').transform(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean())).join(df.reset_index()['School']).head()
|
ID |
Math |
School |
| 0 |
1101 |
34.0 |
S_1 |
| 1 |
1102 |
32.5 |
S_1 |
| 2 |
1103 |
87.2 |
S_1 |
| 3 |
1104 |
80.4 |
S_1 |
| 4 |
1105 |
84.8 |
S_1 |
四、apply函数
1. apply函数的灵活性
可能在所有的分组函数中,apply是应用最为广泛的,这得益于它的灵活性:
对于传入值而言,从下面的打印内容可以看到是以分组的表传入apply中:
df.groupby('School').apply(lambda x:print(x.head(1)))
School Class Gender Address Height Weight Math Physics
ID
1101 S_1 C_1 M street_1 173 63 34.0 A+
School Class Gender Address Height Weight Math Physics
ID
2101 S_2 C_1 M street_7 174 84 83.3 C
apply函数的灵活性很大程度来源于其返回值的多样性:
① 标量返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School').apply(lambda x:x.max())
|
School |
Math |
Height |
| School |
|
|
|
| S_1 |
S_1 |
97.0 |
195 |
| S_2 |
S_2 |
95.5 |
194 |
② 列表返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School').apply(lambda x:x-x.min()).head()
|
Math |
Height |
| ID |
|
|
| 1101 |
2.5 |
14.0 |
| 1102 |
1.0 |
33.0 |
| 1103 |
55.7 |
27.0 |
| 1104 |
48.9 |
8.0 |
| 1105 |
53.3 |
0.0 |
③ 数据框返回值
df[['School','Math','Height']].groupby('School')
.apply(lambda x:pd.DataFrame({'col1':x['Math']-x['Math'].max(),
'col2':x['Math']-x['Math'].min(),
'col3':x['Height']-x['Height'].max(),
'col4':x['Height']-x['Height'].min()})).head()
|
col1 |
col2 |
col3 |
col4 |
| ID |
|
|
|
|
| 1101 |
-63.0 |
2.5 |
-22 |
14 |
| 1102 |
-64.5 |
1.0 |
-3 |
33 |
| 1103 |
-9.8 |
55.7 |
-9 |
27 |
| 1104 |
-16.6 |
48.9 |
-28 |
8 |
| 1105 |
-12.2 |
53.3 |
-36 |
0 |
2. 用apply同时统计多个指标
此处可以借助OrderedDict工具进行快捷的统计:
from collections import OrderedDict
def f(df):
data = OrderedDict()
data['M_sum'] = df['Math'].sum()
data['W_var'] = df['Weight'].var()
data['H_mean'] = df['Height'].mean()
return pd.Series(data)
grouped_single.apply(f)
|
M_sum |
W_var |
H_mean |
| School |
|
|
|
| S_1 |
956.2 |
117.428571 |
175.733333 |
| S_2 |
1191.1 |
181.081579 |
172.950000 |
五、问题与练习
1. 问题
【问题一】 什么是fillna的前向/后向填充,如何实现?
【问题二】 下面的代码实现了什么功能?请仿照设计一个它的groupby版本。
s = pd.Series ([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0])
s1 = s.cumsum()
result = s.mul(s1).diff().where(lambda x: x < 0).ffill().add(s1,fill_value =0)
【问题三】 如何计算组内0.25分位数与0.75分位数?要求显示在同一张表上。
【问题四】 既然索引已经能够选出某些符合条件的子集,那么filter函数的设计有什么意义?
【问题五】 整合、变换、过滤三者在输入输出和功能上有何异同?
【问题六】 在带参数的多函数聚合时,有办法能够绕过wrap技巧实现同样功能吗?
2. 练习
【练习一】: 现有一份关于diamonds的数据集,列分别记录了克拉数、颜色、开采深度、价格,请解决下列问题:
pd.read_csv('data/Diamonds.csv').head()
|
carat |
color |
depth |
price |
| 0 |
0.23 |
E |
61.5 |
326 |
| 1 |
0.21 |
E |
59.8 |
326 |
| 2 |
0.23 |
E |
56.9 |
327 |
| 3 |
0.29 |
I |
62.4 |
334 |
| 4 |
0.31 |
J |
63.3 |
335 |
(a) 在所有重量超过1克拉的钻石中,价格的极差是多少?
(b) 若以开采深度的0.2�.4�.6�.8分位数为分组依据,每一组中钻石颜色最多的是哪一种?该种颜色是组内平均而言单位重量最贵的吗?
(c) 以重量分组(0-0.5,0.5-1,1-1.5,1.5-2,2+),按递增的深度为索引排序,求每组中连续的严格递增价格序列长度的最大值。
(d) 请按颜色分组,分别计算价格关于克拉数的回归系数。(单变量的简单线性回归,并只使用Pandas和Numpy完成)
【练习二】:有一份关于美国10年至17年的非法药物数据集,列分别记录了年份、州(5个)、县、药物类型、报告数量,请解决下列问题:
pd.read_csv('data/Drugs.csv').head()
|
YYYY |
State |
COUNTY |
SubstanceName |
DrugReports |
| 0 |
2010 |
VA |
ACCOMACK |
Propoxyphene |
1 |
| 1 |
2010 |
OH |
ADAMS |
Morphine |
9 |
| 2 |
2010 |
PA |
ADAMS |
Methadone |
2 |
| 3 |
2010 |
VA |
ALEXANDRIA CITY |
Heroin |
5 |
| 4 |
2010 |
PA |
ALLEGHENY |
Hydromorphone |
5 |
(a) 按照年份统计,哪个县的报告数量最多?这个县所属的州在当年也是报告数最多的吗?
(b) 从14年到15年,Heroin的数量增加最多的是哪一个州?它在这个州是所有药物中增幅最大的吗?若不是,请找出符合该条件的药物。
