为什么roc_auc_score()和auc()有不同的结果?
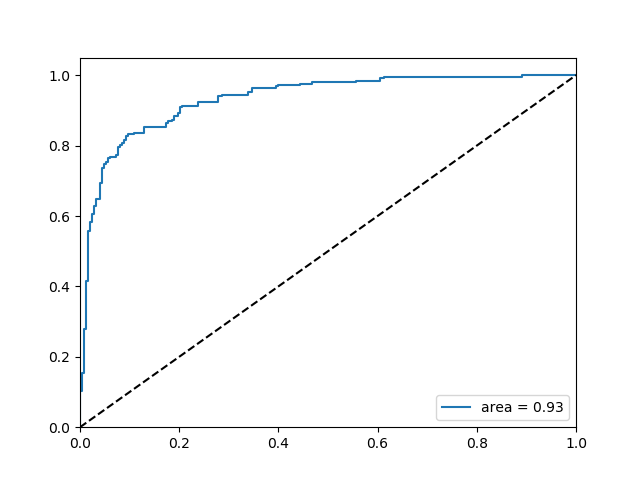
auc():计算ROC曲线下的面积.即图中的area
roc_auc_score():计算AUC的值,即输出的AUC

最佳答案
AUC并不总是ROC曲线下的面积.曲线下面积是某个曲线下的(抽象)区域,因此它比AUROC更通用.对于不平衡类,最好找到精确回忆曲线的AUC.
请参阅sklearn source for roc_auc_score:
def roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average="macro", sample_weight=None): # <...> docstring <...> def _binary_roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, sample_weight=None): # <...> bla-bla <...> fpr, tpr, tresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_score, sample_weight=sample_weight) return auc(fpr, tpr, reorder=True) return _average_binary_score( _binary_roc_auc_score, y_true, y_score, average, sample_weight=sample_weight)
首先获得roc曲线,然后调用auc()来获取该区域.你的问题是predict_proba()调用.对于正常的预测(),输出总是相同的:
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, roc_auc_score est = LogisticRegression(class_weight='auto') X = np.random.rand(10, 2) y = np.random.randint(2, size=10) est.fit(X, y) false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(y, est.predict(X)) print auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate) # 0.857142857143 print roc_auc_score(y, est.predict(X)) # 0.857142857143
如果您为此更改了上述内容,则有时会得到不同的输出:
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(y, est.predict_proba(X)[:,1]) # may differ print auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate) print roc_auc_score(y, est.predict(X))