一. 栈
栈的定义:栈是只允许在一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
1.栈的顺序存储
栈顶指针:S.top,初始设为-1
栈顶元素:S.data[S.top]
进栈操作:栈不满时,栈顶指针先加1,再到栈顶元素
出栈操作:栈非空时,先取栈顶元素,再栈顶指针减1
栈空条件:S.top=-1
栈满条件:S.top=MaxSize-1
栈长:S.top+1
(1)结构
typedef struct{ ElemType data[MaxSize]; int top;//栈顶 }Stack;
(2)初始化空栈
Stack InitStack() { Stack S; S.top=-1; return S; }
(3)判断栈是否为空
int StackEmpty(Stack S) { if(S.top==-1) { return TRUE; } else { return FALSE; } }
(4)进栈
int PushStack(Stack *p,ElemType x) { if(p->top==MaxSize-1) { printf("栈满! "); return FALSE; } p->data[++p->top]=x;//指针先加1,再入栈 return TRUE; }
(5)出栈
int PopStack(Stack *p,ElemType *x) { if(p->top==-1) { printf("栈空! "); return FALSE; } *x=p->data[p->top--];//先出栈,指针再减1 return TRUE; }
(6)读栈顶元素
ElemType GetTop(Stack S) { if(S.top==-1) { printf("栈空!无法读取栈顶元素! "); } else { return S.data[S.top]; } }
2.栈的链式存储

链栈便于多个栈共享存储空间和提高效率,规定所有操作都是再单链表的表头进行,没有用头结点,直接头指针指向栈顶元素。
(1)结构
struct NodeStack{ ElemType data; struct NodeStack *next; };
(2)初始化链栈
NodeStack* Init_NodeStack() { NodeStack *p; p=(NodeStack*)malloc(sizeof(NodeStack)); p->next=NULL; return p; }
(3)判断链栈是否为空
int NodeStack_Empty(NodeStack *head) { if(!head->next) { return TRUE; } else { return FALSE; } }
(4)入栈
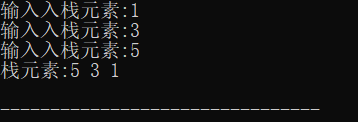
void Push_NodeStack(NodeStack *head) { NodeStack *p=(NodeStack*)malloc(sizeof(NodeStack)); ElemType x; printf("输入入栈元素:"); scanf("%d",&x); p->data=x; p->next=head->next; head->next=p; }
(5)出栈
void Pop_NodeStack(NodeStack *head) { NodeStack *p=(NodeStack*)malloc(sizeof(NodeStack)); p=head->next; head->next=p->next; free(p); }
(6)显示栈元素
void Print_NodeStack(NodeStack *head) { NodeStack *p=head; printf("栈元素:"); while(p->next) { printf("%d ",p->next->data); p=p->next; } printf(" "); }
运行示例: