上一篇文章《STL系列》之vector原理及实现,介绍了vector的原理及实现,这篇文章介绍map的原理及实现。STL实现源码下载。
STL中map的实现是基于RBTree的,我在实现的时候没有采用RBTree,觉得这东西有点复杂,我的map采用的是排序数组(CSortVector)。map中的Key存在排序数据中,通过二分查找判断某个Key是否在map中,时间复杂度为O(logN)。在用一个CVector存Key和Value,为了方便拿到Key和Value,这里有点冗余,Key被存了两次。
现在先介绍我的CSortVector,先贴出完整的代码,如下:

#ifndef _CSORTVECTOR_H_ #define _CSORTVECTOR_H_ namespace cth { template<typename T> class csortvector:public NoCopy { public: typedef const T* const_iterator; typedef T* iterator; csortvector() { initData(0); } csortvector(int capa,const T& val=T()) { initData(capa); newCapacity(capacity_); for (int i=0;i<size_;i++) buf[i]=val; } ~csortvector() { if (buf) { delete[] buf; buf=NULL; } size_=capacity_=0; } int add(const T& t ) { int index=-1; if (size_==0) { newCapacity(calculateCapacity()); buf[size_++]=t; index=0; }else{ int start=0; int end=size_-1; while(start<=end) { index=(start+end)/2; if(buf[index]==t) { goto SORTVECTOR_INSERT; } else if(buf[index]>t) { end=index-1; } else { start=index+1; } } if(buf[index]<t) { index++; } SORTVECTOR_INSERT: insert(index,t); } return index; } void insert(int index,const T& t) { assert(index>=0 && index<=size_); if (size_==capacity_) { newCapacity(calculateCapacity()); } memmove(buf+index+1,buf+index,(size_-index)*sizeof(T)); buf[index]=t; size_++; } int indexOf(const T& t) { int begin=0; int end=size_-1; int index=-1; while (begin<=end) { index=begin+(end-begin)/2; if (buf[index]==t) { return index; }else if (buf[index]<t) { begin=index+1; }else{ end=index-1; } } return -1; } int remove(const T& t) { int index=indexOf(t); if (index>=0) { memmove(buf+index ,buf+index+1,(size_-index)*sizeof(T)); buf[--size_]=T(); } return index; } void erase(const_iterator iter) { remove(*iter); } const_iterator begin() const { return const_iterator(&buf[0]); } const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(&buf[size_]); } const T& operator[](int index) const { assert(size_>0 && index>=0 && index<size_); return buf[index]; } void clear() { if (buf) { for (int i=0;i<size_;i++) { buf[i]=T(); } } size_=capacity_=0; } bool empty() const { return size_==0; } int size() const { return size_; } int capacity() const { return capacity_; } private: void newCapacity(int capa) { assert (capa>size_) ; capacity_=capa; T* newBuf=new T[capacity_]; if (buf) { memcpy(newBuf,buf,size_*sizeof(T) ); delete [] buf; } buf=newBuf; } inline void initData(int capa) { buf=NULL; size_=capacity_=capa>0?capa:0; } inline int calculateCapacity() { return capacity_*3/2+1; } int size_; int capacity_ ; T* buf; }; } #endif
CSortVector和CVector有点类似,只不过CSortVector中的数据在插入的时候需要排序,其他的接口比较相识。CSortVector的关键实现就是二分查找。新增和删除的时候都是通过二分查找,定位到指定的位置,在进行相关操作。这里有必要特意列出二分查找的实现,如下:
int indexOf(const T& t) { int begin=0; int end=size_-1; int index=-1; while (begin<=end) { index=begin+(end-begin)/2; if (buf[index]==t) { return index; }else if (buf[index]<t) { begin=index+1; }else{ end=index-1; } } return -1; }
CSortVector测试代码如下:
void csortvectorTest() { csortvector<int> l; l.add(2); l.add(4); l.add(9); l.add(3); l.add(7); l.add(1); l.add(5); l.add(8); l.add(0); l.add(6); cout<<"任意插入一组数据后,自动排序:"<<endl; for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl<<endl; l.erase(l.begin()); l.erase(l.end()-1); cout<<"删除第一个和最后一个数:"<<endl; for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl<<endl; cout<<"5的下标:"<<l.indexOf(5)<<endl; cout<<"下标为3的数:"<<l[3]<<endl; l.remove(5); cout<<"删除5以后,5的下标是"<<l.indexOf(5)<<endl<<endl; cout<<"最后还剩:"<<endl; for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++) { cout<<l[i]<<" "; } }
运行结果如下:
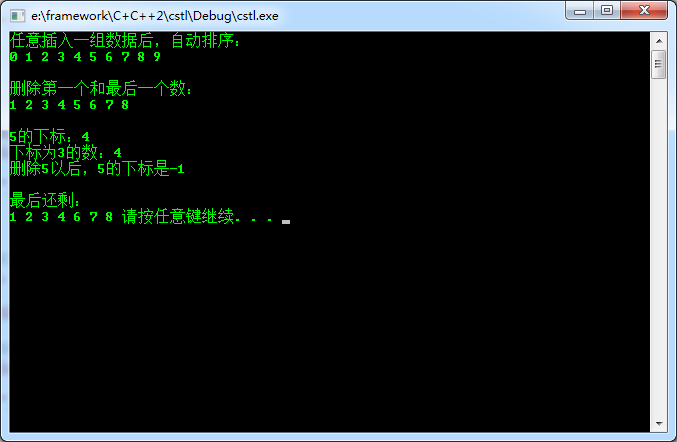
注意:由于CSortVector中的元素要排序,所以其中的元素要实现运算符”<”。
介绍完CSortVector,接下来说说CMap。其实CSortVector已经解决CMap的大部分功能了,后者只需要在前者的基础之上简单的封装即可完事。CMap源码如下:

#ifndef _CMAP_H_ #define _CMAP_H_ #include "csortvector.h" namespace cth { template<typename Key,typename Value> struct pair { typedef Key first_type; typedef Value second_type; pair(){} pair(const Key& key,const Value& val):first(key),second(val){} pair(const pair& other):first(other.first),second(other.second){} Key first; Value second; }; class NoCopy { public: inline NoCopy(){} NoCopy(const NoCopy&); NoCopy& operator=(const NoCopy&); }; template<typename Key,typename Value> class cmap:public NoCopy { public: typedef pair<Key,Value>* iterator; typedef const pair<Key,Value>* const_iterator; cmap(){} int insert(const pair<Key,Value>& item) { iterator iter=find(item.first); if (iter!=end()) { return iter-begin(); } int index=Keys.add(item.first); if (index>=0) { index=Values.insert(Values.begin() + index,item); } return index; } int insert(const Key& key,const Value& val) { pair<Key,Value> item; item.first=key; item.second=val; return insert(item); } Value& operator[](const Key& key) { int index=Keys.indexOf(key); if (index<0) { index=insert(key,Value()); } return Values[index].second; } iterator begin() { return iterator(&*Values.begin()); } iterator end() { return iterator(&*Values.end()); } iterator find(const Key& key) { int index=Keys.indexOf(key); if (index<0) { return end(); }else { return iterator(&Values[index]); } } void erase(const Key& key) { int index=Keys.remove(key) ; if (index>=0) { cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index; Values.erase(iter); } } void erase(const_iterator iter) { int index=Keys.remove(iter->first) ; if (index>=0) { cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index; Values.erase(iter); } } int size() { return Keys.size(); } bool empty() { return Keys.size()==0; } void clear() { Keys.clear(); Values.clear(); } private: csortvector<Key> Keys; cvector<pair<Key,Value>> Values; }; } #endif
插入操作,CMap的插入操作分两种,一种是通过insert方法;另一种是通过操作符[]。
Insert方法是先找到Key在Keys中的位置,如果已经存在就返回,CMap不允许重复,如果不存在就通过二分查找找到对应的位置,插入Key,并在Values中对应的地方插入Value。
通过操作符[]插入:如m[1]=1;刚开始我也不知道这个是怎么实现的,后来突然明白,操作符[]返回的是一个引用,其实就是给我m[1]的返回值赋值,调用的也是返回值的operator=,CMap只用实现operator[]就行。
其他的方法都是一些简单的封装,这里就不在累赘,最后概述一下CMap的实现:
CMap是基于一个排序数组CSortVector实现的,将Key存入排序数据中,Value和Key通过Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中,通过二分查找确定某个Key是否存在,不存在就将这个Key插入排序数据中,返回Key在数组中的索引,并将Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中对应的位置。删除还是通过二分查找寻找,找到就将两个数组中对应的元素删除。
CMap测试代码运行如下:

