1. HashMap介绍
HashMap集合底层是哈希表数据结构,存储的内容是键值对,继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map,Clonable,java.io.Serializable接口,是非线程安全的。
HashMap的构造函数
//指定容量大小和加载因子的构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) //指定容量的构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) //默认构造函数 public HashMap() //包含“子Map”的构造函数 public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
HashMap常用API
map中的常用方法: map集合存储的是key , value 数据 1. put() 集合中添加元素 2. get() 通过key,获取value 3. remove() 移除集合中的元素 4. size() 获取集合中键值对的数量 5. containsKey() 集合中是否包含指定key 6. values() 获取集合中的所有value,返回一个集合
2. HashMap总体结构
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
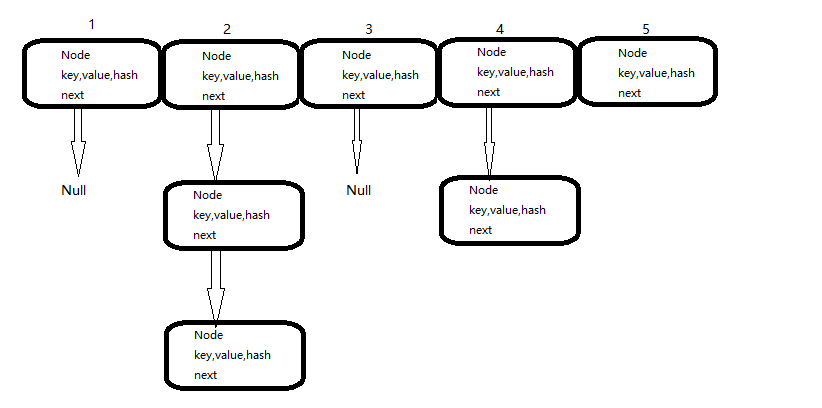
简单来看,HashMap由数组和链表组成,数组是HashMap的主体,链表是主要为了解决哈希冲突存在的,如果所在数组位置不包含链表,则next指向Null,那么查找和添加操作很快;如果包含链表,对于插入操作,首先遍历链表,存在则覆盖,否则新增;对于查询操作,也是需要遍历整个链表,然后equals方法逐一比较。
3. HashMap源码解析
HashMap主干是一个Node数组,数组存储key-value。
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
每个数组包含hash,key,value,next,Node是一个静态内部类
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; //指向下一个节点 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; }
//判断Node是否相等,若两个Node的key和value都相等,则返回true public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true; } return false; } }
可以看出,Node就是一个单链表,Node实现了Map.Entry接口,实现了getKey(),getValue(),setValue(),等方法。
HashMap中的几个重要字段
transient int size; transient int modCount; int threshold; final float loadFactor;
size:实际存储key-value键值对的个数
loadFactor:加载因子,表示HashMap的负载程度可以决定HashMap是否需要扩容,默认值是0.75;HashMap的初始化容量是16,初始化容量和加载因子共同决定HashMap是否要扩容了,也就是说大小为16的HashMap,到了12个元素,就会扩容为32,而不是等到满16个才开始扩容,这样一定程度减缓了哈希冲突。
threshold:阈值,当HashMap中存储的数据数量达到阈值时,就需要扩容。threshold = 容量*加载因子。
modCount:HashMap被改变的次数,HashMap是非线程安全的,再对HashMap跌打时,如果其他线程改变了HashMap的结构时(比如put,remove等操作),会抛出异常ConcurrentModificationException。
HashMap构造函数
//默认构造函数,设置加载因子
public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted }
//指定容量大小构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } //指定容量和加载因子构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); }
//包含子Map构造函数 public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; putMapEntries(m, false); }
clear()
public void clear() { Node<K,V>[] tab; modCount++; if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { size = 0; for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) tab[i] = null; } }
clear()方法的作用是清空hashmap,它是将hashmap的大小置为0,所有的值都设为null实现的
containsKey()
public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getNode(hash(key), key) != null; } final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
containsKey() 作用是检查HashMap中是否包含指定key,返回boolean类型。
通过getNode() 获取key对应的Node,判断Node是否为空。
containsValue()
public boolean containsValue(Object value) { Node<K,V>[] tab; V v; if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { for (Node<K,V> e : tab) { for (; e != null; e = e.next) { if ((v = e.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v))) return true; } } } return false; }
containsValue() 检查HashMap中是否包含指定value,返回boolean类型,遍历检查集合中节点值与value相等的元素。
entrySet()
keySet(),values()和entrySet()三者源码类似,都是返回可迭代对象,调用next()方法
//返回EntrySet对象 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es; return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es; }
//EntrySet继承AbstractSet final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { public final int size() { return size; } public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); } public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new EntryIterator(); } public final boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o; Object key = e.getKey(); Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key); return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e); } public final boolean remove(Object o) { if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o; Object key = e.getKey(); Object value = e.getValue(); return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null; } return false; } public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() { return new EntrySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0); } public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) { Node<K,V>[] tab; if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) { int mc = modCount; for (Node<K,V> e : tab) { for (; e != null; e = e.next) action.accept(e); } if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } }
entrySet()作用是遍历HashMap中的元素
//返回一个新的entry迭代器 public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new EntryIterator(); } //这个迭代器继承HashIterator,实现Iterator接口 final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); } } abstract class HashIterator { Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return Node<K,V> current; // current entry int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail int index; // current slot HashIterator() { expectedModCount = modCount; Node<K,V>[] t = table; current = next = null; index = 0; if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null); } } public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; } //获取下一个元素 final Node<K,V> nextNode() { Node<K,V>[] t; Node<K,V> e = next; if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) { do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null); } return e; } public final void remove() { Node<K,V> p = current; if (p == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); current = null; removeNode(p.hash, p.key, null, false, false); expectedModCount = modCount; } }
通过entrySet() 获取到Iterator的next()方法去遍历HashMap时,实际上是调用nextNode()来遍历整个Node节点。
get()
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
get() 方法的作用是返回HashMap中对应的元素value,和containsKey()方法类型都是调用getNode()方法遍历整个Node
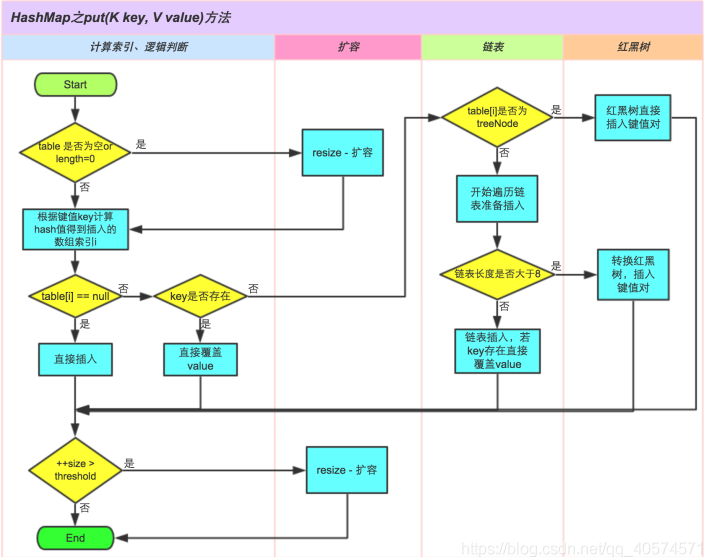
put()
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//table如果为空,重新resize()扩容 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length;
//根据键值key计算hash值,得到要插入位置的数组索引i,如果要插入位置为空,则直接插入 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果key相等,直接覆盖插入 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p;
//table[i]是treeNode,红黑树直接插入 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//遍历链表 else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//链表长度大于8,转换为红黑树直接插入 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; }
//链表插入,若key相等直接覆盖value if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } }
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount;
//超过阈值重新计算大小 if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
put() 作用是向HashMap中添加元素,如果对应的key已经存在HashMap中,则找到该键值对,用新的value覆盖旧的value,返回旧的;如果要添加的键值对key在HashMap中不存在,则添加到对应链表中。
java1.8后引入红黑树,当链表长度大于8时,链表就转换为红黑树,利用红黑树快速增删改查的特点提高HashMap的性能。
附引用流程图:
remove()
public V remove(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) node = p; else if ((e = p.next) != null) { if (p instanceof TreeNode) node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { node = e; break; } p = e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { if (node instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); else if (node == p) tab[index] = node.next; else p.next = node.next; ++modCount; --size; afterNodeRemoval(node); return node; } } return null; }
remove() 的作用是删除“键位key”的元素
4. HashMap的遍历
HashMap一般有两种遍历方式:
(1)通过keySet()获取所有的key值,然后遍历key,获取value;
(2)通过entrySet() 方法转换为一个Set集合,集合中保存元素类型是Map.Entry;
public class MapTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(1,"zhang"); map.put(2,"wang"); map.put(3,"he"); map.put(3,"le"); //keySet() Set<Integer> s = map.keySet(); //1. 通过遍历集合中的key获取value Iterator<Integer> it = s.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ Integer key = it.next(); String value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key +" = "+ value); } //2 . 通过增强for循环遍历 for(Integer i : s){ System.out.println(i + "=" + map.get(i)); } //entrySet() //1. 迭代器 Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set = map.entrySet(); Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it1= set.iterator(); while (it1.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<Integer, String> m= it1.next(); Integer key = m.getKey(); String value = m.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "-->" +value); } //2. 增强循环 for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> mm : set){ System.out.println(mm.getKey() + "---->" + mm.getValue()); } } }
5. HashMap的示例
HashMap中常用方法
public class MapTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(1,"zhang"); map.put(1,"AA"); map.put(2,"BB"); map.put(3,"CC"); map.put(4,"DD"); //map.clear(); String value = map.get(1); System.out.println(value); System.out.println("map集合的数量:"+map.size()); //4 map.remove(2); System.out.println("map集合的数量:"+map.size()); //3 System.out.println(map.containsKey(1)); //true System.out.println(map.containsKey(2)); //false System.out.println(map.containsValue("zhang")); //true System.out.println(map.containsValue("hel")); //false Collection<String> c = map.values(); //foreach for(String s : c){ System.out.println(s); } Map<String,String> map2 = new HashMap<>(); map2.put("AAA","BBB"); map2.put("CCC","DDD"); map2.put("EEE","FFF"); System.out.println(map2.size()); System.out.println(map2.get("AAA")); map2.put("EEE","GGG"); System.out.println(map2.get("EEE")); } }
6. HashMap重写equals()和hashCode()
当HashMap中需要添加的key的类型为自定义类型时,需要重写equals()和hashCode()方法。当key中的变量值(equals计算)和经过计算后的hash值都相等的情况下才可以判断key相等,此时put元素会直接覆盖之前元素,否则会添加元素。
public class HashMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student(1,"AA"); Student s2 = new Student(1,"AA"); System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); System.out.println(s2.hashCode()); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); HashMap hashmap = new HashMap(); hashmap.put(s1,1); hashmap.put(s2,2); System.out.println(hashmap.get(s1)); //2 System.out.println(hashmap.get(s2)); //2 System.out.println(hashmap.size()); //1 } } class Student{ private int id; private String name; public Student(int id, String name){ this.id = id; this.name = name; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student student = (Student) o; return id == student.id && Objects.equals(name, student.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(id, name); } }
当重写equals()和hashCode()方法后,put()元素会直接覆盖之前的元素,输出都是2;取消其中任意一个重写的方法,都会继续添加元素。