前面有介绍过json-lib这个框架,在线博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/04/21/2023805.html
以及Jackson这个框架,在线博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/04/22/2024628.html
它们都可以完成Java对象到XML的转换,但是还不是那么的完善。
还有XStream对JSON及XML的支持,它可以对JSON或XML的完美转换。在线博文:
http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/04/22/2025197.html
以及介绍Castor来完成Java对象到xml的相互转换。在线博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/04/25/2026819.html
Jaxb2完成xml的转换,在线博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/04/26/2029011.html
Jibx对Java对象的转换相对要负责些,它不仅需要配置xml还且还要生成相应的jar文件,已经xsd文件。下面我们就来慢慢看看Jibx转换Java到XML是如何完成的。
一、 准备工作
1、 准备资源
a) 官方示例:http://jibx.sourceforge.net/fromcode/bindgen-examples.html
http://www.java2s.com/Open-Source/Java/XML/JiBX/tutorial/Catalogtutorial.htm
b) Jar下载:http://sourceforge.net/projects/jibx/files/
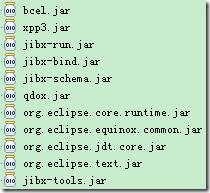
c) 依赖jar包如下:
2、 程序准备代码
package com.hoo.test;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.StringReader;import java.io.StringWriter;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import org.jibx.runtime.BindingDirectory;import org.jibx.runtime.IBindingFactory;import org.jibx.runtime.IMarshallingContext;import org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshallingContext;import org.jibx.runtime.JiBXException;import org.junit.After;import org.junit.Before;import org.junit.Test;import com.hoo.entity.Account;import com.hoo.entity.AccountArray;import com.hoo.entity.Birthday;import com.hoo.entity.ListBean;import com.hoo.entity.MapBean;/** * <b>function:</b> Jibx转换Java到XML * @author hoojo * @createDate 2011-4-25 下午06:47:33 * @file JibxTest.java * @package com.hoo.test * @project WebHttpUtils * @blog http://blog.csdn.net/IBM_hoojo * @email hoojo_@126.com * @version 1.0 */public class JibxTest {
private IBindingFactory factory = null; private StringWriter writer = null; private StringReader reader = null; private Account bean = null;@Before
public void init() {
bean = new Account(); bean.setAddress("北京"); bean.setEmail("email");bean.setId(1);
bean.setName("jack"); Birthday day = new Birthday(); day.setBirthday("2010-11-22");bean.setBirthday(day);
try { factory = BindingDirectory.getFactory(Account.class); } catch (JiBXException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@After
public void destory() {
bean = null;
try { if (writer != null) {writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
if (reader != null) {reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
System.gc();
}
public void fail(Object o) {
System.out.println(o);
}
public void failRed(Object o) {
System.err.println(o);
}
}
IBindingFactory是一个工厂接口,通过BindingDirectory的getFactory工厂方法可以获得某个对象。然后通过这个工程可以获得转换xml文档的上下文。
二、 转换Java到XML、转换XML到Java
1、 转换JavaEntity对象
a) 首先看看Account、Birthday的代码
package com.hoo.entity;public class Account {
private int id;
private String name; private String email; private String address; private Birthday birthday; //getter、setter@Override
public String toString() {return this.id + "#" + this.name + "#" + this.email + "#" + this.address + "#" + this.birthday;
}
}
Birthday
package com.hoo.entity;public class Birthday {
private String birthday; public Birthday(String birthday) { super(); this.birthday = birthday;}
//getter、setter public Birthday() {}@Override
public String toString() {return this.birthday;
}
}
b) 程序代码
@Test
public void bean2XML() {
try { writer = new StringWriter(); // marshal 编组IMarshallingContext mctx = factory.createMarshallingContext();
mctx.setIndent(2);
mctx.marshalDocument(bean, "UTF-8", null, writer);fail(writer);
reader = new StringReader(writer.toString()); //unmarshal 解组IUnmarshallingContext uctx = factory.createUnmarshallingContext();
Account acc = (Account) uctx.unmarshalDocument(reader, null);
fail(acc);
} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
这样还不够,复杂的东西还在后面。Jibx转换XML文档还要经过一系列复杂的程序。
c) 首先,要写bind.xml和schema。不过还好,官方有提高工具类可以用。
org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen或org.jibx.binding.BindingGenerator这两个类都可以,用法如下:
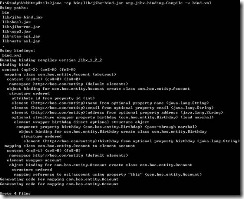
首先用dos进入当前工程目录,然后执行命令:E:\Study\WebHttpUtils>java -cp bin;lib/jibx-tools.jar;lib/log4j-1.2.16.jar org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen -b bind.xml com.hoo.entity.Account
上面的java 是运行某个程序 –cp是依赖的classpath路径的jar、zip等文件,-b 是输出文件名称,是BindGen类的参数。这样会在当前工程目录中生成bind.xml和entity.xsd文件。先看看这2个文件
bind.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<binding value-style="attribute">
<mapping class="com.hoo.entity.Account" name="account">
<value name="id" field="id"/>
<value style="element" name="name" field="name" usage="optional"/>
<value style="element" name="email" field="email" usage="optional"/>
<value style="element" name="address" field="address" usage="optional"/>
<structure field="birthday" usage="optional" name="birthday">
<value style="element" name="birthday" field="birthday" usage="optional"/>
</structure>
</mapping>
</binding>
entity.xsd文件
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:tns="http://hoo.com/entity"
elementFormDefault="qualified" targetNamespace="http://hoo.com/entity"><xs:element type="tns:account" name="account"/>
<xs:complexType name="account">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="name" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="email" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="address" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="birthday" minOccurs="0">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element type="xs:string" name="birthday" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute type="xs:int" use="required" name="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
上面最重要的就是bind.xml文件了,下面编译的时候需要这个文件。Xsd文件可以根据这个文件的内容生成Java的Entity类代码。
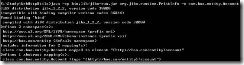
执行完命令后,没有错误就可以运行下面一段命令了。运行命令:
E:\Study\WebHttpUtils>java -cp bin;lib/jibx-bind.jar org.jibx.binding.Compile -v bind.xml
-v是绑定文件的名称
运行后,有如下结果:
d) 然后你就可以运行上面的Java的Junit测试程序了,运行后结果如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<account xmlns="http://hoo.com/entity" id="1">
<name>jack</name>
<email>email</email>
<address>北京</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
1#jack#email#北京#2010-11-22
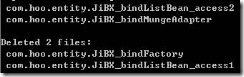
你还可以用命令来查看某个已经生成bind、schema文件的信息,如:
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-run.jar org.jibx.runtime.PrintInfo -c com.hoo.entity.Account
结果如下:
e) 注意,有时候会出现异常信息,如:java.lang.NoSuchFieldException: JiBX_bindingXXXX就要重复下面的命令就可以了。
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-bind.jar org.jibx.binding.Compile -v bind.xml
2、 转换带List集合属性的JavaBean
a) 程序代码
@Test
public void listBean2XML() {
try { ListBean listBean = new ListBean(); List<Account> list = new ArrayList<Account>();list.add(bean);
bean = new Account(); bean.setAddress("china"); bean.setEmail("tom@125.com");bean.setId(2);
bean.setName("tom");Birthday day = new Birthday("2010-11-22");
bean.setBirthday(day);
list.add(bean);
listBean.setList(list);
writer = new StringWriter(); factory = BindingDirectory.getFactory(ListBean.class); // marshal 编组IMarshallingContext mctx = factory.createMarshallingContext();
mctx.setIndent(2);
mctx.marshalDocument(listBean, "UTF-8", null, writer);fail(writer);
reader = new StringReader(writer.toString()); //unmarshal 解组IUnmarshallingContext uctx = factory.createUnmarshallingContext();
listBean = (ListBean) uctx.unmarshalDocument(reader, null);
fail(listBean.getList().get(0));
fail(listBean.getList().get(1));
} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
b) ListBean代码
package com.hoo.entity;import java.util.List;public class ListBean {
private String name; private List list;}
c) 生成bind.xml
执行dos命令:
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-tools.jar;lib/log4j-1.2.16.jar org.jibx.binding.BindingGenerator -f bind.xml com.hoo.entity.ListBean
输出:
d) 执行完后会生产bind.xml
Bind文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<binding value-style="attribute">
<mapping class="com.hoo.entity.ListBean" name="list-bean">
<value style="element" name="name" field="name" usage="optional"/>
<collection field="list" usage="optional" factory="org.jibx.runtime.Utility.arrayListFactory"/>
</mapping>
</binding>
e) 运行Compile工具类
在运行前,一定要将最先前运行的Account那个类的bind.xml文件的内容加入到现在这个bind.xml中,因为ListBean依赖了Account这个类。
命令如下:
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-bind.jar org.jibx.binding.Compile -v bind.xml
运行后你可以看到最后出现这个
f) 运行Test程序,结果如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<list-bean>
<account id="1">
<name>jack</name>
<email>email</email>
<address>北京</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
<account id="2">
<name>tom</name>
<email>tom@125.com</email>
<address>china</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
</list-bean>
1#jack#email#北京#2010-11-22
2#tom#tom@125.com#china#2010-11-223、 转换Java对象数组
a) Test程序
/** * <b>function:</b>转换对象数组 * @author hoojo * @createDate 2011-4-26 下午05:32:03 */@Test
public void arrayBean2XML() {
try { Account[] acc = new Account[2];acc[0] = bean;
bean = new Account(); bean.setName("tom");bean.setId(223);
acc[1] = bean;
AccountArray array = new AccountArray();array.setAccounts(acc);
writer = new StringWriter(); factory = BindingDirectory.getFactory(AccountArray.class); // marshal 编组IMarshallingContext mctx = factory.createMarshallingContext();
mctx.setIndent(2);
mctx.marshalDocument(array, "UTF-8", null, writer);fail(writer);
reader = new StringReader(writer.toString()); //unmarshal 解组IUnmarshallingContext uctx = factory.createUnmarshallingContext();
array = (AccountArray) uctx.unmarshalDocument(reader, null);
fail(array.getAccounts()[0]);
fail(array.getAccounts()[1]);
} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
b) AccountArray代码
package com.hoo.entity;public class AccountArray {
private Account[] accounts;private int size;
public int getSize() {
size = accounts.length;
return size;}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;}
public Account[] getAccounts() { return accounts;}
public void setAccounts(Account[] accounts) {
this.accounts = accounts;}
}
c) 运行命令生成bind.xml文件
命令如下:
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-tools.jar;lib/log4j-1.2.16.jar org.jibx.binding.BindingGenerator -f bind.xml com.hoo.entity.Account com.hoo.entity.AccountArray
因为AccountArray依赖Account,所以后面带2个类
d) 运行Compile命令
java -cp bin;lib/jibx-bind.jar org.jibx.binding.Compile -v bind.xml
e) 执行完后,就可以运行Test程序了,结果如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<account-array size="0">
<account id="1">
<name>jack</name>
<email>email</email>
<address>北京</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
<account id="223">
<name>tom</name>
</account>
</account-array>
1#jack#email#北京#2010-11-22
223#tom#null#null#null
4、 转换带Map结合的JavaEntity对象
a) Test代码
/** * <b>function:</b>转换Map集合 * @author hoojo * @createDate 2011-4-26 下午05:40:34 */@Test
public void mapBean2XML() {
try { MapBean mapBean = new MapBean(); HashMap<String, Account> map = new HashMap<String, Account>(); map.put("No1", bean); bean = new Account(); bean.setAddress("china"); bean.setEmail("tom@125.com");bean.setId(2);
bean.setName("tom");Birthday day = new Birthday("2010-11-22");
bean.setBirthday(day);
map.put("No2", bean);mapBean.setMap(map);
factory = BindingDirectory.getFactory(MapBean.class); writer = new StringWriter(); // marshal 编组IMarshallingContext mctx = factory.createMarshallingContext();
mctx.setIndent(2);
mctx.marshalDocument(mapBean, "UTF-8", null, writer);fail(writer);
reader = new StringReader(writer.toString()); //unmarshal 解组IUnmarshallingContext uctx = factory.createUnmarshallingContext();
mapBean = (MapBean) uctx.unmarshalDocument(reader, null);
fail(mapBean.getMap());
fail(mapBean.getMap().get("No1")); fail(mapBean.getMap().get("No2")); } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
b) MapBean代码
package com.hoo.entity;import java.util.HashMap;public class MapBean {
private HashMap<String, Account> map; public HashMap<String, Account> getMap() { return map;}
public void setMap(HashMap<String, Account> map) {
this.map = map;}
}
c) 生成bind.xml,命令如下
E:\Study\WebHttpUtils>java -cp bin;lib/jibx-tools.jar;lib/log4j-1.2.16.jar org.jibx.binding.BindingGenerator -f bind.xml com.hoo.entity.Account com.hoo.entity.MapBean
运行后,会生产bind.xml;修改bind.xml内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<binding value-style="attribute">
<mapping class="com.hoo.entity.Account" name="account">
<value name="id" field="id" />
<value style="element" name="name" field="name" usage="optional" />
<value style="element" name="email" field="email" usage="optional" />
<value style="element" name="address" field="address" usage="optional" />
<structure field="birthday" usage="optional" name="birthday">
<value style="element" name="birthday" field="birthday" usage="optional" />
</structure>
</mapping>
<mapping class="com.hoo.entity.MapBean" name="map-bean">
<structure field="map" usage="optional" name="map"
marshaller="com.hoo.util.HashMapper" unmarshaller="com.hoo.util.HashMapper">
</structure>
</mapping>
</binding>
注意上面的MapBean的structure元素的内容是经过修改的。一定要带上marshaller或unmarshaller,不然无法转换HashMap的。
d) HashMapper代码
package com.hoo.util;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;import org.jibx.runtime.IAliasable;import org.jibx.runtime.IMarshallable;import org.jibx.runtime.IMarshaller;import org.jibx.runtime.IMarshallingContext;import org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshaller;import org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshallingContext;import org.jibx.runtime.JiBXException;import org.jibx.runtime.impl.MarshallingContext;import org.jibx.runtime.impl.UnmarshallingContext;/** * <b>function:</b>http://www.java2s.com/Open-Source/Java/XML/JiBX/tutorial/example21/HashMapper.java.htm * @file HashMapper.java * @package com.hoo.util * @project WebHttpUtils * @blog http://blog.csdn.net/IBM_hoojo * @email hoojo_@126.com * @version 1.0 */public class HashMapper implements IMarshaller, IUnmarshaller, IAliasable
{private static final String SIZE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "size";
private static final String ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME = "entry";
private static final String KEY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "key";
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
private String m_uri;private int m_index;
private String m_name; public HashMapper() {m_uri = null;
m_index = 0;
m_name = "hashmap";}
public HashMapper(String uri, int index, String name) {
m_uri = uri;
m_index = index;
m_name = name;
}
/* (non-Javadoc) * @see org.jibx.runtime.IMarshaller#isExtension(int) */public boolean isExtension(int index) {
return false;}
/* (non-Javadoc) * @see org.jibx.runtime.IMarshaller#marshal(java.lang.Object, * org.jibx.runtime.IMarshallingContext) */public void marshal(Object obj, IMarshallingContext ictx)
throws JiBXException { // make sure the parameters are as expectedif (!(obj instanceof HashMap)) {
throw new JiBXException("Invalid object type for marshaller");
} else if (!(ictx instanceof MarshallingContext)) {
throw new JiBXException("Invalid object type for marshaller");
} else { // start by generating start tag for containerMarshallingContext ctx = (MarshallingContext)ictx;
HashMap map = (HashMap)obj;
ctx.startTagAttributes(m_index, m_name).
attribute(m_index, SIZE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, map.size()).
closeStartContent();
// loop through all entries in hashmapIterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
ctx.startTagAttributes(m_index, ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME);
if (entry.getKey() != null) {ctx.attribute(m_index, KEY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,
entry.getKey().toString());
}
ctx.closeStartContent();
if (entry.getValue() instanceof IMarshallable) {
((IMarshallable)entry.getValue()).marshal(ctx);
ctx.endTag(m_index, ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME);
} else {throw new JiBXException("Mapped value is not marshallable");
}
}
// finish with end tag for container elementctx.endTag(m_index, m_name);
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc) * @see org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshaller#isPresent(org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshallingContext) */public boolean isPresent(IUnmarshallingContext ctx) throws JiBXException {
return ctx.isAt(m_uri, m_name);}
/* (non-Javadoc) * @see org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshaller#unmarshal(java.lang.Object, * org.jibx.runtime.IUnmarshallingContext) */ public Object unmarshal(Object obj, IUnmarshallingContext ictx) throws JiBXException { // make sure we're at the appropriate start tagUnmarshallingContext ctx = (UnmarshallingContext)ictx;
if (!ctx.isAt(m_uri, m_name)) {ctx.throwStartTagNameError(m_uri, m_name);
}
// create new hashmap if needed int size = ctx.attributeInt(m_uri, SIZE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, DEFAULT_SIZE);HashMap map = (HashMap)obj;
if (map == null) { map = new HashMap(size);}
// process all entries present in documentctx.parsePastStartTag(m_uri, m_name);
while (ctx.isAt(m_uri, ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME)) {Object key = ctx.attributeText(m_uri, KEY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, null);
ctx.parsePastStartTag(m_uri, ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME);
Object value = ctx.unmarshalElement();
map.put(key, value);
ctx.parsePastEndTag(m_uri, ENTRY_ELEMENT_NAME);
}
ctx.parsePastEndTag(m_uri, m_name);
return map;}
public boolean isExtension(String arg0) {
return false;}
}
e) 然后运行Compile命令
E:\Study\WebHttpUtils>java -cp bin;lib/jibx-bind.jar org.jibx.binding.Compile -v bind.xml
f) 结果如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<map-bean>
<map size="2">
<entry key="No2">
<account id="2">
<name>tom</name>
<email>tom@125.com</email>
<address>china</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
</entry>
<entry key="No1">
<account id="1">
<name>jack</name>
<email>email</email>
<address>北京</address>
<birthday>
<birthday>2010-11-22</birthday>
</birthday>
</account>
</entry>
</map>
</map-bean>
{No2=2#tom#tom@125.com#china#2010-11-22, No1=1#jack#email#北京#2010-11-22}1#jack#email#北京#2010-11-22
2#tom#tom@125.com#china#2010-11-22