18.01 Map集合概述和特点
Map接口概述:将键映射到值的对象,一个映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值
Map接口和Collection接口的不同
1.Map是双列的,Collection是单列的
2.Map的键唯一,Collection的子体系Set是唯一的
3.Map集合的数据结构值针对键有效,跟值无关,Collection集合的数据结构是针对元素有效
18.02 Map集合的功能概述
成员方法:
将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联(可选操作)。
如果存在一个键的映射关系,则将其从此映射中移除(可选操作)。
3.void clear():
从此映射中移除所有映射关系(可选操作)。
4.boolean containsKey(Object key):
如果此映射包含指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。
5.boolean containsValue(Object value):
如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。
6.boolean isEmpty():
如果此映射未包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。
7.int size():
返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。
返回指定键所映射的值;如果此映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回 null。
返回此映射中包含的键的 Set 视图。
10.Collection<V> values()
返回此映射中包含的值的 Collection 视图。
11.Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。
18.03 Map集合的基本功能测试
map.put("001", "旺财"); :第一次存储直接存储元素,返回null
map.put("001", "小强"); :不是第一次存储,用新值将以前的值替换掉,返回以前的值
map.remove("001"); :根据键删除键值对元素,并返回键所对应的值,没有则返回空
18.04 Map集合的获取功能测试
1 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
2
3 map.put("001", "小明");
4 map.put("002", "旺财");
5 map.put("003", "小强");
6 //根据键获取值
7 System.out.println(map.get("002"));//旺财,没有该键返回null
8 System.out.println("-----");
9 //获取集合中所有键的集合
10 Set<String> set = map.keySet();
11 for(String key : set)
12 {
13 System.out.println(key);
14 }
15 System.out.println("-----");
16 //获取集合中所有值的集合
17 Collection<String> coll = map.values();
18 for(String value : coll)
19 {
20 System.out.println(value);
21 }
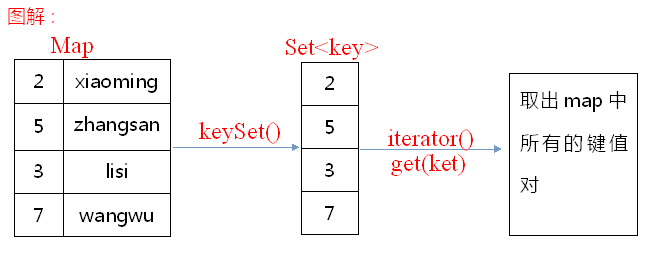
18.05 Map集合的遍历之键找值
根据键找值:
获取所有键的集合,遍历键的集合,获取到每一个键,根据键找值
1 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
2 map.put("001", "小明");
3 map.put("002", "旺财");
4 map.put("003", "小强");
5
6 //获取所有的键
7 Set<String> set = map.keySet();
8 for(String key : set)
9 {
10 //根据键找值
11 String value = map.get(key);
12 System.out.println(key+":"+value);
13 }
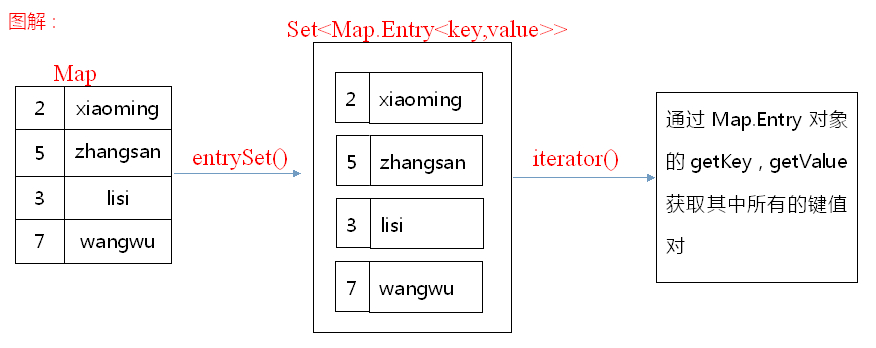
18.06 Map集合的遍历之键值对对象找键和值
根据键值对对象找键和值:
获取所有键值对对象的集合,遍历键值对对象的集合,获取到每一个键值对对象,根据键值对对象找键和值
1 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
2 map.put("001", "小明");
3 map.put("002", "旺财");
4 map.put("003", "小强");
5 //获取所有键值对对象的集合
6 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set = map.entrySet();
7 //遍历键值对对象的集合,获取每一个键值对对象
8 for(Map.Entry<String, String> me : set)
9 {
10 //根据键值对对象获取键和值
11 String key = me.getKey();
12 String value = me.getValue();
13 System.out.println(key+":"+value);
14 }
18.07 Map集合遍历的两种方式比较图解
18.08 HashMap集合键是Stirng值是String的案例
HashMap类概述:键是哈希表结构,可以保证键的唯一性
1 HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
2
3 map.put("001", "小明");
4 map.put("002", "旺财");
5 map.put("003", "小强");
6 map.put("004", "小红");
7 Set<String> set = map.keySet();
8 for(String key : set)
9 {
10 String value = map.get(key);
11 System.out.println(key+"--"+value);
12 }
18.09 HashMap集合键是Student值是String的案例
1 // 创建集合对象
2 HashMap<Student, String> hm = new HashMap<Student, String>();
3
4 hm.put(new Student("小明",23), "001");
5 hm.put(new Student("小强",15), "002");
6 hm.put(new Student("旺财",13), "003");
7 hm.put(new Student("张三",17), "004");
8 hm.put(new Student("小强",15), "005");
9
10 // 遍历
11 Set<Student> set = hm.keySet();
12 for (Student key : set)
13 {
14 String value = hm.get(key);
15 System.out.println(key.getName() + "---" + key.getAge() + "---"
16 + value);
17 }
当键是自定义对象时,需重写hashCode()和equals()方法
18.10 LinkedHashMap的概述和使用
Map接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。
由哈希表保证键的唯一性
由链表保证键的有序
1 LinkedHashMap<String, String> hm = new LinkedHashMap<String,String>();
2
3 // 创建并添加元素
4 hm.put("2345", "hello");
5 hm.put("1234", "world");
6 hm.put("3456", "java");
7 hm.put("1234", "javaee");
8 hm.put("3456", "android");
9
10 // 遍历
11 Set<String> set = hm.keySet();
12 for (String key : set)
13 {
14 String value = hm.get(key);
15 System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
16 }
运行结果:
2345---hello 1234---javaee 3456---android
18.11 TreeMap集合键是String值是String的案例
TreeMap类概述:键是红黑树结构,可以保证键的排序和唯一性
1 // 创建集合对象
2 TreeMap<String, String> tm = new TreeMap<String, String>();
3
4 // 创建元素并添加元素
5 tm.put("hello", "你好");
6 tm.put("world", "世界");
7 tm.put("java", "爪哇");
8 tm.put("world", "世界2");
9 tm.put("javaee", "爪哇EE");
10
11 // 遍历集合
12 Set<String> set = tm.keySet();
13 for (String key : set)
14 {
15 String value = tm.get(key);
16 System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
17 }
运行结果:
hello---你好 java---爪哇 javaee---爪哇EE world---世界2
18.12 TreeMap集合键是Student值是String的案例
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建集合对象
6 TreeMap<Student, String> tm = new TreeMap<Student, String>(new Comparator<Student>()
7 {
8 @Override
9 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
10 {
11 // 主要条件
12 int num = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
13 // 次要条件
14 int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(
15 s2.getName()) : num;
16 return num2;
17 }
18 });
19
20 tm.put(new Student("小明",23), "001");
21 tm.put(new Student("小强",15), "002");
22 tm.put(new Student("旺财",13), "003");
23 tm.put(new Student("张三",17), "004");
24 tm.put(new Student("小强",15), "005");
25
26 Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> set = tm.entrySet();
27 for(Map.Entry<Student, String> me : set)
28 {
29 Student key = me.getKey();
30 String value = me.getValue();
31 System.out.println(key.getName()+":"+key.getAge()+":"+value);
32 }
33 }
34 }
运行结果:
旺财:13:003 小强:15:005 张三:17:004 小明:23:001
18.13 统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数案例图解
"aababcabcdabcde",获取字符串中每一个字母出现的次数要求结果:a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)

18.14 统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数案例代码实现
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 定义一个字符串(改进为键盘录入)
6 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
7 System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
8 String line = sc.nextLine();
9
10 // 定义一个TreeMap集合
11 TreeMap<Character, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<Character, Integer>();
12
13 //把字符串转换为字符数组
14 char[] chs = line.toCharArray();
15
16 //遍历字符数组,得到每一个字符
17 for(char ch : chs)
18 {
19 //拿刚才得到的字符作为键到集合中去找值,看返回值
20 Integer i = tm.get(ch);
21
22 //是null:说明该键不存在,就把该字符作为键,1作为值存储
23 if(i == null)
24 {
25 tm.put(ch, 1);
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 //不是null:说明该键存在,就把值加1,然后重写存储该键和值
30 i++;
31 tm.put(ch,i);
32 }
33 }
34
35 //定义字符串缓冲区变量
36 StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
37
38 //遍历集合,得到键和值,进行按照要求拼接
39 Set<Character> set = tm.keySet();
40 for(Character key : set)
41 {
42 Integer value = tm.get(key);
43 sb.append(key).append("(").append(value).append(")");
44 }
45
46 //把字符串缓冲区转换为字符串输出
47 String result = sb.toString();
48 System.out.println("结果:"+result);
49 }
50 }
运行结果:
请输入一个字符串: aasdgrfedcsdf 结果:a(2)c(1)d(3)e(1)f(2)g(1)r(1)s(2)
18.15 HashMap集合嵌套HashMap集合的案例
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 大集合对象
6 HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> bigMap = new HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>>();
7
8 // 集合对象1
9 HashMap<String, Integer> hm1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
10 // 添加元素
11 hm1.put("小明", 20);
12 hm1.put("小强", 22);
13 // 把集合添加到大集合
14 bigMap.put("集合1", hm1);
15
16 // 集合对象2
17 HashMap<String, Integer> hm2 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
18 // 添加元素
19 hm2.put("旺财", 5);
20 hm2.put("张三", 23);
21 // 把集合添加到大集合
22 bigMap.put("集合2", hm2);
23
24 //遍历集合
25 Set<String> bigMapset = bigMap.keySet();
26 for(String bigMapKey : bigMapset)
27 {
28 System.out.println(bigMapKey);
29 HashMap<String, Integer> value = bigMap.get(bigMapKey);
30 Set<String> set = value.keySet();
31 for(String s : set)
32 {
33 Integer i = value.get(s);
34 System.out.println(" "+s+":"+i);
35 }
36 }
37 }
38 }
运行结果:
集合1
小强:22
小明:20
集合2
旺财:5
张三:23
18.16 集合多层嵌套的代码体现
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建大集合
6 HashMap<String, HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>>> czbkMap = new HashMap<String, HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>>>();
7
8 // 北京校区数据
9 HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>> bjCzbkMap = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>>();
10 ArrayList<Student> array1 = new ArrayList<Student>();
11 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27);
12 Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30);
13 array1.add(s1);
14 array1.add(s2);
15 ArrayList<Student> array2 = new ArrayList<Student>();
16 Student s3 = new Student("赵雅芝", 28);
17 Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 29);
18 array2.add(s3);
19 array2.add(s4);
20 bjCzbkMap.put("基础班", array1);
21 bjCzbkMap.put("就业班", array2);
22 czbkMap.put("北京校区", bjCzbkMap);
23
24 // 西安校区数据
25 HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>> xaCzbkMap = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>>();
26 ArrayList<Student> array3 = new ArrayList<Student>();
27 Student s5 = new Student("范冰冰", 27);
28 Student s6 = new Student("刘意", 30);
29 array3.add(s5);
30 array3.add(s6);
31 ArrayList<Student> array4 = new ArrayList<Student>();
32 Student s7 = new Student("李冰冰", 28);
33 Student s8 = new Student("张志豪", 29);
34 array4.add(s7);
35 array4.add(s8);
36 xaCzbkMap.put("基础班", array3);
37 xaCzbkMap.put("就业班", array4);
38 czbkMap.put("西安校区", xaCzbkMap);
39
40 // 遍历集合
41 Set<String> czbkMapSet = czbkMap.keySet();
42 for (String czbkMapKey : czbkMapSet)
43 {
44 System.out.println(czbkMapKey);
45 HashMap<String, ArrayList<Student>> czbkMapValue = czbkMap.get(czbkMapKey);
46 Set<String> czbkMapValueSet = czbkMapValue.keySet();
47 for (String czbkMapValueKey : czbkMapValueSet)
48 {
49 System.out.println(" " + czbkMapValueKey);
50 ArrayList<Student> czbkMapValueValue = czbkMapValue.get(czbkMapValueKey);
51 for (Student s : czbkMapValueValue)
52 {
53 System.out.println(" " + s.getName() + "---"+ s.getAge());
54 }
55 }
56 }
57 }
58 }
运行结果:
北京校区
就业班
赵雅芝---28
武鑫---29
基础班
林青霞---27
风清扬---30
西安校区
就业班
李冰冰---28
张志豪---29
基础班
范冰冰---27
刘意---30
18.17 HashMap和Hashtable的区别
1:Hashtable和HashMap的区别
Hashtable:线程安全,效率低。不允许null键和null值
HashMap:线程不安全,效率高。允许null键和null值
2:List,Set,Map等接口是否都继承子Map接口?
List,Set不是继承自Map接口,它们继承自Collection接口
Map接口本身就是一个顶层接口
18.18 Collections工具类的概述
Collections类概述:针对集合操作的工具类,都是静态方法
Collection和Collections的区别:
Collection:是单列集合的顶层接口,有子接口List和Set。
Collections:是针对集合操作的工具类,有对集合进行排序和二分查找的方法
18.19 Collections工具类的常见方法讲解
Collections成员方法
1.public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list):
根据元素的自然顺序对指定列表按升序进行排序。
2.public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list,T key):
使用二分搜索法搜索指定列表,以获得指定对象。
3.public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll):
根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定 collection 的最大元素。
4.public static void reverse(List<?> list):
反转指定列表中元素的顺序。
5.public static void shuffle(List<?> list):
使用默认随机源对指定列表进行置换。所有置换发生的可能性都是大致相等的。
例:
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建集合对象
6 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
7
8 // 添加元素
9 list.add(30);
10 list.add(20);
11 list.add(50);
12 list.add(10);
13 list.add(40);
14
15 System.out.println("原始:" + list);
16 //排序 默认情况下是自然顺序
17 Collections.sort(list);
18 System.out.println("排序:" + list);
19 // 二分查找
20 System.out.println("查找:"+Collections.binarySearch(list, 30));
21 // 最大值
22 System.out.println("最大值:"+Collections.max(list));
23 // 反转
24 Collections.reverse(list);
25 System.out.println("反转:" + list);
26 //随机置换
27 Collections.shuffle(list);
28 System.out.println("随机:" + list);
29 }
30 }
运行结果:
原始:[30, 20, 50, 10, 40] 排序:[10, 20, 30, 40, 50] 查找:2 最大值:50 反转:[50, 40, 30, 20, 10] 随机:[20, 10, 30, 50, 40]
18.20 ArrayList存储自定义对象并排序案例
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建集合对象
6 List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
7
8 // 创建学生对象
9 Student s1 = new Student("小明", 27);
10 Student s2 = new Student("旺财", 30);
11 Student s3 = new Student("小强", 28);
12 Student s4 = new Student("张三", 29);
13
14 // 添加元素对象
15 list.add(s1);
16 list.add(s2);
17 list.add(s3);
18 list.add(s4);
19
20 // 排序
21 // 自然排序必须实现 Comparable 接口
22 //Collections.sort(list);
23 // 比较器排序
24 // 如果同时有自然排序和比较器排序,以比较器排序为主
25 Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Student>()
26 {
27 @Override
28 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
29 {
30 int num = s2.getAge() - s1.getAge();
31 int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()): num;
32 return num2;
33 }
34 });
35 // 遍历集合
36 for (Student s : list)
37 {
38 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
39 }
40 }
41 }
运行结果:
旺财---30 张三---29 小强---28 小明---27
18.21 模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌
模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌
分析:
A:创建一个牌盒、B:装牌、C:洗牌、D:发牌、E:看牌
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建一个牌盒
6 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>();
7
8 // 定义一个花色数组
9 String[] colors = { "♠", "♥", "♣", "♦" };
10 // 定义一个点数数组
11 String[] numbers = { "A", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10",
12 "J", "Q", "K" };
13 // 装牌
14 for (String color : colors)
15 {
16 for (String number : numbers)
17 {
18 array.add(color.concat(number));
19 }
20 }
21 array.add("小王");
22 array.add("大王");
23
24 // 洗牌
25 Collections.shuffle(array);
26
27 // System.out.println("array:" + array);
28
29 // 发牌
30 ArrayList<String> player1 = new ArrayList<String>();
31 ArrayList<String> player2 = new ArrayList<String>();
32 ArrayList<String> player3 = new ArrayList<String>();
33 ArrayList<String> diPai = new ArrayList<String>();
34
35 for (int x = 0; x < array.size(); x++)
36 {
37 if (x >= array.size() - 3)
38 {
39 diPai.add(array.get(x));
40 }
41 else if (x % 3 == 0)
42 {
43 player1.add(array.get(x));
44 }
45 else if (x % 3 == 1)
46 {
47 player2.add(array.get(x));
48 }
49 else if (x % 3 == 2)
50 {
51 player3.add(array.get(x));
52 }
53 }
54
55 // 看牌
56 lookPoker("玩家1", player1);
57 lookPoker("玩家2", player2);
58 lookPoker("玩家3", player3);
59
60 lookPoker("底牌", diPai);
61 }
62
63 public static void lookPoker(String name, ArrayList<String> array)
64 {
65 System.out.print(name + "的牌是:");
66 for (String s : array)
67 {
68 System.out.print(s + " ");
69 }
70 System.out.println();
71 }
72 }
运行结果:
玩家1的牌是:♦10 ♥4 ♠K ♠5 ♦6 ♥K ♦8 ♥2 ♥3 ♣8 ♣3 ♣4 ♦7 ♠Q ♣10 ♠3 ♠6 玩家2的牌是:♦9 ♦5 ♦A ♣5 ♦3 ♥8 ♣2 ♥J ♦J ♥5 ♦4 ♠9 ♠10 小王♣A ♥Q ♥7 玩家3的牌是:♠A ♣6 ♦2 ♦K ♣9 ♣K ♣7 ♦Q ♠4 ♥9 ♠7 大王♣Q ♥10 ♠8 ♣J ♠2 底牌的牌是:♥A ♥6 ♠J
18.22 模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌并对牌进行排序的代码实现
思路:
A:创建一个HashMap集合
B:创建一个ArrayList集合
C:创建花色数组和点数数组
D:从0开始往HashMap里面存储编号,并存储对应的牌,同时往ArrayList里面存储编号即可。
E:洗牌(洗的是编号)
F:发牌(发的也是编号,为了保证编号是排序的,就创建TreeSet集合接收)
G:看牌(遍历TreeSet集合,获取编号,到HashMap集合找对应的牌)
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建一个HashMap集合
6 HashMap<Integer, String> hm = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
7
8 // 创建一个ArrayList集合
9 ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
10
11 // 创建花色数组和点数数组
12 // 定义一个花色数组
13 String[] colors = { "♠", "♥", "♣", "♦" };
14 // 定义一个点数数组
15 String[] numbers = { "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q",
16 "K", "A", "2", };
17
18 // 从0开始往HashMap里面存储编号,并存储对应的牌,同时往ArrayList里面存储编号即可。
19 int index = 0;
20
21 for (String number : numbers)
22 {
23 for (String color : colors)
24 {
25 String poker = color.concat(number);
26 hm.put(index, poker);
27 array.add(index);
28 index++;
29 }
30 }
31 hm.put(index, "小王");
32 array.add(index);
33 index++;
34 hm.put(index, "大王");
35 array.add(index);
36
37 // 洗牌(洗的是编号)
38 Collections.shuffle(array);
39
40 // 发牌(发的也是编号,为了保证编号是排序的,就创建TreeSet集合接收)
41 TreeSet<Integer> player1 = new TreeSet<Integer>();
42 TreeSet<Integer> player2 = new TreeSet<Integer>();
43 TreeSet<Integer> player3 = new TreeSet<Integer>();
44 TreeSet<Integer> diPai = new TreeSet<Integer>();
45
46 for (int x = 0; x < array.size(); x++)
47 {
48 if (x >= array.size() - 3)
49 {
50 diPai.add(array.get(x));
51 } else if (x % 3 == 0)
52 {
53 player1.add(array.get(x));
54 } else if (x % 3 == 1)
55 {
56 player2.add(array.get(x));
57 } else if (x % 3 == 2)
58 {
59 player3.add(array.get(x));
60 }
61 }
62
63 // 看牌(遍历TreeSet集合,获取编号,到HashMap集合找对应的牌)
64 lookPoker("玩家1", player1, hm);
65 lookPoker("玩家2", player2, hm);
66 lookPoker("玩家3", player3, hm);
67 lookPoker("底牌", diPai, hm);
68 }
69
70 // 写看牌的功能
71 public static void lookPoker(String name, TreeSet<Integer> ts,
72 HashMap<Integer, String> hm)
73 {
74 System.out.print(name + "的牌是:");
75 for (Integer key : ts)
76 {
77 String value = hm.get(key);
78 System.out.print(value + " ");
79 }
80 System.out.println();
81 }
82 }
运行结果:
玩家1的牌是:♠3 ♦3 ♥4 ♣4 ♥5 ♣5 ♠6 ♣8 ♥9 ♦10 ♥J ♣J ♦Q ♣A ♠2 ♣2 大王 玩家2的牌是:♠5 ♦5 ♣7 ♦7 ♠9 ♥10 ♦J ♠Q ♣Q ♠K ♣K ♠A ♥A ♦A ♥2 ♦2 小王 玩家3的牌是:♥3 ♣3 ♠4 ♦4 ♥6 ♣6 ♠7 ♥7 ♥8 ♦8 ♣9 ♠10 ♣10 ♠J ♥Q ♥K ♦K 底牌的牌是:♦6 ♠8 ♦9
