题目
A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The height of the tree depends on the selected root. Now you are supposed to find the root that results in a highest tree. Such a root is called the deepest root.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=10000) which is the number of nodes, and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N. Then N-1 lines follow, each describes an edge by given the two adjacent nodes’ numbers.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print each of the deepest roots in a line. If such a root is not unique, print them in increasing order of their numbers. In case that the given graph is not a tree, print “Error: K components” where K is the number of connected components in the graph.
Sample Input 1:
5
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
Sample Output 1:
3
4
5
Sample Input 2:
5
1 3
1 4
2 5
3 4
Sample Output 2:
Error: 2 components
题目分析
已知图的顶点N和边N-1,判断所给图是否是一棵树,如果是,查找并打印最高树的所有根节点(从小到大)
- 判断图为树有两个条件:只有一个连通分量(否则为森林);无环(已知顶点数为N,边为N-1的连通图一定是树)
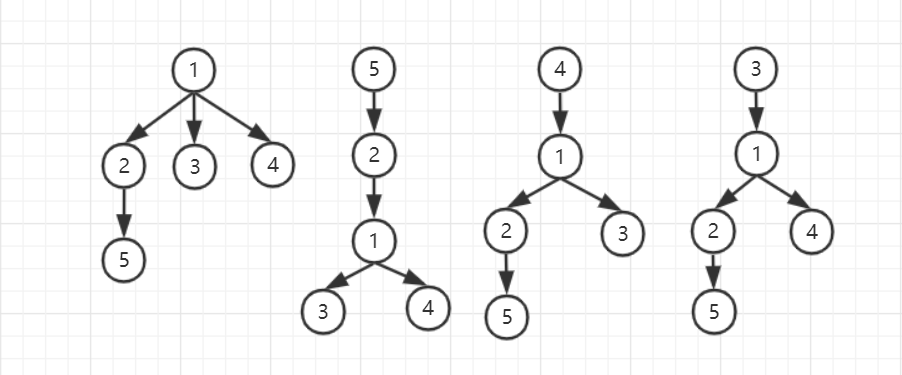
- 最高树的所有根节点,其含义可以从样例中推导得出(起始顶点不同,寻找出的最高树不同)
解题思路
1. 存储顶点和边
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
2. 计算连通分量个数
连通分量等于1时,满足条件
- DFS
- BFS
- 并查集
3. 查找最大高度树的根节点
- 任意取一个顶点,求其能到达的最远的节点集合A,如测试样例1中:取1,可以得到5,3,4
- 任取取A集合中一个顶点,求其能到达的最远的节点集合B,如取A集合中3,可以得到4,5
- 集合A和集合B的并集去重排序,即为答案
Code
Code 01(邻接矩阵 并查集)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边
set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest roots
int maxh,n,father[maxn],vis[maxn];
/*
并查集判断连通分量树
两次dfs求the deepest root
*/
int init() { /* 并查集 初始化 */
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)father[i]=i;
}
int find(int x) { /* 并查集 查 */
int a = x;
while(x!=father[x]) {
x=father[x];
}
while(a!=father[a]) { // 路径压缩
int temp=a;
a=father[a];
father[a]=x;
}
return x;
}
void Union(int a,int b) { /* 并查集 并 */
int fa=find(a);
int fb=find(b);
if(fa<fb)father[fb]=fa;
else father[fa]=fb;
}
void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */
vis[a]=1;
if(h>maxh) {
temp.clear();
temp.push_back(a); // the deepest root
maxh=h;
} else if(h==maxh)
temp.push_back(a);
for(int i=0; i<g[a].size(); i++) {
if(vis[g[a][i]]==0)
dfs(g[a][i],h+1);
}
}
void pts() {
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
vs.insert(temp[i]);
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
init();
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
Union(a,b);
}
// 统计连通分量数
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
vs.insert(find(i));
}
if(vs.size()>1) {
printf("Error: %d components",vs.size());
return 0;
}
vs.clear(); //vs重置,方便下面使用
dfs(1,1); // 第一次dfs,任意取一个顶点,获取最深根集合A
pts(); //将集合A存入set
fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组
//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest root
dfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合B
pts(); //将集合B存入set
for(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果
printf("%d
",*it);
}
return 0;
}
Code 02(邻接矩阵 DFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边
set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest roots
int n,maxh,vis[maxn];
/*
第一次dfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A
第二次dfs 求the deepest root集合B
集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案
*/
void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */
vis[a]=1;
if(h>maxh) {
temp.clear();
temp.push_back(a); // the deepest root
maxh=h;
} else if(h==maxh)
temp.push_back(a);
for(int i=0; i<g[a].size(); i++) {
if(vis[g[a][i]]==0)
dfs(g[a][i],h+1);
}
}
void pts() {
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
vs.insert(temp[i]);
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// 统计连通分量数
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(vis[i]==0){
dfs(i,0);
pts(); //将集合A存入set
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt>1) {
printf("Error: %d components",cnt);
return 0;
}
fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组
//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest root
dfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合B
pts(); //将集合B存入set
for(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果
printf("%d
",*it);
}
return 0;
}
Code 03(邻接矩阵 BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边
set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest roots
int n,maxh,vis[maxn];
struct node {
int v;
int h;
};
/*
第一次bfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A
第二次bfs 求the deepest root集合B
集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案
*/
void bfs(int a) { /* dfs */
vis[a]=1;
queue<node> q;
q.push({a,0});
while(!q.empty()) {
node now = q.front();
q.pop();
if(now.h>maxh) {
temp.clear();
temp.push_back(now.v); // the deepest root
maxh=now.h;
} else if(now.h==maxh)
temp.push_back(now.v);
for(int i=0; i<g[now.v].size(); i++)
if(vis[g[now.v][i]]==0){
q.push({g[now.v][i],now.h+1});
vis[g[now.v][i]]=1;
}
}
}
void pts() {
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
vs.insert(temp[i]);
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// 统计连通分量数
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(vis[i]==0) {
bfs(i);
pts(); //将集合A存入set
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt>1) {
printf("Error: %d components",cnt);
return 0;
}
fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组
//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest root
bfs(temp[0]);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合B
pts(); //将集合B存入set
for(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果
printf("%d
",*it);
return 0;
}
Code 04(邻接表 DFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
vector<int> temp; //邻接表 存储边
set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest roots
int n,maxh,vis[maxn],g[maxn][maxn];
/*
第一次dfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A
第二次dfs 求the deepest root集合B
集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案
*/
void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */
vis[a]=1;
if(h>maxh) {
temp.clear();
temp.push_back(a); // the deepest root
maxh=h;
} else if(h==maxh)
temp.push_back(a);
for(int i=1; i<maxn; i++)
if(g[a][i]==1 && vis[i]==0)
dfs(i,h+1);
}
void pts() {
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
vs.insert(temp[i]);
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a][b]=1;
g[b][a]=1;
}
// 统计连通分量数
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(vis[i]==0) {
dfs(i,0);
pts(); //将集合A存入set
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt>1) {
printf("Error: %d components",cnt);
return 0;
}
fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组
//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest root
dfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合B
pts(); //将集合B存入set
for(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果
printf("%d
",*it);
}
return 0;
}
Code 05(邻接表 BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
vector<int> temp; //邻接表 存储边
set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest roots
int n,maxh,vis[maxn],g[maxn][maxn];
struct node {
int v;
int h;
};
/*
第一次bfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A
第二次bfs 求the deepest root集合B
集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案
*/
void bfs(int a) { /* dfs */
vis[a]=1;
queue<node> q;
q.push({a,0});
while(!q.empty()) {
node now = q.front();
q.pop();
if(now.h>maxh) {
temp.clear();
temp.push_back(now.v); // the deepest root
maxh=now.h;
} else if(now.h==maxh)
temp.push_back(now.v);
for(int i=1; i<maxn; i++)
if(g[now.v][i]==1 && vis[i]==0){
q.push({i,now.h+1});
vis[i]=1;
}
}
}
void pts() {
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
vs.insert(temp[i]);
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a][b]=1;
g[b][a]=1;
}
// 统计连通分量数
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
if(vis[i]==0) {
bfs(i);
pts(); //将集合A存入set
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt>1) {
printf("Error: %d components",cnt);
return 0;
}
fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组
//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest root
bfs(temp[0]);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合B
pts(); //将集合B存入set
for(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果
printf("%d
",*it);
return 0;
}