定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类,工厂方法使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类。
优点:
1、可以使代码结构清晰,有效地封装变化。在编程中,产品类的实例化有时候是比较复杂和多变的,通过工厂模式,将产品的实例化封装起来,使得调用者根本无需关心产品的实例化过程,只需依赖工厂即可得到自己想要的产品。
2、对调用者屏蔽具体的产品类。如果使用工厂模式,调用者只关心产品的接口就可以了,至于具体的实现,调用者根本无需关心。即使变更了具体的实现,对调用者来说没有任何影响。
3、降低耦合度。产品类的实例化通常来说是很复杂的,它需要依赖很多的类,而这些类对于调用者来说根本无需知道,如果使用了工厂方法,我们需要做的仅仅是实例化好产品类,然后交给调用者使用。对调用者来说,产品所依赖的类都是透明的。
缺点:
1、添加新产品时,除了增加新产品类外,还要提供与之对应的具体工厂类,系统类的个数将成对增加,在一定程度上增加了系统的复杂度,有更多的类需要编译和运行,会给系统带来一些额外的开销。
2、虽然保证了工厂方法内的对修改关闭,但对于使用工厂方法的类,如果要换用另外一种产品,仍然需要修改实例化的具体工厂。
要素:
1、工厂接口。工厂接口是工厂方法模式的核心,与调用者直接交互用来提供产品。在实际编程中,有时候也会使用一个抽象类来作为与调用者交互的接口,其本质上是一样的 。
2、工厂实现。在编程中,工厂实现决定如何实例化产品,是实现扩展的途径,需要有多少种产品,就需要有多少个具体的工厂实现。
3、产品接口。产品接口的主要目的是定义产品的规范,所有的产品实现都必须遵循产品接口定义的规范。产品接口是调用者最为关心的,产品接口定义的优劣直接决定了调用者代码的稳定性。同样,产品接口也可以用抽象类来代替,但要注意最好不要违反里氏替换原则。
4、产品实现。实现产品接口的具体类,决定了产品在客户端中的具体行为。
实现:
工厂方法实现的类图:
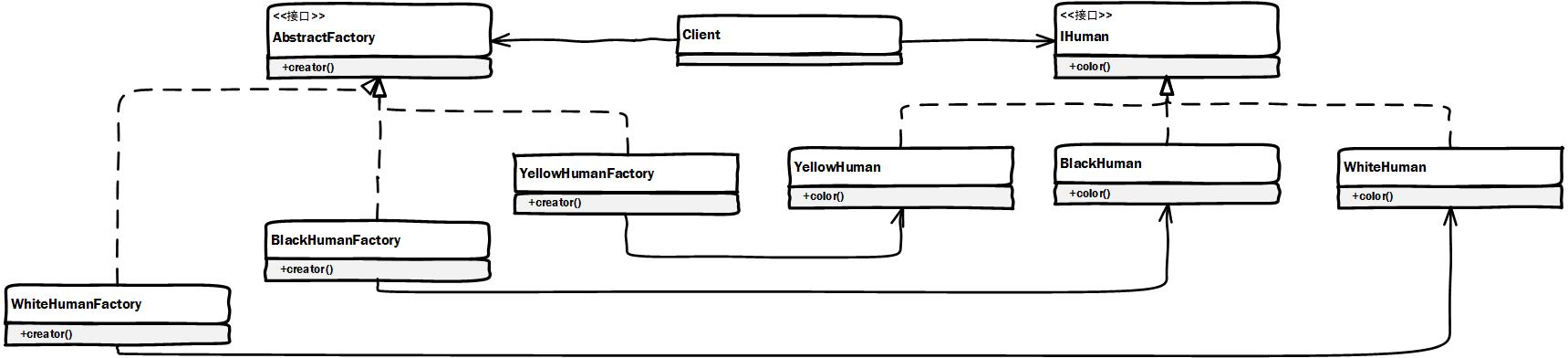
通过工厂方法模式实现如下:
人类接口的定义:

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public interface IHuman { void color(); }
人类定义的实现:

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class BlackHuman implements IHuman { public void color() { System.out.println(" i am black"); } }

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class WhiteHuman implements IHuman { public void color() { System.out.println("i am white"); } }

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class YellowHuman implements IHuman { public void color() { System.out.println("i am yellow"); } }
抽象工厂接口(IAbstractHumanFactory)的定义:

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public interface IAbstractHumanFactory { IHuman creator(); }
具体工厂的实现:

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class BlackHumanFactory implements IAbstractHumanFactory { public IHuman creator() { try { return BlackHuman.class.newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class WhiteHumanFactory implements IAbstractHumanFactory { public IHuman creator() { try { return WhiteHuman.class.newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; public class YellowHumanFactory implements IAbstractHumanFactory { public IHuman creator() { try { return YellowHuman.class.newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
调用:

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod; import com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.extend.BrownHumanFactory; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // 直接调用 // IAbstractHumanFactory factory = new WhiteHumanFactory(); // IHuman human = factory.creator(); // human.color(); // // factory=new BlackHumanFactory(); // human=factory.creator(); // human.color(); // 也可以这样调用 try { show(WhiteHumanFactory.class); show(YellowHumanFactory.class); show(BrownHumanFactory.class); } catch (InstantiationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } static void show(Class<? extends IAbstractHumanFactory> clazz) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { IAbstractHumanFactory factory = clazz.newInstance(); IHuman human = factory.creator(); human.color(); } }
在面对简单工厂中描述的两个扩展问题上,工厂方法模式,可以很优雅的进行扩展。
1、增加棕色人种的时候,只需要实现棕色人种的工厂类,和棕色人种就可以了。

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.extend; import com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.IHuman; public class BrownHuman implements IHuman { public void color() { System.out.println("this is a brown"); } }

package com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.extend; import com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.IAbstractHumanFactory; import com.lidaming.design02.factorymethod.IHuman; public class BrownHumanFactory implements IAbstractHumanFactory { public IHuman creator() { try { return BrownHuman.class.newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
2、如果需要造动物和植物呢?
扩展难度是很大的,几乎是无法扩展
总结:
工厂方法模式通过面向对象编程中的多态性来将对象的创建延迟到具体工厂中,从而解决了简单工厂模式中存在的问题,也很好地符合了开放封闭原则(即对扩展开发,对修改封闭)。
参考:
http://blog.jobbole.com/78064/
http://blog.csdn.net/zhengzhb/article/details/7348707
