旅行商问题,即TSP问题(Traveling Salesman Problem)又译为旅行推销员问题、货郎担问题,是数学领域中著名问题之一。
假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。
路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。
选用python和matplotlib.pyplot图形化
import math
import copy
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy.lib.function_base import average
class TSP():
citys_position=[] #城市坐标
population=[] #种群数组
fitness=[] #适应度数组
citys_size=10 #城市个数
population_size=100 #种群大小
rate_crossover=0.1 #交叉率
rate_mutation=0.01 #变异率
iteration_num=200 #最大迭代次数
best_dist=0x3f3f3f3f3f #记录最优距离
dist_list=[] #记录当前距离
best_dist_list=[] #记录最优距离
best_individual=[] #记录目前最优旅行方案
#加载城市坐标
def load_citys_position(self):
self.citys_position=[
[18,54],[87,76],[74,78],[71,71],[25,38],
[58,35],[4,50],[13,40],[18,40],[24,42],
# [71,44],[64,60],[68,58],[83,69],[58,69],
# [54,62],[51,67],[37,84],[41,94],[2,99]
]
#加载初始种群
def load_population(self):
for i in range(self.population_size):
temp=[]
while len(temp)<self.citys_size:
ite = random.randint(0,self.citys_size-1)
if ite not in temp:
temp.append(ite)
self.population.append([])
for j in temp:
self.population[i].append(j)
# print(self.population)
#初始化
def __init__(self):
self.load_citys_position()
self.load_population()
self.get_fitness()
self.choice()
#城市距离-染色体权值
def city_dist(self,i,j):
x=self.citys_position[i]
y=self.citys_position[j]
return math.sqrt(pow(x[0]-y[0],2)+pow(x[1]-y[1],2))
#种群距离集
def population_dist(self):
now_dist_list=[]
for i in range(len(self.population)):
now_dist=0
for j in range(1,len(self.population[i])):
now_dist+=self.city_dist(self.population[i][j],self.population[i][j-1])
now_dist_list.append(now_dist)
return now_dist_list
#适应度函数
def get_fitness(self):
self.dist_list=self.population_dist()
now_best_dist=min(self.dist_list)
now_best_dist_index=self.dist_list.index(now_best_dist)
now_fitness=[]
if now_best_dist<self.best_dist:
self.best_dist_list.append(now_best_dist)
self.best_dist=now_best_dist
self.best_individual=self.population[now_best_dist_index]
else :
self.best_dist_list.append(self.best_dist)
for i in range(len(self.dist_list)):
now_fitness.append(self.best_dist/self.dist_list[i])
self.fitness=now_fitness
# print("self.best_dist:",self.best_dist," now_dist_list:",now_dist_list)
# print("self.fitness:",self.fitness)
#变异
def mutation(self):
for i in range(len(self.population)):
now_rate=random.random()
if(now_rate<self.rate_mutation):
#随机出两个点进行片段翻转
index1=random.randint(0,len(self.population[i])-1)
index2=random.randint(0,len(self.population[i])-1)
if index1>index2:
temp=index1
index1=index2
index2=temp
self.population[i][index1:index2]=list(reversed(self.population[i][index1:index2]))
#交叉互换
def crossover(self):
last_index=-1;
for i in range(len(self.population)):
now_rate=random.random();
if(now_rate<self.rate_crossover):
if(last_index==-1):
last_index=i
else : #顺序交叉,保留前一个染色体的中间段,交换两端
index1=random.randint(0,len(self.population[last_index])-1)
index2=random.randint(0,len(self.population[last_index])-1)
if index1>index2:
temp=index1
index1=index2
index2=temp
temp_list=[] #取出中间段
for j in range(index1,index2+1):
temp_list.append(self.population[last_index][j])
next_gen=[] #存储交叉互换后的基因
index_temp=0
for j in range(len(self.population[i])):
if self.population[i][j] not in temp_list:
next_gen.append(self.population[i][j])
else :
next_gen.append(temp_list[index_temp])
index_temp+=1
self.population[last_index]=next_gen #赋新基因
last_index=i;
#选择函数
def choice(self):
#最优解覆盖
for i in range(len(self.fitness)):
if self.fitness[i]<0.5:
# print("self.fitness[i]:",self.fitness[i]," self.dist_list[i]:",self.dist_list[i]," best_dist:",self.best_dist)
# print("self.population[i]:",self.population[i],"self.best_individual:",self.best_individual)
# print(" ")
self.population[i]=self.best_individual
self.fitness[i]=1
#进化,主函数
def evolution(self):
now_iteration_num=0
while now_iteration_num<self.iteration_num:
now_iteration_num+=1
self.crossover()
self.mutation()
self.get_fitness()
self.choice()
#可视化数据
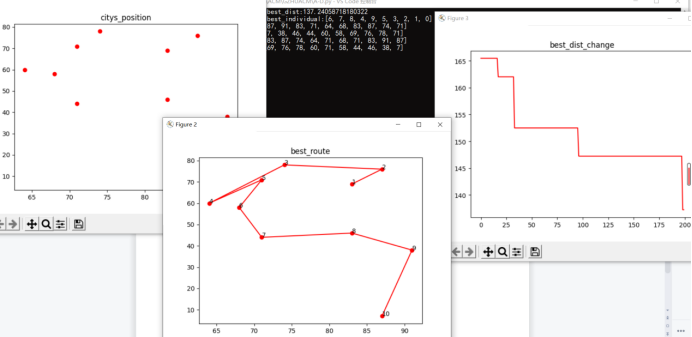
def plot_show(self):
print("self.best_dist",end=":")
print(self.best_dist)
print("self.best_individual",end=":")
print(self.best_individual)
x1=[]
y1=[]
x2=[]
y2=[]
for i in range(len(self.citys_position)):
x1.append(self.citys_position[i][0])
y1.append(self.citys_position[i][1])
for i in range(len(self.best_individual)):
x2.append(self.citys_position[self.best_individual[i]][0])
y2.append(self.citys_position[self.best_individual[i]][1])
print("x1:",end="")
print(x1)
print("y1:",end="")
print(y1)
print("x2:",end="")
print(x2)
print("y2:",end="")
print(y2)
plt.title("citys_position")
plt.scatter(x1,y1,color='r',marker='o' ); #画点
plt.figure();
plt.title("best_route")
plt.plot(x2,y2,color='r',marker='o' ); #画点
for i in range(len(x2)):
plt.text(x2[i],y2[i],i+1)
plt.figure();
plt.title("best_dist_change")
plt.plot(self.best_dist_list,color='r')
plt.show()
def main():
tsp=TSP()
tsp.evolution()
tsp.plot_show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()