Queues and Priority Queues are data structures which are known to most computer scientists. The Queue occurs often in our daily life. There are many people lined up at the lunch time.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2 L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2 L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
InputInput a length L (0 <= L <= 10 6) and M.OutputOutput K mod M(1 <= M <= 30) where K is the number of E-queues with length L.Sample Input
3 8
4 7
4 8
Sample Output
6
2
1
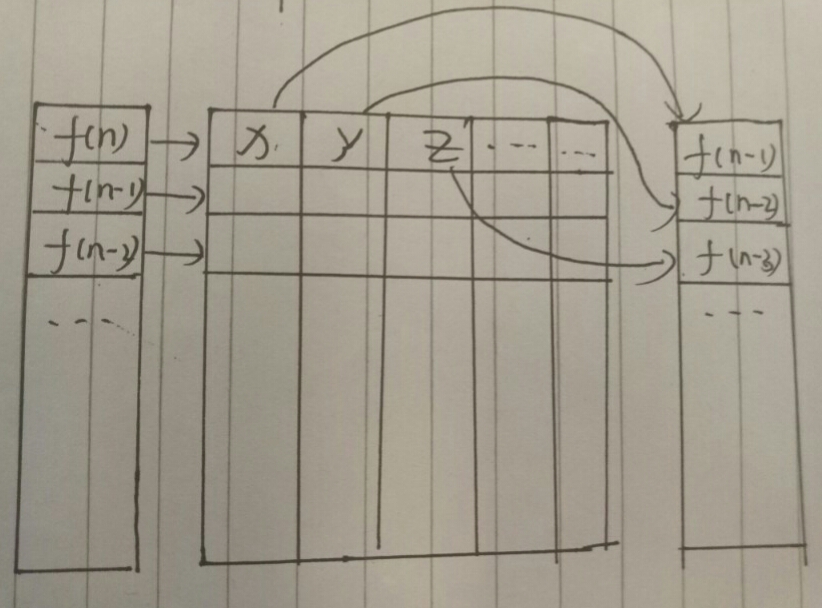
下图是对矩阵的理解,对左边每一个f(n),需要m个f(x)就在第x排记录m。
如图,f(n)=x*f(n-1)+y*f(n-2)+z*f(n-3)...
本题的公式是f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4),分别对最后一位是f或者讨论即可得出。

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<memory>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=4;
int Mod;
struct mat
{
int m[maxn][maxn],len;
mat(){memset(m,0,sizeof(m));len=maxn;}
mat friend operator * (mat a,mat b){
mat d;
for(int i=0;i<a.len;i++)
for(int j=0;j<a.len;j++){
d.m[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<a.len;k++)
d.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%Mod;
}
return d;
}
mat friend operator^(mat a,int k) {
mat c;
for(int i=0;i<c.len;i++) c.m[i][i]=1;
while(k){
if(k&1) c=a*c;
a=a*a;
k>>=1;
}
return c;
}
};
int main()
{
int n,k;
mat ans,x,c;
x.m[0][0]=x.m[0][2]=x.m[0][3]=x.m[1][0]=x.m[2][1]=x.m[3][2]=1;
ans.m[0][0]=9;
ans.m[1][0]=6;
ans.m[2][0]=4;
ans.m[3][0]=2;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&Mod)){
if (n<=4){
printf("%d
",ans.m[4-n][0]%Mod);
}
else {
c=x^(n-4);
c=c*ans;
printf("%d
",c.m[0][0]%Mod);
}
}
return 0;
}
