一、Spring JDBC相关类
1.1 DriverManagerDataSource
DriverManagerDataSource主要包含数据库连接地址,用户名,密码。
属性及含义如下配置所示:
<bean id = "dataSource" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<!-- 指定JDBC驱动 --> <property name = "driverClassName" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<!--设置数据库连接地址--> <property name = "url" value = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring" />
<!-- 设置用户名和密码 --> <property name = "username" value = "root" /> <property name = "password" value = "123456" /> </bean>
1.2JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate是实现数据库操作的核心类,其中包含一系列对数据库的操作。
包含execute()、update()、query()等方法。
既然是对数据库进行操作,那么必须知道数据库的URL,用户名密码。
所有JdbcTemplate中应该包含DriverManagerDataSource。
将DriverManagerDataSource配置到JdbcTemplate中:
<!--设置数据源-->
<bean id = "dataSource" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name = "driverClassName" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name = "url" value = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring" /> <property name = "username" value = "root" /> <property name = "password" value = "123456" /> </bean> <!--在jdbcTemplate中设置数据源--> <bean id = "jdbcTemplate" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name = "dataSource" ref = "dataSource" /> </bean>
模板设置好了,我们就可以使用模板了。
一般在对数据库进行具体操作的类中定义一个JdbcTemplate类型的属性,
然后将 id = jdbcTemplate的bean注入到数据库操作类中对应的属性。
需要导入的jar文件:
我们先结合jdbcTemplate中的execute() 方法来看一实例
execute(String sql)执行指定sql语句
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd" > <!--配置数据源--> <bean id = "dataSource" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name = "driverClassName" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name = "url" value = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring" /> <property name = "username" value = "root" /> <property name = "password" value = "123456" /> </bean> <!--配置jdbc模板--> <bean id = "jdbcTemplate" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name = "dataSource" ref = "dataSource" /> </bean> </beans>
测试
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; public class JDBCTemplateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate)ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate"); jt.execute("create table account(" + "id int primary key auto_increment," + "username varchar(50)," + "balance double)"); System.out.println("创建成功"); } }
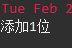
创建成功后,数据库中会多出一个account表。
本例是获取JdbcTemplate,执行了一个建表语句。
我们再来看下JdbcTemplate中的update方法。
update主要用于插入、更新、删除数据,一般会返回一个受影响的行数。
int update(String sql),执行指定语句返回受影响的行数。
int update(String sql,Object... args);执行sql语句,可以设置语句参数。
Accout.java
public class Account { private Integer id; private String username; private Double balance; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", balance=" + balance + "]"; } }
AccountDao.java (数据操作接口)
public interface AccountDao { public int addAccount(Account account); public int updateAccount(Account account); public int deleteAccount(int id); }
AccountDaoImpl.java
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{ private JdbcTemplate jt; //此处的属性通过xml文件注入 public void setJt(JdbcTemplate jt) { this.jt = jt; } @Override//添加 public int addAccount(Account account) { String sql = "insert into account(username,balance) value(?,?)"; Object[] obj = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance() }; int num = jt.update(sql,obj); return num; } @Override//修改 public int updateAccount(Account account) { String sql = "update account set username=?,balance=?,where id = ?"; Object[] obj = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance(), account.getId() }; int num = jt.update(sql,obj); return num; } @Override//删除 public int deleteAccount(int id) { String sql = "delete from account where id = ?"; int num = jt.update(sql,id); return num; } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd" > <bean id = "dataSource" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name = "driverClassName" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name = "url" value = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring" /> <property name = "username" value = "root" /> <property name = "password" value = "123456" /> </bean> <bean id = "jdbcTemplate" class = "org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name = "dataSource" ref = "dataSource" /> </bean> <bean id = "accountDao" class = "com.spring.db.AccountDaoImpl"> <property name="jt" ref = "jdbcTemplate"></property> <!--将jdbcTemplate注入AccountDaoImpl类中属性jt-->
</bean> </beans>
测试添加
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; public class JDBCTemplateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDaoImpl)ac.getBean("accountDao"); Account account = new Account(); account.setId(2); account.setUsername("hcf"); account.setBalance(1000.0); accountDao.addAccount(account); System.out.println("添加" + accountDao.addAccount(account) + "位"); } }
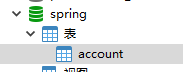
执行成功后,表中会多出一组数据。
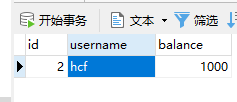
AccountImpl执行添加方法,其内部实际上是JdbcTemplate jt执行具体的语句,
而JdbcTemplate jt是通过xml配置到AccountImpl的jt属性中的.
query方法主要用于查询,可以返回查询的结果集。
public <T> T queryForObject(String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper, Object... args)
执行指定语句,args用于设置语句参数,返回一个对象,RowMapper数据库中一行元素
与一个类之间的映射,简单的看做是将数据库一行元素填充到一个类的对象中。
类中属性名要和数据库列名相同。
rowMapper通过RowMapper的实现类BeanPropertyRowMapper(Class<T> mappedClass)构造方法构造。
这个属性确定了返回对象的具体类型。
public <T> List<T> query(String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper)
此方式返回的是一个结果集。
public <T> List<T> query(String sql, Object[] args, RowMapper<T> rowMapper)
此方法可以设置参数,同时返回结果集
在AccountDao.java中添加两个方法
public Account findAccountById(int id); public List<Account> findAllAccounts();
在AccountDaoImpl.java中添加实现
@Override public Account findAccountById(int id) { String sql = "select * from account where id = ?"; //设置映射,即表中一行记录对应一个Accout对象(数据库中列名要和对象属性名一致) RowMapper<Account> rp = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); return this.jt.queryForObject(sql, rp, id); } @Override public List<Account> findAllAccounts() { String sql = "select * from account"; RowMapper<Account> rp = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); return this.jt.query(sql,rp); }
测试:
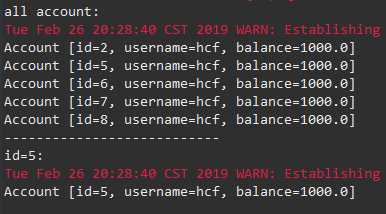
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; public class JDBCTemplateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDaoImpl)ac.getBean("accountDao"); System.out.println("all account:"); for(Account account:accountDao.findAllAccounts()) { System.out.println(account); } System.out.println("---------------------------"); System.out.println("id=5:"); System.out.println(accountDao.findAccountById(5)); System.out.println(""); } }

表中需要先有一些数据。