什么是Spring且能做什么
- Spring是一个开源框架,它由Rod Johnson创建。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。
- Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。
- Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。
- 目的:解决企业应用开发的复杂性
- 功能:使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,并提供了更多的企业应用功能
- 范围:任何Java应用
- 简单来说,Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
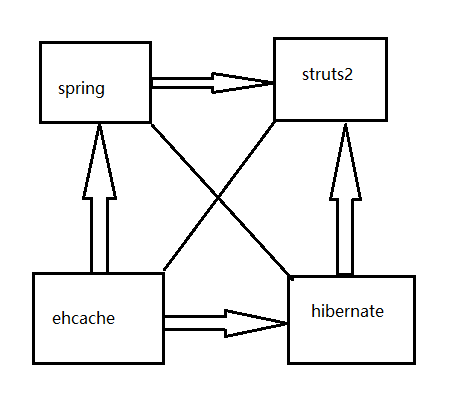
图解,如果框架太多的话,会导致开发复杂性大大提高,框架与框架之间到处串联;
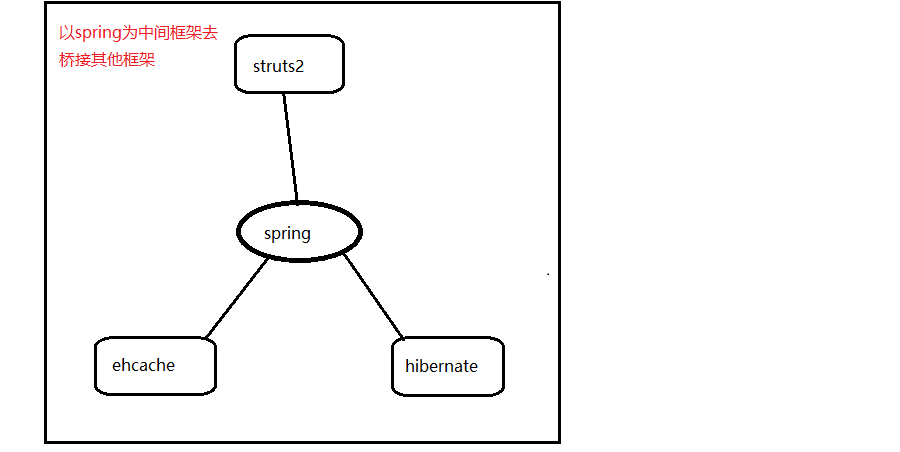
但是如果以spring框架为中心去串联其他框架,就大大降低了开发的复杂性
什么是控制反转(Ioc)
- 控制反转(IoC=Inversion of Control)IoC,用白话来讲,就是由容器控制程序之间的(依赖)关系,而非传统实现中,由程序代码直接操控。这也就是所谓“控制反转”的概念所在:(依赖)控制权由应用代码中转到了外部容器,控制权的转移,是所谓反转。
- IoC还有一个另外的名字:“依赖注入 (DI=Dependency Injection)” ,即由容器动态的将某种依赖关系注入到组件之中
案例:实现Spring的IoC
IOC/DI
将以前由程序员实例化对象/赋值的工作交给了spring处理
Biz层
创建一个接口类,写一个方法接口
package com.ht.ioc.biz; /** * 需求: * 上传文件: * 完成的思路:完成功能好 文件上传就行了 * @author Administrator * */ public interface UserBiz { public void read(); }
为了体现出差距和弊端,就写俩个实现类吧
UserBizipml01
public class UserBizimpl implements UserBiz{ @Override public void read() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("本是青灯不归客,却因浊酒留风尘。"); } }
UserBizipml02
public class UserBizipml02 implements UserBiz{ @Override public void read() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("星光不问赶路人,岁月不负有心人。"); } }
写一个测试类去调用web层的测试方法让他在控制台上实现效果
package com.ht.ioc.test; import com.ht.ioc.web.UserAction; /** * 模拟浏览器请求后台 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //实例化一个用户web类 UserAction userAction=new UserAction(); userAction.text03();//调用web层中的测试方法 } }
在web层中调用接口不同的实现类
public class UserAction { // 实例化一个接口 private UserBiz userBiz = new UserBizimpl(); public void text03() { userBiz.read(); } }
效果图:

public class UserAction { // 实例化一个接口 private UserBiz userBiz = new UserBizipml02(); public void text03() { userBiz.read(); } }
效果图:

由此也可以看出来弊端:
当需求变化非常快的时候,不便于维护,因为维护的权利是属于程序员的
spring的ioc就是解决这一个问题的
将维护代码的权利由程序员转交给spring容器来完成
如何在spring当中定义和配置一个JavaBean(使用无参构造方法+set方法创建一个JavaBean)
- id:在容器中查找Bean的id(唯一、且不能以/开头)
- class:bean的完整类名
- name:在容器中查找Bean的名字(唯一、允许以/开头、允许多个值,多个值之间用逗号或空格隔开)
- scope:(singleton|prototype)默认是singleton
- singleton(单例模式):在每个Spring IoC容器中一个bean定义对应一个对象实例
- prototype(原型模式/多例模式):一个bean定义对应多个对象实例
- abstract:将一个bean定义成抽象bean(抽象bean是不能实例化的),抽象类一定要定义成抽象bean,非抽象类也可以定义成抽象bean
- parent:指定一个父bean(必须要有继承关系才行)
- init-method:指定bean的初始化方法
-
constructor-arg:使用有参数构造方法创建javaBean
set注入
- 基本数据类型
userAction类
public class UserAction { private int uid; private String uname; private List<String> hobby =new ArrayList<String>(); public void setUid(int uid) { this.uid = uid; } public void setUname(String uname) { this.uname = uname; } public void setHobby(List<String> hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public int getUid() { return uid; } public String getUname() { return uname; } public List<String> getHobby() { return hobby; } /** * set注入ע * */ public void text01() { System.out.println("uid:"+this.uid); System.out.println("uname:"+this.uname); System.out.println("hobby:"+this.hobby); } }
spring-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="userAction" class="com.ht.ioc.web.UserAction"> <property name="uid" values="23"></property> <property name="uname" values="zk"></property> <!-- <constructor-arg name="uid" value="22"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="uname" value="zs"></constructor-arg> --> <property name="hobby"> <list> <value>青灯</value> <value>15</value> <value>古镇</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试类
public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // UserAction userAction=new UserAction(); // userAction.text03(); // userAction.text01(); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/spring-context.xml"); UserAction userAction = (UserAction) context.getBean("userAction"); userAction.text01(); } }
运行结果:
uid:23
uname:zk
hobby:[青灯,15,古镇]
2.set注入(引用类型)
useAction类改变一下
private UserBiz userBiz; // private UserBiz userBiz = new UserBizipml02(); public UserBiz getUserBiz() { return userBiz; } public void setUserBiz(UserBiz userBiz) { this.userBiz = userBiz; }
spring-context.xml
<bean id="userAction" class="com.ht.ioc.biz.impl.UserBizimpl"></bean> <bean id="userAction" class="com.ht.ioc.web.UserAction"> <!-- <property name="uid" values="23"></property> <property name="uname" values="zk"></property> --> <constructor-arg name="uid" value="22"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="uname" value="zs"></constructor-arg> <property name="hobby"> <list> <value>青灯</value> <value>15</value> <value>古镇</value> </list> </property> </bean>
运行效果
uid:22
uname:zs
hobby:[青灯,15,古镇]
构造注入
userAction类
public UserAction() { super(); } public UserAction(int uid, String uname, List<String> hobby) { super(); this.uid = uid; this.uname = uname; this.hobby = hobby; }
spring-context.xml
<bean id="userAction" class="com.ht.ioc.web.UserAction"> <!-- <property name="uid" values="23"></property> <property name="uname" values="zk"></property> --> <constructor-arg name="uid" value="22"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="uname" value="zs"></constructor-arg> <property name="hobby"> <list> <value>青灯</value> <value>15</value> <value>古镇</value> </list> </property> </bean>
自动装置
-
在spring-context.xml里加上
default-autowire="byType"
因为是根据类别进行查询,所以出现多个实体类时就不行了
- 在spring-context.xml里加上
default-autowire="byName"
这是根据名字查询,追踪的位置比较清晰,所以就不会报错
tomcat管理spring
实现思路:
如何将spring的上下文交给tomcate上下文进行管理
首先spring上下文为什么tomact?
分析: 目前工程中的所有javabean都交给了spring进行管理,那么浏览器发送请求,请求的是tomcat,
由tomcat来处理请求,tomcat处理请求一般来说都要访问数据库,数据库是由Dao层访问的,
Dao层的实体类又是spring的上下文管理,那就意味着,tomcat要处理请求,必须拿到spring的上下文,
才能拿到Dao层的javabean
上代码:
SpringLoadListener类
package com.ht.ioc.test; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringLoadListener implements ServletContextListener{ private String springXmlLocation=""; @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("启动........"); ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext(); springXmlLocation=servletContext.getInitParameter("springXmlLocation"); if(null==springXmlLocation||"".equals(springXmlLocation)) { springXmlLocation ="/spring-context.xml"; } System.out.println("springXmlLocation:"+springXmlLocation); ApplicationContext springContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(springXmlLocation); servletContext.setAttribute("spring_context_key", springContext); } }
userServlet类
package com.ht.ioc.test; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.ht.ioc.web.UserAction; @WebServlet("/user") public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet{ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext(); ApplicationContext springContext = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("spring_context_key"); UserAction bean = (UserAction) springContext.getBean("userAction"); bean.text03(); } }
谢谢观看!