AOP:面向切面编程,是Spring的两大基石之一。
AOP:作用
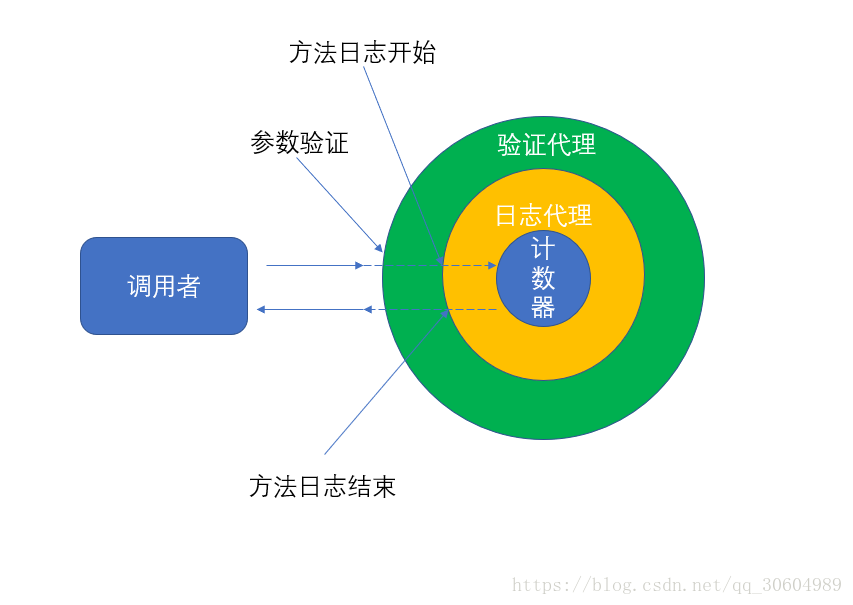
1、日志
按照以前的写法,会造成:
1)、代码混乱,越来越多的非业务需求(日志、验证等)加入后,原有的业务方法急剧膨胀,每个方法在处理核心业务逻辑的同时还必须兼顾其他的点。
2)、代码分散,以日志需求为例,只是为了满足这个单一的需求,就不得不在多个模块方法中加入重复相同的日志代码,如果日志需求变化,则要大量修改。
package aop; /** * @author chenpeng * @date 2018/6/3 21:33 */ public class ArithmeticCalculatorLogImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { //每个方法都要这样加日志,麻烦 System.out.println("add....."+(i+j)); return i+j; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { System.out.println("sub....."+(i-j)); return i-j; } @Override public int mul(int i, int j) { System.out.println("mul....."+(i*j)); return i*j; } @Override public int div(int i, int j) { System.out.println("div....."+(i/j)); return i/j; } }
使用动态代理解决上述问题
一、代理设计模式的原理:使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后用该代理对象取代原始对象,任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理,代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。
使用动态代理类:
package aop; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author chenpeng * @date 2018/6/3 21:33 */ public class ArithmeticCalculatorLogProxyImpl { //要代理的对象 private ArithmeticCalculator target; public ArithmeticCalculatorLogProxyImpl(ArithmeticCalculator target) { this.target = target; } public ArithmeticCalculator getLogProxy(){ ArithmeticCalculator proxy=null; //代理对象由哪一个类加载器负责加载 ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader(); //代理方法的类型,即代理的类型中有哪些方法 Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculator.class}; //当调用代理对象的方法时,应该执行的代码 InvocationHandler i = new InvocationHandler() { /** * * @param proxy:正在返回的那个代理对象,一般情况下,在invoke方法中不使用该对象 * @param method:正在被调用的方法 * @param args:调用方法时传入的参数 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); //日志 System.out.println("The method "+methodName+" begin with "+ Arrays.asList(args)); //执行的方法 Object result = method.invoke(target,args); //日志 System.out.println("The method "+methodName+" end with "+Arrays.asList(result)); return result; } }; proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,interfaces,i); return proxy; } }
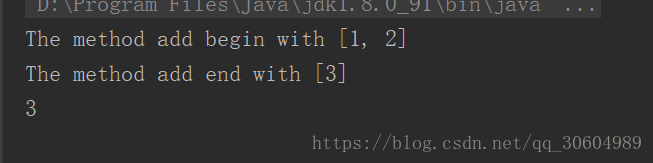
import aop.ArithmeticCalculator; import aop.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl; import aop.ArithmeticCalculatorLogProxyImpl; /** * @author chenpeng * @date 2018/6/3 21:52 */ public class aopTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //被代理的对象 ArithmeticCalculator target = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl(); //获取代理 ArithmeticCalculator proxy = new ArithmeticCalculatorLogProxyImpl(target).getLogProxy(); int result = proxy.add(1,2); System.out.println(result); } }
虽然动态代理可以解决这些麻烦的问题,但是还不够强大,AOP更加强大
AOP
面向切面编程,是一种新的方法论,是对传统的OOP(面向对象编程)的补充。
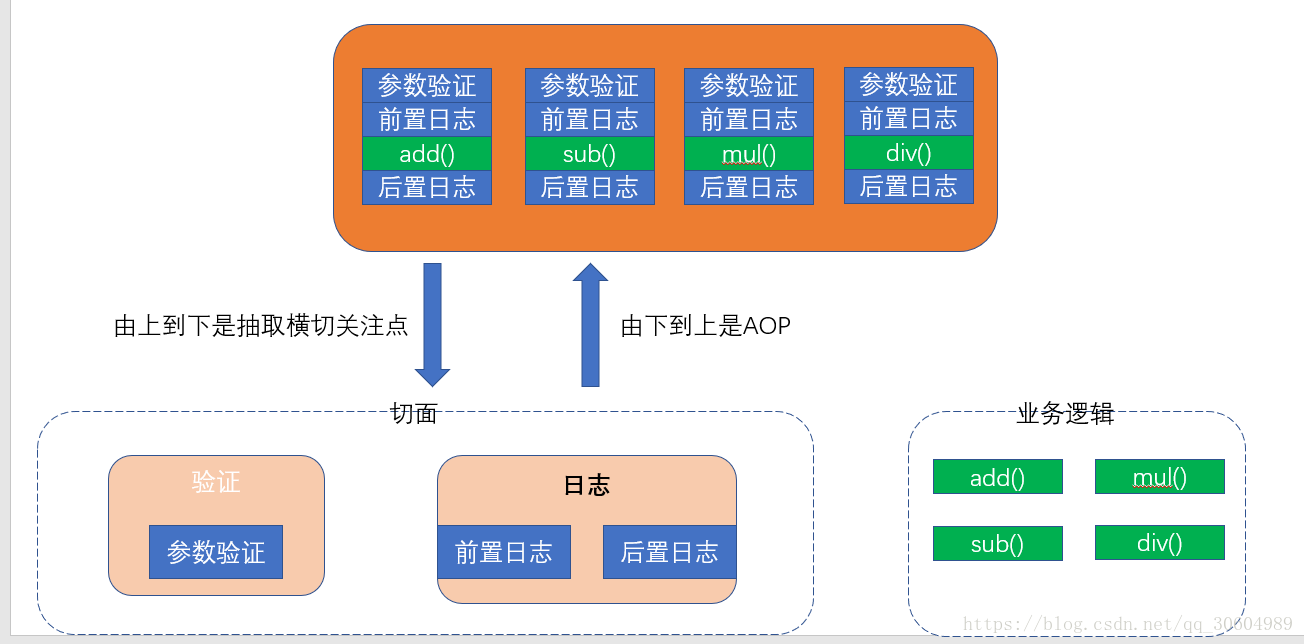
AOP的主要编程对象是切面,而切面模块化横切关注点。
在应用AOP编程的时候,仍然需要定义公共功能,但可以明确的定义这个功能在哪里,以什么方式应用,并且不必修改受影响的类,这样一来,横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里。
AOP的好处:
—每个事物逻辑位于一个位置,代码不分散,便于维护升级
—业务模块更加简洁,只包含核心的业务代码。
切面:横切关注点抽取出被模块化的特殊对象。
通知:切面必须要完成的工作。(就是切面中具体的方法,如验证、日志)
目标:被通知的对象(也就是上图的业务逻辑)
代理:向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象
连接点:程序执行的某个特定的位置,如类的某个方法调用前、调用后、方法抛出异常后等。连接点由两个信息确定:方法表示程序执行点,相对点表示的方位
切点:每个类拥有多个连接点,AOP通过切点定位到特定的连接点。类比:连接点相当于数据库中的记录,切点相当于查询条件。切点和连接点不是一一对应的,一个切点对应多个连接点,切点通过Pointcut接口进行描述。使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。