Problem Description
题目原文是英文的,而且比较繁琐。我修饰转述如下:
小强被海盗抓到了,海盗把他和他的船“小强号”关在一个水狱里。
小强拿到了小红给他的一张水狱地图,地图由h行w列字符组成(3 <= h;w <= 500), ,字符共有四种:
S:小强和他的“小强号”的起始位置,他要从这里逃跑。
#:不能逾越的石墙
. : 水道,小强号可以直接通过
@:栅栏水道
已知:
小强打开栅栏需要d分钟 (0 <= d <= 50);
小强号通过单位水道的时间为1分钟;
水狱一定有出口。
输入:
t (一共有t组测试数据)
h w d 以及水狱地图 (每组测试数据输入一次)
输出:
小强出狱的最短时间(和路线)。
Sample Input
2
6 5 7
#####
#S . .#
#@# .#
# . . .#
#@###
# .###
4 5 3
#####
#S# .#
#@ . .#
###@#
Sample Output
16
11
分析:
从S点开始,广度优先搜索,寻找出口。
code广度优先搜索:

1 //code:(普通广度搜索,超时) 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define N 501 6 int h,w,d,sx,sy,t,big,i,j; 7 int tv[N][N]; //到达水域某个位置的最短时间 8 char maze[N][N];//记录水狱的地图 9 int offset[4][2]={{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}};//可以移动的四个方向 10 struct pos 11 {int x;int y;}; 12 int bfs() 13 { 14 int mymin=big; 15 pos start,temp,temp1; 16 start.x=sx,start.y=sy; 17 tv[sx][sy]=0; 18 19 queue<pos> q; 20 q.push(start); 21 while(!q.empty()) 22 { 23 temp=q.front(); 24 q.pop(); 25 //检测是否逃出水域,更新最短逃出时间 26 if(temp.x==0||temp.x==h-1||temp.y==0||temp.y==w-1) 27 if(mymin>tv[temp.x][temp.y]+1) 28 mymin=tv[temp.x][temp.y]+1; 29 //探索当前位置的下一个位置 30 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 31 { 32 pos temp1;//下一步的位置 33 temp1.x=temp.x+offset[i][0]; 34 temp1.y=temp.y+offset[i][1]; 35 //判断下一步的位置是否超出地图 36 if(temp1.x<0||temp1.x>=h||temp1.y<0||temp1.y>=w) 37 continue; 38 //下一步的位置是水道 39 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='.') 40 { 41 if(tv[temp1.x][temp1.y]>tv[temp.x][temp.y]+1) 42 { 43 tv[temp1.x][temp1.y]=tv[temp.x][temp.y]+1; 44 q.push(temp1); 45 } 46 } 47 //下一步的位置是栅栏 48 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='@') 49 { 50 if(tv[temp1.x][temp1.y]>tv[temp.x][temp.y]+d+1) 51 { 52 tv[temp1.x][temp1.y]=tv[temp.x][temp.y]+1+d; 53 q.push(temp1); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 return mymin; 59 } 60 int main() 61 { 62 cin>>t; 63 while(t--) 64 { 65 cin>>h>>w>>d; 66 big=h*w*d;//逃出水域的时间的上限 67 getchar(); 68 for(i=0;i<h;i++) 69 { 70 for(j=0;j<w;j++) 71 { 72 scanf("%c",&maze[i][j]);//cin>>maze[i][j]; 73 tv[i][j]=big; 74 if(maze[i][j]=='S')//小强出逃的起点位置 75 {sx=i;sy=j;} 76 } 77 getchar(); 78 } 79 printf("%d\n",bfs());//cout<<bfs()<<endl; 80 } 81 //for(;;); 82 }
由于有栅栏,不能保证搜索的当前结点是“耗时最少”的优先搜索,对当前结点耗时v取权重,采用优先队列。
code:改用优先队列,以到达该结点的时间v为权重,每次使v最小的结点出队,即所谓“A算法”

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 501 5 int h,w,d,sx,sy,t,i,j; 6 bool used[N][N]; 7 char maze[N][N]; 8 int offset[4][2]={{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}};//方向数组 9 struct pos 10 {int x;int y;int v;}; 11 struct cmp//这样之后出队序列就是由小到大,搜索结点时优先搜索v(从S到当前结点耗费的时间)小的结点。 12 { 13 bool operator()(const pos &p1,const pos &p2) 14 return p1.v>p2.v; 15 }; 16 int bfs() 17 { 18 pos start,temp,temp1;//start为搜索起点,temp为当前搜索的结点,temp1为当前结点的扩展结点 19 start.x=sx,start.y=sy,start.v=0; 20 priority_queue<pos,vector<pos>,cmp> q;//注意拉,用优先级队列,小根堆 21 q.push(start); 22 while(!q.empty()) 23 { 24 temp=q.top(); 25 q.pop(); 26 //若temp结点从队列中出来,一定是水道或者栅栏,如果处于地图边缘,只要在该位置划船1分钟就出水狱了 27 if(temp.x==0||temp.x==h-1||temp.y==0||temp.y==w-1) 28 return temp.v+1; 29 //对当前结点进行上下左右四个方向的搜索 30 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 31 { 32 pos temp1; 33 temp1.x=temp.x+offset[i][0]; 34 temp1.y=temp.y+offset[i][1]; 35 //拓展位置如果超过地图或者先前已经被搜索过,直接略过 36 if(used[temp1.x][temp1.y]==1||temp1.x<0||temp1.x>=h||temp1.y<0||temp1.y>=w) 37 continue; 38 //拓展结点为 "." 水道,可以入队 39 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='.') 40 { 41 temp1.v=temp.v+1; 42 q.push(temp1); 43 used[temp1.x][temp1.y]=1; 44 } 45 //拓展结点temp1为“@”栅栏,可以入队,入队时已经算好从S到temp1的时间 temp1.v 46 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='@') 47 { 48 temp1.v=temp.v+1+d; 49 q.push(temp1); 50 used[temp1.x][temp1.y]=1; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 int main() 56 { 57 cin>>t; 58 while(t--) 59 { 60 cin>>h>>w>>d; 61 getchar();//为了在后面使用scanf读入字符,解决换行问题 62 for(i=0;i<h;i++) 63 { 64 for(j=0;j<w;j++) 65 { 66 scanf("%c",&maze[i][j]); 67 used[i][j]=0; 68 if(maze[i][j]=='S') 69 {sx=i;sy=j;} 70 } 71 getchar();//为了使用scanf读入字符,解决换行问题 72 } 73 printf("%d\n",bfs()); 74 } 75 }
code:A*算法
在A算法基础上做改进,对结点以预测总耗费时间作为权重按由小到大排序。
预测总耗费时间=当前耗费时间+预期最小耗费时间。
预期最小耗费时间=该结点距离地图最近边缘的距离。
只需要在源代码上修改队列排序函数:cmp
int mymin(int a,int b,int c,int d) { a=a<b?a:b; c=c<d?c:d; return (a<c?a:c); } struct cmp{ bool operator()(const pos &p1,const pos &p2) {return (p1.v+mymin(p1.x,p1.y,h-1-p1.x,w-1-p1.y)>p2.v+mymin(p2.x,p2.y,h-1-p2.x,w-1-p2.y));} };
code:在A算法基础上打印路径
 View Code
View Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 501 5 int h,w,d,sx,sy,t,i,j,ex,ey; 6 struct pos 7 {int x;int y;int v;}; 8 int offset[4][2]={{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}};//方向数组 up left down right 9 bool used[N][N]; 10 char maze[N][N]; 11 pos lastp[N][N]; 12 struct cmp//这样之后出队序列就是由小到大,搜索结点时优先搜索v(从S到当前结点耗费的时间)小的结点。 13 { 14 bool operator()(const pos &p1,const pos &p2) 15 {return (p1.v>p2.v);} 16 }; 17 int bfs() 18 { 19 pos start,temp,temp1;//start为搜索起点,temp为当前搜索的结点,temp1为当前结点的扩展结点 20 start.x=sx,start.y=sy,start.v=0; 21 priority_queue<pos,vector<pos>,cmp> q;//注意拉,用优先级队列,小根堆 22 q.push(start); 23 while(!q.empty()) 24 { 25 temp=q.top(); 26 q.pop(); 27 //若temp结点从队列中出来,一定是水道或者栅栏,如果处于地图边缘,只要在该位置划船1分钟就出水狱了 28 if(temp.x==0||temp.x==h-1||temp.y==0||temp.y==w-1) 29 { 30 ex=temp.x; 31 ey=temp.y; 32 return temp.v+1; 33 } 34 //对当前结点进行上下左右四个方向的搜索 35 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 36 { 37 pos temp1; 38 temp1.x=temp.x+offset[i][0]; 39 temp1.y=temp.y+offset[i][1]; 40 //拓展位置如果超过地图或者先前已经被搜索过,直接略过 41 if(used[temp1.x][temp1.y]==1||temp1.x<0||temp1.x>=h||temp1.y<0||temp1.y>=w) 42 continue; 43 //拓展结点为 "." 水道,可以入队 44 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='.') 45 { 46 temp1.v=temp.v+1; 47 q.push(temp1); 48 used[temp1.x][temp1.y]=1; 49 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].x=temp.x; 50 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].y=temp.y; 51 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].v=temp1.v; 52 } 53 //拓展结点temp1为“@”栅栏,可以入队,入队时已经算好从S到temp1的时间 temp1.v 54 if(maze[temp1.x][temp1.y]=='@') 55 { 56 temp1.v=temp.v+1+d; 57 q.push(temp1); 58 used[temp1.x][temp1.y]=1; 59 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].x=temp.x; 60 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].y=temp.y; 61 lastp[temp1.x][temp1.y].v=temp1.v; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 void show() 67 { 68 69 printf("the path:\n"); 70 cout<<ex<<" "<<ey<<endl; 71 int i,j; 72 i=ex,j=ey; 73 while(maze[i][j]!='S')//(!(i==sx&&j==sy)) 74 { 75 maze[i][j]=' '; 76 cout<<i+1<<" "<<j+1<<endl; 77 int ii,jj; 78 ii=i;jj=j; 79 i=lastp[ii][jj].x; 80 j=lastp[ii][jj].y; 81 } 82 printf("the route:\n"); 83 for(i=0;i<h;i++) 84 { 85 for(j=0;j<w;j++) 86 { 87 cout<<maze[i][j]; 88 } 89 cout<<endl; 90 } 91 cout<<endl; 92 } 93 int main() 94 { 95 cin>>t; 96 while(t--) 97 { 98 cin>>h>>w>>d; 99 getchar();//为了在后面使用scanf读入字符,解决换行问题 100 for(i=0;i<h;i++) 101 for(j=0;j<w;j++) 102 used[i][j]=0; 103 for(i=0;i<h;i++) 104 { 105 for(j=0;j<w;j++) 106 { 107 scanf("%c",&maze[i][j]); 108 used[i][j]=0; 109 if(maze[i][j]=='S') 110 {sx=i;sy=j;} 111 } 112 getchar();//为了使用scanf读入字符,解决换行问题 113 } 114 printf("the shortest time:%d\n",bfs()); 115 show(); 116 } 117 118 }
测试数据:
 View Code
View Code
1 2 2 6 5 7 3 ##### 4 #S..# 5 #@#.# 6 #...# 7 #@### 8 #.### 9 the shortest time:16 10 the path: 11 5 1 12 6 2 13 5 2 14 4 2 15 4 3 16 4 4 17 3 4 18 2 4 19 2 3 20 the route: 21 ##### 22 #S # 23 #@# # 24 # # 25 # ### 26 # ### 27 28 4 5 3 29 ##### 30 #S#.# 31 #@..# 32 ###@# 33 the shortest time:11 34 the path: 35 3 3 36 4 4 37 3 4 38 3 3 39 3 2 40 the route: 41 ##### 42 #S#.# 43 # # 44 ### #
迷宫问题
A*从n*n的举证左上角走到右下角的最短用时:
/*
迷宫问题,找一条最短的路径。
初始状态:(0,0)
终止状态:(n-1, n-1)
g(i,j): (0,0) 到 (i,j)的路径长度;
h(i,j): (i,j) 到(n-1,n-1)的路径长度的估计值;
h(i,j)=2n-i-j;
*表示障碍
o表示通道
给出一个地图,求从地图左上角到达右下角需要的最短时间
*/
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #define M 201 4 using namespace std; 5 struct pos {int x;int y;int v;}; 6 pos offset[4]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};//一个店的相邻位置 7 char maze[M][M]; //maze记录地图的布置 8 int step[M][M]; //step[i][j]表示达到i,j位置的最优步数 9 int m,n; 10 struct cmp 11 { 12 //用于优先级队列中的堆排序,A算法。 13 bool operator()(const pos &p1,const pos &p2) 14 { 15 return (p1.v+(m+n-p1.x-p1.y) > p2.v+(m+n-p2.x-p2.y)); 16 } 17 }; 18 int BFS(pos start) 19 { 20 pos headNode,neibNode; 21 step[start.x][start.y]=0; 22 priority_queue<pos,vector<pos>,cmp> q; 23 q.push(start); 24 while(!q.empty()) 25 { 26 headNode=q.top(); 27 q.pop(); 28 for(int i=0;i<4;i++) 29 { 30 neibNode.x = headNode.x + offset[i].x; 31 neibNode.y = headNode.y + offset[i].y; 32 neibNode.v = headNode.v + 1; 33 //相邻点超过边界,过滤掉 34 if( neibNode.x>=m || neibNode.y>=n || neibNode.x<0 || neibNode.y<0 ) 35 continue; 36 //相邻点为石头 或者 不是最优尝试,过滤掉 37 if( maze[neibNode.x][neibNode.y]=='*' || neibNode.v>=step[neibNode.x][neibNode.y]) 38 continue; 39 q.push(headNode); 40 step[headNode.x][headNode.y]=next.v; 41 //如果到达目的地,返回 42 if( neibNode.x==m-1 && neibNode.y==n-1 ) 43 return headNode.v; 44 } 45 } 46 return 0; 47 } 48 int main() 49 { 50 int i,j; 51 pos start; 52 start.x=0;start.y=0;start.v=0; 53 while(cin>>n) 54 { 55 m=n; 56 for(i=0;i<m;i++) 57 { 58 for(j=0;j<n;j++) 59 { 60 cin>>maze[i][j]; 61 step[i][j]=m*n; 62 } 63 } 64 cout<<BFS(start)<<endl; 65 } 66 }
 测试数据:
测试数据:
 View Code
View Code网上转的priority_queue用法的例子 转自http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5e518b010100kbts.html
|
STL之优先队列 原本以为priority_queue很简单,才知道原来懂的只是最简单的形式。 头文件:#include<queue> 优先队列,也就是原来我们学过的堆,按照自己定义的优先级出队时。默认情况下底层是以Vector实现的heap。 既然是队列,也就只有入队、出队、判空、大小的操作,并不具备查找功能。 函数列表: 用途就不用多说了吧,例如Huffman编码、分支限界、A*启发式都需要用到优先队列存放信息。 来看最常用的几个功能,了解一下其中的知识点: 一:最基本的功能
二:次基本的功能
三 应该掌握的功能:
例子:
|
问题描述:
有一个背包,容重为W,有n件物品,每件物品对应一个物品价值v和物品重量w。装哪些物品到背包中可使包中价值最大?
输入:
W n
(W表示背包容量 n表示物品数量)
接下来再输入n行 每行为两个正整数 w v(分别表示一个物品的重量和价值)
输出:
bestsum (表示背包中能装物品的最大价值)
best choice(表示背包中最大价值为物品选择方式)
sample in:
75 4
20 20
10 20
30 24
45 35
sample out:
best choice:0,1,3
best sum:75
分析:
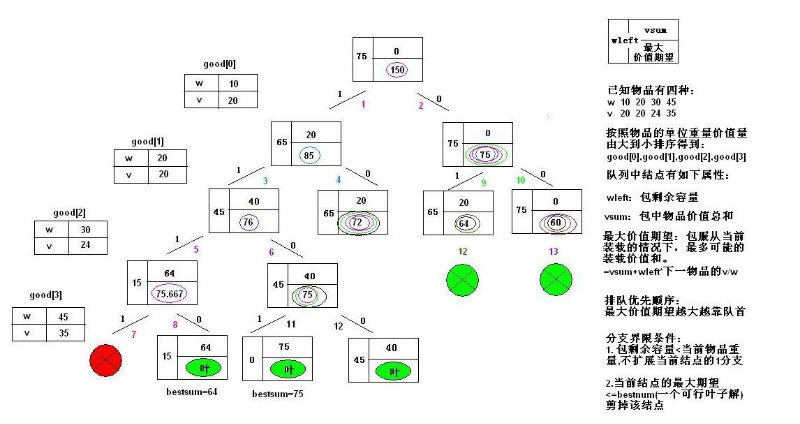
分支界限分析:
1.
假设现在正在处理节点temp,
如果temp.wleft>=good[temp.num].w
就不进行temp的next1拓展,即不把第temp.num放入背包。
这是对广搜完全遍历的一种剪枝
2.
假设现在正在处理节点temp,temp的最大价值期望为expectsumv
expectsumv=temp.vsum+good[temp.num].v*temp.wleft/good[temp.num].w;
如果expectsumv<=bestsum,该节点就不值得被扩展。这样temp节点的子树就被剪枝了
code:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int W,n,bestSum,lowbound; 7 string bestChoice; 8 //node indicates good 9 struct node 10 { 11 int w; 12 int v; 13 }; 14 node good[1000]; 15 //node2 indicates searching node 16 struct node2 17 { 18 int num;//consider which good,the numth good has been considered,0 means none goods has been dealt; 19 //num=2 表示good【0】和good【1】已经考虑过了 20 int wleft;//weight left 21 int vsum; // sum of value 22 string choice;//a string of choice 23 }; 24 struct cmp 25 { 26 bool operator()(const node2 &p1,const node2 &p2) 27 { 28 // p.num==n,表示叶子节点,叶子节点优先 29 if(p1.num==n) 30 return 1; 31 if(p2.num==n) 32 return 0; 33 // 非叶子节点通过上界算优先级 34 return (p1.vsum+float(good[p1.num].v*p1.wleft)/float(good[p1.num].w))>(p2.vsum+float(good[p2.num].v*p2.wleft)/float(good[p2.num].w)); 35 //return (p1.vsum+float(good[p1.num].v*p1.wleft)/float(good[p1.num].w))>(p2.vsum+float(good[p2.num].v*p2.wleft)/float(good[p2.num].w)); 36 37 } 38 }; 39 40 bool cmpnode(const node &a,const node &b) 41 { 42 return a.v*b.w>b.v*a.w; 43 } 44 void bfs(node2 start) 45 { 46 47 priority_queue<node2,vector<node2>,cmp> q; 48 q.push(start); 49 while(!q.empty()) 50 { 51 node2 temp=q.top(); 52 q.pop(); 53 if(temp.num==n) 54 { 55 if(temp.vsum>bestSum) 56 { 57 bestSum=temp.vsum; 58 bestChoice=temp.choice; 59 } 60 } 61 //分支界限约束2 62 //该节点的最好期望比 已知可行的bestSum下界高 才扩展该活结点 63 //if(temp.vsum+good[temp.num].v*temp.wleft/good[temp.num].w>=bestSum) 64 else if(temp.vsum*good[temp.num].w+good[temp.num].v*temp.wleft>bestSum*good[temp.num].w) 65 { 66 //add good[temp.num] 67 if(temp.wleft>=good[temp.num].w)// 分支界限约束1 68 { 69 node2 next1; 70 next1.num=temp.num+1; 71 next1.vsum=temp.vsum+good[temp.num].v; 72 next1.wleft=temp.wleft-good[temp.num].w; 73 //莫名奇妙的错误,当char *strnum,时出错 segmentation error。 74 char strnum[1000]; 75 itoa(temp.num,strnum,10); 76 string str=strnum; 77 next1.choice=temp.choice+str+" "; 78 //next1.choice+=(strnum); 79 //cout<<next1.choice<<endl; 80 q.push(next1); 81 } 82 //not add good[temp.num] 83 node2 next0; 84 next0.num=temp.num+1; 85 next0.vsum=temp.vsum; 86 next0.wleft=temp.wleft; 87 next0.choice=temp.choice; 88 q.push(next0); 89 } 90 } 91 } 92 int main() 93 { 94 int i,j,k; 95 while(cin>>W>>n) 96 { 97 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 98 cin>>good[i].w>>good[i].v; 99 sort(good,good+n,cmpnode); 100 cout<<"put in order accordingto v/w by decrease"<<endl; 101 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 102 cout<<good[i].w<<" "<<good[i].v<<endl; 103 104 bestChoice=""; 105 bestSum=0; 106 //lowbound=0; 107 /* 108 bestSum目前知道的可行的最好情况(也是节点拓展的下界),如果节点的最好期望 小于下界,则不值得拓展,成为死节点 109 当有叶子节点出队时更新。 110 */ 111 node2 start; 112 start.num=0; 113 start.wleft=W; 114 start.vsum=0; 115 start.choice=""; 116 //cout<<"*******"<<endl; 117 bfs(start); 118 119 cout<<"best choice: "<<bestChoice<<endl; 120 cout<<"best sum is:"<<bestSum<<endl; 121 122 } 123 }
/*
75 4
20 20
10 20
30 24
45 35
*/
