直接上题目:
输入描述:
The first line is the number of test cases. For each test case, there is only one line containing a string(the length of strings is less than or equal to 500000), this string only consists of lowercase letters.
输出描述:
For each test case, output a integer donating the number of one-and-half palindromic substrings.
输入
1
ababcbabccbaabc
输出
2
说明
In the example input, there are two substrings which are one-and-half palindromic strings, abab and abcbabc.
题意很简单,算是一到”水题“(相对于别人是)
题意:
输入T个样咧,每个样例包含若干字符,,然后从这个字符串里找出若干个符合条件的子字符串,输出个数,符合条件:S[i]=S[2n−i]=S[2n+i−2](1≤i≤n)
eg:abcbabc 中abcba和cbabc分别为回文串就符合条件
思路:找中心点呗,,找两个中心点可以互达的两个回文串
a b a b c b a b c c b a a b c p[i]
回文长度: 0 1 1 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
显而易见可以有:abab 和abcbabc两个符合条件
枚举后面那个点 找到[i-p[i],i-1]有多少个数可以到当前点
维护前面每一个点最远可达位置 i+p[i];
找到[i-p[i],i-1]有多少个最远可达位置 >=i;
区间[l,r]大于x的数的个数 可持久线段树log
N st
L 往左
R 往右
出口 1,N
最少修改 次数使得走
运用马拉车(Manacher's Algorithm 马拉车算法):
这个马拉车算法Manacher‘s Algorithm是用来查找一个字符串的最长回文子串的线性方法,由一个叫Manacher的人在1975年发明的,这个方法的最大贡献是在于将时间复杂度提升到了线性,这是非常了不起的。对于回文串想必大家都不陌生,就是正读反读都一样的字符串,比如 "bob", "level", "noon" 等等,那么如何在一个字符串中找出最长回文子串呢,可以以每一个字符为中心,向两边寻找回文子串,在遍历完整个数组后,就可以找到最长的回文子串。但是这个方法的时间复杂度为O(n*n),并不是很高效,下面我们来看时间复杂度为O(n)的马拉车算法。
由于回文串的长度可奇可偶,比如"bob"是奇数形式的回文,"noon"就是偶数形式的回文,马拉车算法的第一步是预处理,做法是在每一个字符的左右都加上一个特殊字符,比如加上'#',那么
bob --> #b#o#b#
noon --> #n#o#o#n#
这样做的好处是不论原字符串是奇数还是偶数个,处理之后得到的字符串的个数都是奇数个,这样就不用分情况讨论了,而可以一起搞定。接下来我们还需要和处理后的字符串t等长的数组p,其中p[i]表示以t[i]字符为中心的回文子串的半径,若p[i] = 1,则该回文子串就是t[i]本身,那么我们来看一个简单的例子:
# 1 # 2 # 2 # 1 # 2 # 2 #
1 2 1 2 5 2 1 6 1 2 3 2 1
由于第一个和最后一个字符都是#号,且也需要搜索回文,为了防止越界,我们还需要在首尾再加上非#号字符,实际操作时我们只需给开头加上个非#号字符,结尾不用加的原因是字符串的结尾标识为'�',等于默认加过了。通过p数组我们就可以找到其最大值和其位置,就能确定最长回文子串了,那么下面我们就来看如何求p数组,需要新增两个辅助变量mx和id,其中id为最大回文子串中心的位置,mx是回文串能延伸到的最右端的位置,这个算法的最核心的一行如下:
p[i] = mx > i ? min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i) : 1;
可以这么说,这行要是理解了,那么马拉车算法基本上就没啥问题了,那么这一行代码拆开来看就是
如果mx > i, 则 p[i] = min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i)
否则, p[i] = 1
当 mx - i > P[j] 的时候,以S[j]为中心的回文子串包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,由于 i 和 j 对称,以S[i]为中心的回文子串必然包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,所以必有 P[i] = P[j],见下图。
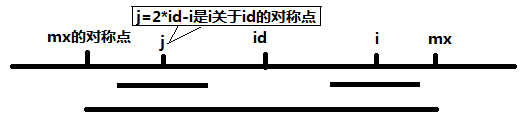
当 P[j] >= mx - i 的时候,以S[j]为中心的回文子串不一定完全包含于以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,但是基于对称性可知,下图中两个绿框所包围的部分是相同的,也就是说以S[i]为中心的回文子串,其向右至少会扩张到mx的位置,也就是说 P[i] >= mx - i。至于mx之后的部分是否对称,就只能老老实实去匹配了。
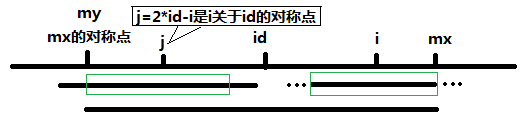
对于 mx <= i 的情况,无法对 P[i]做更多的假设,只能P[i] = 1,然后再去匹配了。
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string Manacher(string s) {
// Insert '#'
string t = "$#";
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
t += s[i];
t += "#";
}
// Process t
vector<int> p(t.size(), 0);
int mx = 0, id = 0, resLen = 0, resCenter = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < t.size(); ++i) {
p[i] = mx > i ? min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i) : 1;
while (t[i + p[i]] == t[i - p[i]]) ++p[i];
if (mx < i + p[i]) {
mx = i + p[i];
id = i;
}
if (resLen < p[i]) {
resLen = p[i];
resCenter = i;
}
}
return s.substr((resCenter - resLen) / 2, resLen - 1); //获得字符串s中 从第(rescenter-reslen)/2位开始的长度为reslen-1的字符串
//默认时的长度为从开始位置到尾
}
int main() {
string s1 = "12212";
cout << Manacher(s1) << endl;
string s2 = "122122";
cout << Manacher(s2) << endl;
string s = "waabwswfd";
cout << Manacher(s) << endl;
}
算法有了,可还不够哦,还需要一点东西:可持续化线段树(这里先不写,线段树会分出开单独记)
是不是觉得思路贼简单,有种你就写代码:(大佬给的,自己现在还是写不出来的)
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define LL long long const int N=5e5+10; const LL INF=1e18+10; const double eps=1e-6; char a[N],str[N]; int p[N]; void manacher(int l) { int i,j=0,k,ans=0; //for(i=1;i<=l;++i)str[i<<1]=s[i],str[(i<<1)+1]='#'; //str[1]='#';str[l*2+1]='#';str[0]='&';str[l*2+2]='$'; //l=l*2+1;j=0; for(int i=1;i<=l;i++)str[i]=a[i]; str[0]='&';str[l+1]='$'; for(i=1;i<=l;) { while(str[i-j-1]==str[i+j+1])++j; p[i]=j;if(j>ans)ans=j; for(k=1;k<=j&&p[i]-k!=p[i-k];++k)p[i+k]=min(p[i-k],p[i]-k); i+=k;j=max(j-k,0); } } int n; struct Chairmantree { int rt[N*30],ls[N*30],rs[N*30],sum[N*30]; int tot; void init() { tot=0; } void build(int l,int r,int &pos) { pos=++tot; sum[pos]=0; if(l==r)return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; build(l,mid,ls[pos]); build(mid+1,r,rs[pos]); } void update(int p,int c,int pre,int l,int r,int &pos) { pos=++tot; ls[pos]=ls[pre]; rs[pos]=rs[pre]; sum[pos]=sum[pre]+c; if(l==r)return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(p<=mid) update(p,c,ls[pre],l,mid,ls[pos]); else update(p,c,rs[pre],mid+1,r,rs[pos]); } int query(int s,int t,int L,int R,int l,int r) { if(L<=l&&r<=R) return sum[t]-sum[s]; int mid=(l+r)>>1; int ans=0; if(L<=mid) ans+=query(ls[s],ls[t],L,R,l,mid); if(R>mid) ans+=query(rs[s],rs[t],L,R,mid+1,r); return ans; } }; Chairmantree tree; int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { scanf("%s",a+1); n=strlen(a+1); manacher(n); LL ans=0; tree.init(); tree.build(1,n,tree.rt[0]); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) tree.update(i+p[i],1,tree.rt[i-1],1,n,tree.rt[i]); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(!p[i])continue; ans+=tree.query(tree.rt[i-p[i]-1],tree.rt[i-1],i,n,1,n); } printf("%lld ",ans); for(int i=0;i<=tree.tot;i++) tree.rt[i]=0,tree.ls[i]=0,tree.rs[i]=0,tree.sum[i]=0; } return 0; }
就这样算不算补题啊!