本文摘自于《Spring Cloud微服务 入门 实战与进阶》一书。 作者:尹吉欢
Spring Boot的方便体现在简化了很多繁琐的配置,对开发人员来说是一个福音,通过引入各种Spring Boot Starter包可以快速的搭建出一个项目的脚手架。
目前提供的Spring Boot Starter包有:
- spring-boot-starter-web:快速构建基于Spring MVC的Web项目,使用Tomcat做默认嵌入式容器。
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis:操作Redis。
- spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb:操作Mongodb。
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa:操作Mysql。
- spring-boot-starter-activemq:操作Activemq。
- 等等......
自动配置非常方便,当我们要操作Mongodb的时候,只需要引入spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb的依赖,然后配置Mongodb的链接信息 spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost/test就可以使用MongoTemplate来操作数据,MongoTemplate的初始化工作全部交给Starter来完成。
自动配置麻烦的是当出现错误时,排查问题的难度上升了。自动配置的逻辑都在Spring Boot Starter中,要快速的能够定位问题,那么你必须得了解Spring Boot Starter的内部原理。接下来我们自己动手来实现一个Spring Boot Starter。
开发Starter步骤:
- 创建Starter项目
- 定义Starter需要的配置(Properties)类
- 编写自动配置类
- 编写spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
- 编写配置提示文件spring-configuration-metadata.json(不是必须的)
创建一个项目spring-boot-starter-demo,Pom.xml配置如下:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies>
创建一个配置类,用于在属性文件中配置值,相当于spring.data.mongo这种形式
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import lombok.Data; @Data @ConfigurationProperties("spring.user") public class UserPorperties { private String name; }
@ConfigurationProperties指定了配置的前缀,也就是spring.user.name=XXX
再定义一个Client,相当于MongoTemplate,里面定一个方法,用于获取配置中的值
public class UserClient { private UserPorperties userPorperties; public UserClient() { } public UserClient(UserPorperties p) { this.userPorperties = p; } public String getName() { return userPorperties.getName(); } }
一个最基本的Starter包定义好了,但目前肯定是不能使用UserClient ,因为我们没有去自动构建UserClient 的实例,接下来开始构建UserClient
@Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(UserPorperties.class) public class UserAutoConfigure { @Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.user", value = "enabled", havingValue = "true") public UserClient userClient(UserPorperties userPorperties) { return new UserClient(userPorperties); } }
Spring Boot会默认扫描跟启动类平级的包,如果我们的Starter跟启动类不在同一个主包下,如何让UserAutoConfigure 生效?
第一种方式:
在resources下创建一个META-INF文件夹,然后在META-INF文件夹中创建一个spring.factories文件,文件中指定自动配置的类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.cxytiandi.demo.UserAutoConfigure
Spring Boot启动时会去读取spring.factories文件,然后根据配置激活对应的配置类,到底为止就简单的实现了一个Starter包。
现在可以在其他的项目中引入这个Starter包:
<dependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>
引入之后就直接可以使用UserClient,UserClient 在项目启动的时候已经自动初始化好。
@RestController public class UserController{ @Autowired private UserClient userClient; @GetMapping("/user/name") public String getUserName() { return userClient.getName(); } }
很多时候我们不想引入了Starter包就执行初始化的逻辑,想要用户来指定是否要开启Starter包的自动配置功能,比如常用的@EnableAsync这个注解就是用于开启调用方法异步执行的功能。
同样的我们也可以通过注解的方式来开启是否自动配置,如果用注解的方式,那么spring.factories就不需要编写了,下面来看怎么定义启用自动配置的注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @Import({UserAutoConfigure.class}) public @interface EnableUserClient { }
核心是@Import({UserAutoConfigure.class})这行代码,通过导入的方式实现把UserAutoConfigure实例加入SpringIOC容器中,这样就能开启自动配置了。
使用方式就是在启动类上加上该注解,代码入下:
@EnableUserClient @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args); } }
在某些场景下,UserAutoConfigure中会配置多个对象,对于这些对象,不想全部配置,也想让用户指定需要开启配置的时候再去构建对象,这个时候我们可以通过@ConditionalOnProperty来指定是否开启配置的功能,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.user", value = "enabled", havingValue = "true") public UserClient userClient(UserPorperties userPorperties){ return new UserClient(userPorperties); }
通过上面的配置,只有当启动类加了@EnableUserClient并且配置文件中spring.user.enabled=true的时候才会自动配置UserClient 。
在自定义Starter包的过程中,还有一点也比较重要,就是需要对配置的内容项进行提示,需要注意的是Eclipse中是不支持提示的,我用的Spring Tools 4 for Eclipse,如下图:
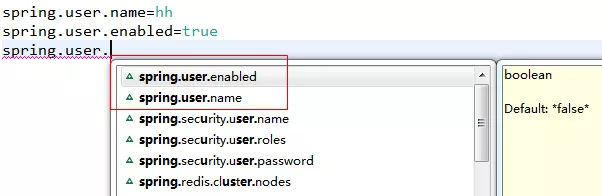
定义提示内容需要在META-INF中创建一个spring-configuration-metadata.json
{ "properties":[ { "name":"spring.user.name", "defaultValue":"cxytinadi" }, { "name":"spring.user.enabled", "type":"java.lang.Boolean", "defaultValue":false } ] }
-
name:配置名
-
type:配置的数据类型
-
defaultValue:默认值