原文地址:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dsANLERHskYhPWlnabnjhg 作者:指北君
1 CompletableFuture的静态方法使用
CompleteableFuture的静态方法有如下
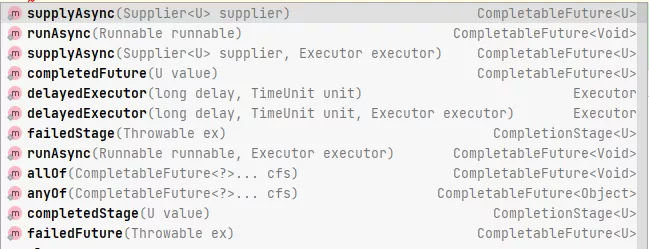
之前的文章里面已经讲过suuplyAsync,以及runAsync。我们就直接看其他方法
delayedExcutor
delayedExcutor其作用是构建一个延迟执行任务的Excutor,默认使用ForkJoinPool. 也可以使用自定义的Excutor。
一个延迟5秒执行任务的Excutor,默认使用使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()。
Executor executor = CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(5l, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
allof和anyof
allof和anyof 为等待多个CompletableFuture完成之后返回一个CompletableFuture。
-
allof返回无result,
-
anyof返回为最先完成的CompletableFuture。
可以看如下示例。
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> { try {Thread.sleep(4 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "supplyAsync1"; }); CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "supplyAsync2"; }); CompletableFuture.anyOf(supplyAsync1,supplyAsync2).thenAccept((str)-> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " anyOf complete : " + str); }); CompletableFuture.allOf(supplyAsync1,supplyAsync2).thenAccept((str)-> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " allOf complete "+ str ); });
执行结果如下:
start second: 2021-10-24T12:39:40.562001600 2021-10-24T12:39:42.611118800 anyOf complete : supplyAsync2 2021-10-24T12:39:44.611233200 allOf complete null
failedStage和failedFuture是返回一个已知异常的CompletableFuture。这个下面和其他异常一起举例。
2 CompletableFuture的其余方法使用
CompletableFuture中方法可以大致分为run,apply,accept几个类别。其对应的参数分别为Runnable,Function,Consummer等几个函数式表达式。
1. run代表当前CompletableFuture完成后执行的一些列操作,无输入参数,无返回结果,所以只是Runnable为参数。()-> { option }
2. apply代表以当前CompletableFuture完成后的结果为参数进行的操作,并且会返回一个新的CompletableFuture,所以以Function为参数。(s)-> {return s;}
3. accept代表以当前CompletableFuture完成后的结果为参数,执行的操作,无返回结果,直接消费。以Consumer为参数,(s)-> { option }。
2.1 Run方法
Run方法相关参数为Runnable,为直接执行的操作。
thenRun 完成之后直接执行。
thenRunAsync 使用线程池异步执行,线程池默认为ForkJoinPool.commonPool
runAfterBoth/ runAfterEither 两个CompletableFuture同时完成或者某一个完成就执行的操作。
runAfterBothAsync/runAfterEitherAsync 同理为使用线程池异步执行的操作。
public class CompletableFutureThenRun { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(" CompletableFutureThenRun main start : " + LocalDateTime.now()); CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(" CompletableFutureThenRun cf1: " + LocalDateTime.now()); try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "supplyAsync"; }); CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { System.out.println(" CompletableFutureThenRun cf2: " + LocalDateTime.now()); try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2,()-> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterBoth: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); cf1.runAfterBothAsync(cf2,()-> { System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterBothAsync: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); cf1.runAfterEither(cf2,()-> { System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterEither: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); cf1.runAfterEitherAsync(cf2,()-> { System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterEitherAsync: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); cf1.thenRunAsync(()-> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun thenRunAsync: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); cf1.thenRun(()-> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" CompletableFutureThenRun thenRun: " + LocalDateTime.now()); }); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " CompletableFutureThenRun last: " + LocalDateTime.now()); try { Thread.sleep(10*1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
上述执行结果:
CompletableFutureThenRun main start : 2021-10-25T01:48:52.416000900 CompletableFutureThenRun cf1: 2021-10-25T01:48:52.492008500 CompletableFutureThenRun cf2: 2021-10-25T01:48:52.493008600 main CompletableFutureThenRun last: 2021-10-25T01:48:52.495008800 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-7 CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterEitherAsync: 2021-10-25T01:48:54.495208800 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-3 CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterEither: 2021-10-25T01:48:54.495208800 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-5 CompletableFutureThenRun thenRun: 2021-10-25T01:48:57.493508600 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-3 CompletableFutureThenRun thenRunAsync: 2021-10-25T01:48:57.494508700 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-3 CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterBoth: 2021-10-25T01:48:57.494508700 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-3 CompletableFutureThenRun runAfterBothAsync: 2021-10-25T01:48:57.495508800
apply 与accept相关的方法类似,此处不一一举例了。
下面我们根据一些情景举例来说明方法如何使用:
2.2 多个 CompletableFuture组合在一起执行
情景一:先去取快递,然后再去买菜,然后回家做饭。
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 正在取快递! "); try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "快递1"; }).thenApply((str) -> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 拿到了: "+str); System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 买菜中。。。 "); try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return str + " 和 蔬菜"; }).thenApply((str2)-> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 现在有了: ["+str2+"]"); try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "带着 [" + str2 + " ]回家做饭" ; }); System.out.println( LocalDateTime.now() + " 美好的一天: "+ cf.join());
下面看一下上面的执行结果,
2021-10-25T01:10:16.831465600 正在取快递! 2021-10-25T01:10:18.861668600 拿到了: 快递1 2021-10-25T01:10:18.911673600 买菜中。。。 2021-10-25T01:10:20.911873600 现在有了: [快递1 和 蔬菜] 2021-10-25T01:10:16.831465600 美好的一天: 带着 [快递1 和 蔬菜 ]回家做饭
可以看到最后一行输出的时间比较早,这是因为join会阻塞线程,直到此CompletableFuture执行完并获取到值。
情景二:和女朋友一起出门,我去取快递,女朋友去买菜,然后一起回家做饭。
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 正在取快递! "); try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "快递"; }); CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 女朋友正在买菜! "); try {Thread.sleep(4 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return "蔬菜"; }); cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2,(str1 ,str2 )->{ System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " ["+ str1 + "]["+str2+"] 带回来了,开始做饭 "); }).join();
此处使用 thenAcceptBoth 需要在两个CompletableFuture都完成的情况下,才能执行,所以最后使用join()使其阻塞到可以执行当前的操作。
情景三:和女朋友一起出门,我去取快递,女朋友去买菜,谁先弄完谁就先回去。
cf1.acceptEither(cf2,(str1 )-> { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " ["+ str1 +"] 带回来了,先回家吧! "); }).join();
我先拿到了快递,就快快的回家了,然后就挨了一顿毒打。
2.3 在两个CompletableFuture运行后再次计算
晚饭过后和女朋友讨论做什么事情,然而发生了分歧:
CompletableFuture<List<String>> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("看电影", "打扑克"); System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 晚饭后女朋友说,想要: " + strings); try {Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return strings; }); CompletableFuture<List<String>> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("看电影", "打游戏"); System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 晚饭后,我想: " + strings); try {Thread.sleep(4 * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} return strings; }); cf1.thenCombine(cf2,(list1,list2) -> { System.out.println("遭受了一顿毒打之后。。。!!!"); List<String> collect = list1.stream().filter(str -> list2.contains(str)).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " 综合两个人的想法,最终决定: " + collect); return collect; }).join();
女朋友想看电影,或者打扑克,但是我想打游戏。最后遭受一顿毒打之后,还是说出了或者看电影。最终选择了看电影。
4 CompletableFuture的异常处理
CompletableFuture和异常相关的方法有如下
4.1 whenComplete/whenCompleteAsync
CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
whenCompletable使用有BiConsumer里面会有两个参数,下边是一个示例。参数需要两个分别为str,exception, 如果有异常exception有值,str为null。如果stringCompletableFuture正常完成,则exception为null。但是不管是否有异常,表达式里面的方法均会执行。
有点类似try finally{},有没有异常均可执行。
CompletableFuture<String> whenCompleteCF = stringCompletableFuture.whenComplete((str, exception) -> { if(exception != null){ System.out.println("whenComplete : " + exception); exception.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("whenComplete execute whither error throw "); });
4.2 exceptionally
exceptionally方法中为一个Function参数,需要一个输入值,为当前CompletableFuture抛出的异常。
其返回值有两个结果:
1. 如果当前CompletableFuture无异常完成,则返回与原CompletableFuture的result相同的CompletableFuture,注意知识result相同,并不是同一个类。
2. 如果当前CompletableFuture有异常抛出,那么返回新的CompletableFuture以及新处理后的result。
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { throw new RuntimeException(" CompletableFuture throw one exception"); // return "cc"; }); CompletableFuture<String> exceptionally = stringCompletableFuture.exceptionally((exception) -> { System.out.println("exceptionally only execute when error throw "); return "exception"; }); System.out.println("exceptionally : " + exceptionally.join());
上述示例无异常抛出时结果如下:
exceptionally :cc
有异常抛出时结果如下:
exceptionally only execute when error throw exceptionally :exception
4.3 handle/handleAsync
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)
handle 和 whenComplete 比较类似,无论有没有异常,里面的方法均会执行到。但是有有一些区别,handle参数为BiFunction,有返回值,whenComplet的参数为BiComsumer 无返回值。
下面的实例中,如果有异常则参数中的str为null,如果没有异常exception为null。
CompletableFuture<String> handle = stringCompletableFuture.handle((str, exception) -> { System.out.println("handle : " + str); if(exception != null ){ System.out.println("stringCompletableFuture1 have exception :" ); exception.printStackTrace(); } return "handle complete "; });
有异常的执行结果:
stringCompletableFuture1 have exception :
handle.join(); :handle complete
无异常的执行结果
handle :cc
handle.join(); :handle complete
4.4 failedStage/failedFuture
failedStage和failedFuture均为静态方法,会返回一个已完成的给定异常的CompletableFuture。
failedStage返回的是CompletionStage,failedFuture返回为CompletableFuture对象
CompletionStage<Object> test_exception = CompletableFuture.failedStage(new RuntimeException("test exception")); CompletableFuture<Object> test_exception1 = CompletableFuture.failedFuture(new RuntimeException("test exception"));
最后给一个可以直接食用的示例,可以根据不同的需求进行改良哦!
public static Map<String, List<Integer>> testMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); static { testMap.put("A", Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5)); testMap.put("B", Arrays.asList(6,7,8,9,10)); testMap.put("C", Arrays.asList(11,12,13,14,15)); testMap.put("D", Arrays.asList(21,22,23,24,25)); testMap.put("E", Arrays.asList(31,32,33,34,35)); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(" CompletableFutureDemo5 main start : " + LocalDateTime.now()); List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E"); ExecutorService testPool = new ForkJoinPool(4); List<CompletableFuture<List<Integer>>> collect = strings.stream().map( key -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return obtainTheList(key); },testPool).exceptionally((exc)->{ System.out.println(" hit the exception " ); throw new RuntimeException(exc); }) ).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(" CompletableFutureDemo5 supplyAsync end : " + LocalDateTime.now()); try { List<List<Integer>> integerCollect = collect.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList()); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(" catch the exception " + e.getMessage()); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(" CompletableFutureDemo5 main end : " + LocalDateTime.now()); try { Thread.sleep(5*1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static List<Integer> obtainTheList(String key) { List<Integer> integers = testMap.get(key); if( key.equals("C") ){ throw new RuntimeException("exception test !"); } try { Thread.sleep(2*1000); System.out.println(" obtainTheList thread name : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() +" : "+ LocalDateTime.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return integers==null? new ArrayList() :integers; }
总结
本片用了一些示例来讲解CompletableFuture,我们可以在开发中的一些场景中使用起来了。特别是异步多线程去拿一些数据的时候,非常好用哦。
详细的Demo,请看传送门:https://github.com/javatechnorth/java-study-note/tree/master/multiThread/src/main/java/org/javanorth/currency/completableFuture
作者:指北君,操千曲而后晓声,观千剑而后识器。