strongswan SA分析(一)
1 概念
下面主要介绍两个本文将要阐述的核心概念。他们是SA和SP。注意,这不是一篇不需要背景知识的文章。作者认为你适合阅读接下来内容的的前提是,你已经具备了一下三方面的知识:
- a. 什么是VPN。
- b. 什么是IPsec,包括IKE,ESP,strongswan都是什么等。
- c. 一般的linux使用方法和常见概念。
1.1 什么是SAD,SPD
SAD是Security Association Database的缩写。
SPD是Security Policy Database的缩写。
SAD是用来存储SA的数据库。SPD是用来存储SP的数据库。
1.2 什么是SPI
SPI是Security Parameter Index的缩写。是有一组数字(长度?)。被使用在SAD和SPD里作为索引的一部分。是由IKE协商的两侧客户端随机选择的UUID?。0-255是被保留的值,禁止在SPI中使用。
1.3 什么是SA
SA是Security Association的缩写。SA是一组算法和算法参数(包括key)的集合,用来完成单个方向的数据流加密和验证任务。通过SPI加数据包的目的地址可以唯一查找到一个SA。
包含的属性:
- 加密算法
- 属性
- key
- 验证算法
- 属性
- key
- SPI
- 目的地址
1.4 什么是SP
SP是Security Policy的缩写。SP是一条规则,决定一条流(flow)是否需要被IPsec处理。SP的处理有三种方式:
- 丢弃
- 不处理
- 处理
需要被IPsec处理的流,会被指向到一个template。一个template可以理解为指向一个SA,template包含以下属性:
- 协议
- AH或ESP。
- 模式
- transport或tunnel模式。
- pattern
- 源IP加目的IP对。
- NAT的PORT对。
SP有一个方向属性,取值分别为:
- out
- in
- fwd
1.5 总结
在整个IPsec的数据流转逻辑中,SP用来表达What todo。SA用来表达How todo。
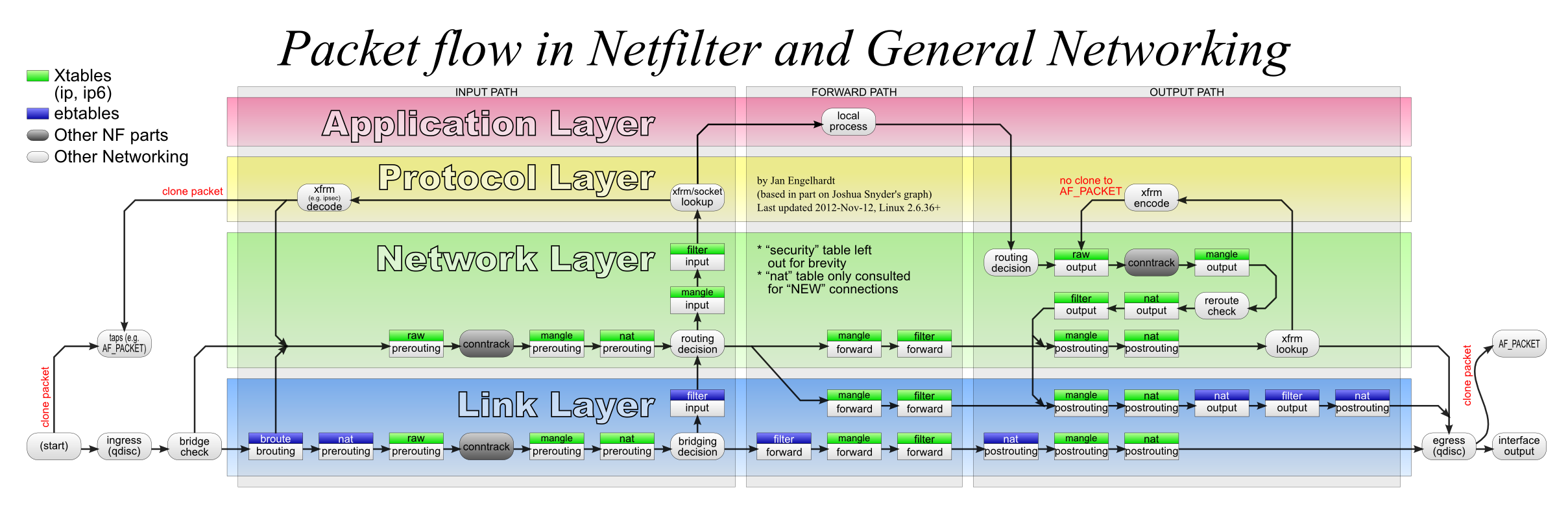
2 数据流
简单的说。明文报在通过IPsec VPN设备变成ESP发出去的过程是:
- 查找路由。
- 查找policy决定是否需要被ESP
- 查找SA并加密封装。
- 加密封装后的包再查路由。
IPsec报在通过IPsec VPN设备变成非加密包发出去的过程:
- 查找路由。
- 查找policy决定是否需要要解ESP
- 查找SA并解密解封装。
- 解密解封装后的包再查路由。
2.1 举个栗子
路由
[root@T9 sbin]# ip route
default via 192.168.7.1 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
10.129.0.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 10.129.0.1 metric 100
192.168.7.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.7.129 metric 100
policy
[root@T9 sbin]# ip xfrm policy
src 10.9.0.0/16 dst 10.129.0.0/16
dir fwd priority 383616 ptype main
tmpl src 192.168.7.9 dst 192.168.7.129
proto esp reqid 1 mode tunnel
src 10.9.0.0/16 dst 10.129.0.0/16
dir in priority 383616 ptype main
tmpl src 192.168.7.9 dst 192.168.7.129
proto esp reqid 1 mode tunnel
src 10.129.0.0/16 dst 10.9.0.0/16
dir out priority 383616 ptype main
tmpl src 192.168.7.129 dst 192.168.7.9
proto esp reqid 1 mode tunnel
sa
[root@T9 sbin]# ip xfrm state
src 192.168.7.129 dst 192.168.7.9
proto esp spi 0xc42ac7f3 reqid 1 mode tunnel
replay-window 0 flag af-unspec
auth-trunc hmac(sha256) 0x5f7b99e.....eb20948fb2f8fc713caf2d43b4 128
enc cbc(aes) 0x48144872d5f4f9a6a762b68785e6f265
src 192.168.7.9 dst 192.168.7.129
proto esp spi 0xc1c8ad99 reqid 1 mode tunnel
replay-window 32 flag af-unspec
auth-trunc hmac(sha256) 0x7efc5d2172.....0c0dedf053b0b6ae5aa2f012 128
enc cbc(aes) 0x808efcfaa45a543b69efe08158accaa3
3 理解linux kernel中的sa概念和管理
3.1 提供给用户的sa接口
理解kernel sa对用户展示的形态,可以帮助我们理解linux kernel对于ipsec sa的建模和抽象。对我们在VPN产品的sa模块设计中将提供帮助。
3.1.1 使用racoon配置sa
setkey add 192.168.0.1 192.168.1.2 esp 0x10001
-m tunnel
-E des-cbc 0x3ffe05014819ffff
-A hmac-md5 "authentication!!"
从以上信息可以很容易开始各个参数表达的含义,其中-E代表加密算法和它的key,-A代表验证算法和它的key。0x10001为spi。
3.1.2 使用racoon配置policy
setkey spdadd 10.0.11.41/32[21] 10.0.11.33/32[any] any
-P out ipsec esp/tunnel/192.168.0.1-192.168.1.2/require
第一行代表五元组,any代表协议。第二行代表policy的具体描述:方向,action,template。
3.1.3 总结
通过以上两个小节的描述,读者应该已经很容易的总结出了配置一个SA和一个policy所需要提供的最基本的信息了。作者将在本章的最后,对sa和poliyc所包含的所有必须信息进行一个统一的总结。
另外,通过上文的语法,我们应该能够发现,policy与sa之间的match操作,是需要一个稍负责的匹配逻辑来实现的,而不仅仅是一个简单的匹配关系。
3.2 netlink的SA接口
strongswan是目前使用两种方式与内核进行ipsec的配置交互,分别为netlink和pfkey。如官方文档所述,netlink是strongswan默认启用的,变成stable的接口方式。整个调研工作也是以netlink方式为出发点展开的,现简单介绍如下。
3.2.1 什么是netlink
netlink是复用了socket方式的内核与用户态IPC方法。
这里有一篇写的非常好的文章,讲netlink为什么会产生。由于人家写的实在是太好了,我已经没有什么可写的了,只能做个概要,如下:

因为作者图画是业余的,所以看懂的这个概要图的前提是,你必须懂得BSD socket的api如何使用。
3.2.2 接口方式
用netlink方式配置ipsec的方法。
netlink的一般用法
初始化socket
与常规的socket用法相同,只是传入参数是netlink定义的特有参数。
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol)
bind(fd, (struct sockaddr*)&nladdr, sizeof(nladdr));
下发配置信息到kernel
使用socket的标准send,write接口将特定格式的参数下发给kernel。
参数格式如下:
struct nlmsghdr
{
__u32 nlmsg_len; /* Length of message */
__u16 nlmsg_type; /* Message type*/
__u16 nlmsg_flags; /* Additional flags */
__u32 nlmsg_seq; /* Sequence number */
__u32 nlmsg_pid; /* Sending process PID */
};
这个参数结构体是传入参数的头部,紧接着这个头部之后的内存是真正的参数的值。它的解析方法由nlmsg_type的值来确定。它的结尾由nlmsg_len的数值来决定。
添加sa
添加sa的时候,nlmsghdr后面的参数为结构体
struct xfrm_usersa_info
nlmsg_type的值为:XFRM_MSG_NEWSA
这部分内容定义在系统文件下:
/usr/include/linux/xfrm.h
这个结构体后边,还需要追加算法部分的信息,如下:
struct xfrm_algo
struct xfrm_algo_auth
添加policy
添加policy的时候,nlmsghdr后面的参数为结构体
struct xfrm_userpolicy_info
nlmsg_type的值为:XFRM_MSG_NEWPOLICY
这部分内容定义在系统文件下:
/usr/include/linux/xfrm.h
3.3 xfrm的SA接口
3.3.1 什么是xfrm
xfrm(transform)是一个IP包转发框架。主要实现以下三部分功能:
- IPsec protocol suite
- IP Payload Compression Protocol
- Mobile IPv6
3.3.2 内核代码
linux/net/xfrm/
主要函数
Xfrm_lookup() xfrm lookup(SPD and SAD) method
Xfrm_input() xfrm processing for an ingress packet
Xfrm_output() xfrm processing for an egress packet
Xfrm4_rcv() IPv4 specific Rx method
Xfrm6_rcv() IPv6 specific Rx method
Esp_input() ESP processing for an ingress packet
Esp_output() ESP processing for an egress packet
Ah_output() AH processing for an ingress packet
Ah_input() ESP processing for an egress packet
xfrm_policy_alloc() allocates an SPD object
Xfrm_policy_destroy() frees an SPD object
xfrm_ policy_lookup SPD lookup
xfrm_policy_byid() SPD lookup based on id
Xfrm_policy_insert() Add an entry to SPD
Xfrm_Policy_delete() remove an entry from SPD
Xfrm_bundle_create() creates a xfrm bundle
Xfrm_policy_delete() releases the resources of a policy object
Xfrm_state_add() add an entry to SAD
Xfrm_state_delete() free and SAD object
Xfrm_state_alloc() allocate an SAD object
xfrm_state_lookup_byaddr() src address based SAD lookup
xfrm_state_find() SAD look up based on dst
xfrm_state_lookup() SAD lookup based on spi
3.3.3 API
api文件
include/uapi/linux/xfrm.h
主要的API
XFRM_MSG_NEWSA To add a new SA to SAD
XFRM_MSG_DELSA To delete a new SA to SAD
XFRM_MSG_GETSA To get a new SA to SAD
XFRM_MSG_FLUSHSA To flush SAD
XFRM_MSG_NEWPOLICY To add a new policy to SPD
XFRM_MSG_DELPOLICY To delete a new policy to SPD
XFRM_MSG_GETPOLICY To get a new policy to SPD
XFRM_MSG_FLUSHPOLICY To flush SPD
3.3.4 sa的传入参数
struct xfrm_usersa_info {
struct xfrm_selector sel; // 被加密网段?为啥要有这个?
struct xfrm_id id; // 目的ip,spi,协议ah/esp
xfrm_address_t saddr; // 源ip
struct xfrm_lifetime_cfg lft;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cur curlft;
struct xfrm_stats stats;
__u32 seq;
__u32 reqid;
__u16 family;
__u8 mode; // transport / tunnel
__u8 replay_window;
__u8 flags;
};
算法参数是追加在SA结构体之后的内存块,根据不同的类型决定不同的结构。示例:
struct xfrm_algo {
char alg_name[64];
unsigned int alg_key_len; /* in bits */
char alg_key[0];
};
struct xfrm_algo_auth {
char alg_name[64];
unsigned int alg_key_len; /* in bits */
unsigned int alg_trunc_len; /* in bits */
char alg_key[0];
};
3.3.5 policy的传入参数
struct xfrm_userpolicy_info {
struct xfrm_selector sel; //网段:ip,port,协议
struct xfrm_lifetime_cfg lft;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cur curlft;
__u32 priority; //
__u32 index;
__u8 dir; //方向:in out fwd
__u8 action; // allow, block
__u8 flags;
__u8 share;
};
4 xfrm的实现
4.1 用于存储sa的内部数据结构
struct xfrm_state {
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS
struct net *xs_net;
#endif
union {
struct hlist_node gclist;
struct hlist_node bydst;
};
struct hlist_node bysrc;
struct hlist_node byspi;
atomic_t refcnt;
spinlock_t lock;
struct xfrm_id id;
struct xfrm_selector sel;
struct xfrm_mark mark;
u32 tfcpad;
u32 genid;
/* Key manager bits */
struct xfrm_state_walk km;
/* Parameters of this state. */
struct {
u32 reqid;
u8 mode;
u8 replay_window;
u8 aalgo, ealgo, calgo;
u8 flags;
u16 family;
xfrm_address_t saddr;
int header_len;
int trailer_len;
u32 extra_flags;
} props;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cfg lft;
/* Data for transformer */
struct xfrm_algo_auth *aalg;
struct xfrm_algo *ealg;
struct xfrm_algo *calg;
struct xfrm_algo_aead *aead;
/* Data for encapsulator */
struct xfrm_encap_tmpl *encap;
/* Data for care-of address */
xfrm_address_t *coaddr;
/* IPComp needs an IPIP tunnel for handling uncompressed packets */
struct xfrm_state *tunnel;
/* If a tunnel, number of users + 1 */
atomic_t tunnel_users;
/* State for replay detection */
struct xfrm_replay_state replay;
struct xfrm_replay_state_esn *replay_esn;
/* Replay detection state at the time we sent the last notification */
struct xfrm_replay_state preplay;
struct xfrm_replay_state_esn *preplay_esn;
/* The functions for replay detection. */
struct xfrm_replay *repl;
/* internal flag that only holds state for delayed aevent at the
* moment
*/
u32 xflags;
/* Replay detection notification settings */
u32 replay_maxage;
u32 replay_maxdiff;
/* Replay detection notification timer */
struct timer_list rtimer;
/* Statistics */
struct xfrm_stats stats;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cur curlft;
struct tasklet_hrtimer mtimer;
/* used to fix curlft->add_time when changing date */
long saved_tmo;
/* Last used time */
unsigned long lastused;
/* Reference to data common to all the instances of this
* transformer. */
const struct xfrm_type *type;
struct xfrm_mode *inner_mode;
struct xfrm_mode *inner_mode_iaf;
struct xfrm_mode *outer_mode;
/* Security context */
struct xfrm_sec_ctx *security;
/* Private data of this transformer, format is opaque,
* interpreted by xfrm_type methods. */
void *data;
};
会被插入两个hash表
1. Hash table by (spi,daddr,ah/esp) to find SA by SPI. (input,ctl)
2. Hash table by (daddr,family,reqid) to find what SAs exist for given
destination/tunnel endpoint. (output)
4.2 用于存储sa的内部数据结构
struct xfrm_policy {
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS
struct net *xp_net;
#endif
struct hlist_node bydst;
struct hlist_node byidx;
/* This lock only affects elements except for entry. */
rwlock_t lock;
atomic_t refcnt;
struct timer_list timer;
struct flow_cache_object flo;
atomic_t genid;
u32 priority;
u32 index;
struct xfrm_mark mark;
struct xfrm_selector selector;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cfg lft;
struct xfrm_lifetime_cur curlft;
struct xfrm_policy_walk_entry walk;
struct xfrm_policy_queue polq;
u8 type;
u8 action;
u8 flags;
u8 xfrm_nr;
u16 family;
struct xfrm_sec_ctx *security;
struct xfrm_tmpl xfrm_vec[XFRM_MAX_DEPTH];
};
4.3 数据结构之间的存储结构
TODO
4.4 关键函数
xfrm_lookup()
xfrm_output()
xfrm4_policy_check() // 在ipv4中被调用。
5 strongswan中的sa
5.1 概述
从IKE协议的角度上,有两个SA,一个叫IKE_SA,一个叫CHILD_SA。本章讨论的sa,特指下图中的CHILD_SA。
本篇文章,通篇讨论的SA指的都是这里的CHILD_SA。
CHILD_SA在strongswan的框架里,主要存在与两个部分。
- IKE协商过程。
CHILD_SA是IKE协商过程中的输出。IKE协商过程结束后,IKE-SA Manager将CHILD_SA交个strongswan框架。 - IPsec隧道建立过程。
CHILD_SA是IKE协商过程中的输入。strongswan框架将CHILD_SA交给libcharon plugin由特定的plugin与kernel通信,在kernel中完成IPsec tunnel的建立过程。 - IPsec在转发过程。
这部分和strongswan的框架没有了关系,由内核完成。
+---------------------------------+ +----------------------------+
| Credentials | | Backends |
+---------------------------------+ +----------------------------+
+------------+ +-----------+ +------+ +----------+
| receiver | | | | | +------+ | CHILD_SA |
+----+-------+ | Scheduler | | IKE- | | IKE- |--+----------+
| | | | SA |--| SA | | CHILD_SA |
+-------+--+ +-----------+ | | +------+ +----------+
<->| socket | | | Man- |
+-------+--+ +-----------+ | ager | +------+ +----------+
| | | | | | IKE- |--| CHILD_SA |
+----+-------+ | Processor |--------| |--| SA | +----------+
| sender | | | | | +------+
+------------+ +-----------+ +------+
+---------------------------------+ +----------------------------+
| Bus | | Kernel Interface |
+---------------------------------+ +----------------------------+
| | |
+-------------+ +-------------+ V
| File-Logger | | Sys-Logger | //////
+-------------+ +-------------+
5.1.1 strongswan中的plugin
上一小节提到了plugin,接下来讲解plugin。
有两类plugins。一类是libstrongswan的plugin,一类是libcharon的plugin。
libstrongswan的plugin主要提供加密,认证,数据库相关的功能。
libcharon的plugin主要提供“specific needs”。。。我们接下来要讨论的与sa下发相关的plugin都在
libcharon这一类里。他们包括:
- kernel-libipsec
用户态的转发平面,目前还处于高实验性阶段。转发性能没有kernel。主要用来满足不能使用kernel转发的场景。 - kernel-netlink
使用netlink接口与linux kernel的xfrm模块交互。目前输出稳定使用阶段,默认首选。 - kernel-iph
windows操作系统的接口。 - kernel-pfkey
使用pkkey接口与linux kernel的xfrm模块进行交互,高实验性阶段。 - kernel-wfp
windows操作系统的接口。
本文,只关心kernel-netlink的plugin。
5.2 启动过程
5.2.1 概述
strongswan的启动方式有多种。可以和各种不同的系统对接,包括systemd,networkmanager等。
- starter
ipsec命令使用的守护进程。用ipsec start命令,就会启动这个进程。 - charon-nm
networkmanager的plugin。什么是nm的plugin? - charon-systemd
按照systemd的daemon style实现的一个进程。由systemd启动。 - charon-svc
windows的服务。
各种启动方式的最终目的都是启动最终目的都是启动charon进程。所以,最简的启动方法就是:
- 直接运行charon进程
当然,这种方式没有daemon守护,但是功能完整。
5.2.2 调试方法
如上一小节所述。charon进程可以直接运行。所以调试的时候直接使用gdb运行charon就可以了。
# gdb `which charon`
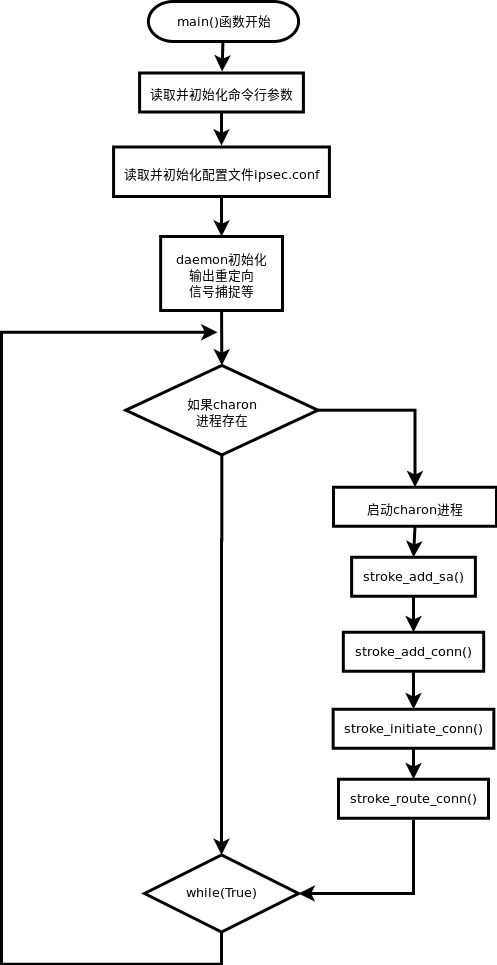
5.2.3 starter的启动过程
starter的启动方法是通过ipsec脚本执行start命令,这样便启动了strongswan服务。
# ipsec start
ipsec脚本
源码位置
strongswan-5.7.1/src/ipsec/_ipsec
ipsec脚本解析start参数后,会执行如下命令,启动daemon进程starter
${IPSEC_DIR}/starter --daemon charon
starter进程
源码位置
strongswan-5.7.1/src/starter/starter.c
starter的主要功能是启动charon进程,并进行守护。
- daemon的初始工作
重定向输出,signal响应等。 - 启动charon
- 加载ipsec.conf中的配置。
流程图
charon进程
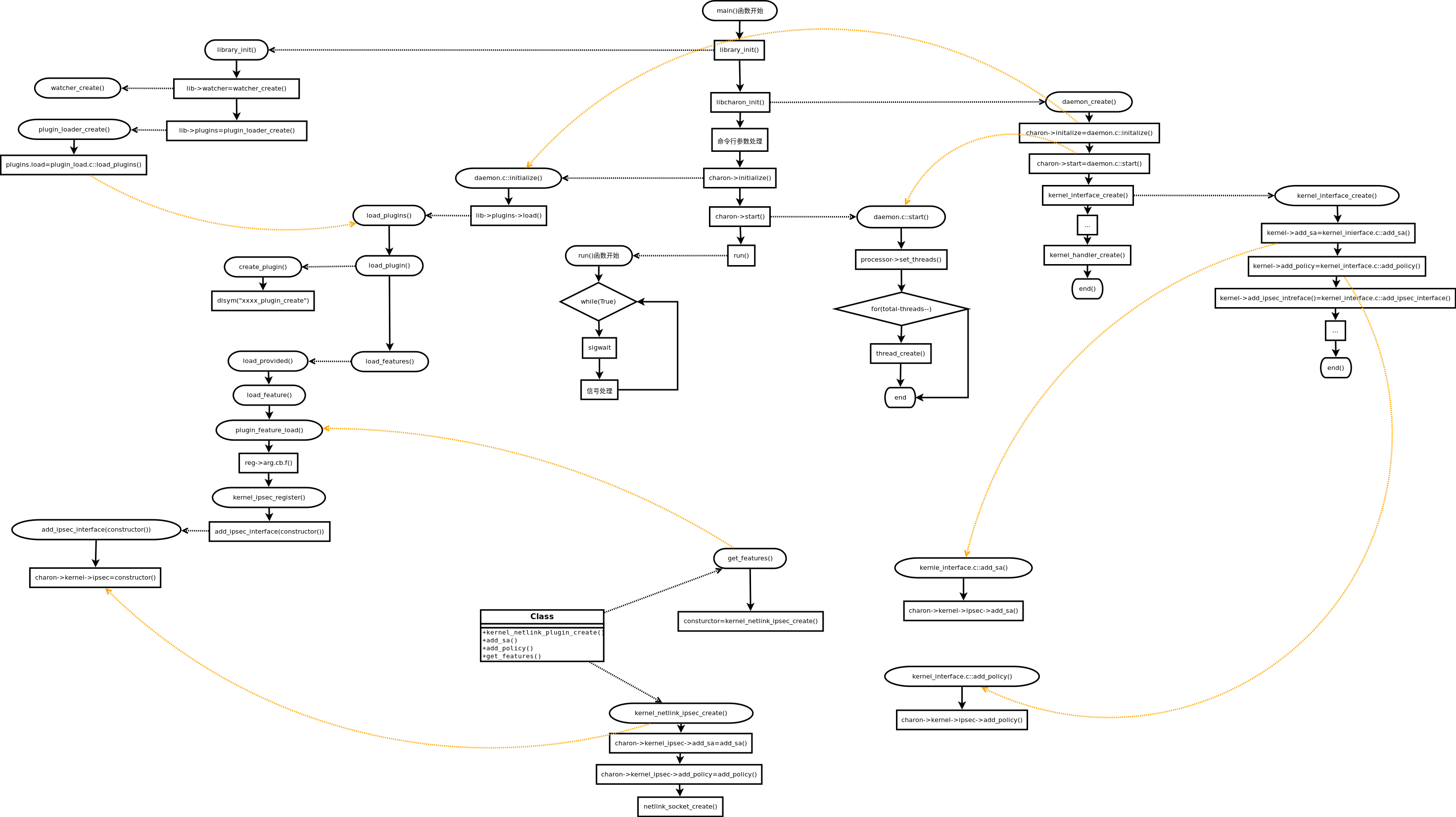
charon进程运行启动成功后,启动16个子线程执行不同的job。
整个charon中的任务调度围绕着task和job两个核心概念进行。
流程图
实线代表流程图;虚线代表调用栈。
5.2.4 systemd的启动过程
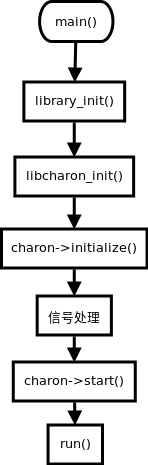
systemd的启动过程首先使用systemd的service配置脚本。然后启动systemd的charon守护进程。
最后通过守护进程启动charon进程。
systemd脚本
源码位置
strongswan-5.7.1/init/systemd-swanctl/strongswan-swanctl.service.in
service脚本在启动过程执行两个操作。
- 启动charon-systemd进程。
- 执行swanctl --load-all --noprompt命令
charon-systemd进程
源码位置
strongswan-5.7.1/src/charon-systemd/charon-systemd.c
charon-systemd进程是charon进程的另一个入口。charon-systemd进程不会在启动新的进程,charon-systemed进程就是处理业务的主进程,有systemd进行守护。
所以,charon-systemd只有main函数中的少量内容与charon不同。其他逻辑与charon进程完全相同。
流程图
5.3 调用过程
运行过程中,与SA相关的两个部分主要就是add_sa与add_policy两个地方。
当charon进程收到一个message的时候,会以job的形式分发给standby的业务线程进行处理。
最后通过kernel对象调用kernel_interface接口中的add_sa和add_policy两个函数。接口会根据
具体注册的plugin调用各plugin的相应,add_as, add_policy函数。
例如,netlink的plugin。
在该plugin的这两个函数中,会通过netlink的接口最终调用内核的xfrm接口完成sa和policy的下发和更新等操作。
详见3.2和3.3两个章节。
5.4 数据结构
strongswan中的sa数据结构
定义在文件 kernel_ipsec.h 中,由id和data两个结构共同组成。
struct kernel_ipsec_sa_id_t {
/** Source address */
host_t *src;
/** Destination address */
host_t *dst;
/** SPI */
uint32_t spi;
/** Protocol (ESP/AH) */
uint8_t proto;
/** Optional mark */
mark_t mark;
};
/**
* Data required to add an SA to the kernel
*/
struct kernel_ipsec_add_sa_t {
/** Reqid */
uint32_t reqid;
/** Mode (tunnel, transport...) */
ipsec_mode_t mode;
/** List of source traffic selectors */
linked_list_t *src_ts;
/** List of destination traffic selectors */
linked_list_t *dst_ts;
/** Network interface restricting policy */
char *interface;
/** Lifetime configuration */
lifetime_cfg_t *lifetime;
/** Encryption algorithm */
uint16_t enc_alg;
/** Encryption key */
chunk_t enc_key;
/** Integrity protection algorithm */
uint16_t int_alg;
/** Integrity protection key */
chunk_t int_key;
/** Anti-replay window size */
uint32_t replay_window;
/** Traffic Flow Confidentiality padding */
uint32_t tfc;
/** IPComp transform */
uint16_t ipcomp;
/** CPI for IPComp */
uint16_t cpi;
/** TRUE to enable UDP encapsulation for NAT traversal */
bool encap;
/** no (disabled), yes (enabled), auto (enabled if supported) */
hw_offload_t hw_offload;
/** Mark the SA should apply to packets after processing */
mark_t mark;
/** TRUE to use Extended Sequence Numbers */
bool esn;
/** TRUE to copy the DF bit to the outer IPv4 header in tunnel mode */
bool copy_df;
/** TRUE to copy the ECN header field to/from the outer header */
bool copy_ecn;
/** Whether to copy the DSCP header field to/from the outer header */
dscp_copy_t copy_dscp;
/** TRUE if initiator of the exchange creating the SA */
bool initiator;
/** TRUE if this is an inbound SA */
bool inbound;
/** TRUE if an SPI has already been allocated for this SA */
bool update;
};
strongswan中的policy数据结构
定义在文件 kernel_ipsec.h 和 ipsec_types.h 中。
struct kernel_ipsec_policy_id_t {
/** Direction of traffic */
policy_dir_t dir;
/** Source traffic selector */
traffic_selector_t *src_ts;
/** Destination traffic selector */
traffic_selector_t *dst_ts;
/** Optional mark */
mark_t mark;
/** Network interface restricting policy */
char *interface;
};
/**
* Data required to add/delete a policy to/from the kernel
*/
struct kernel_ipsec_manage_policy_t {
/** Type of policy */
policy_type_t type;
/** Priority class */
policy_priority_t prio;
/** Manually-set priority (automatic if set to 0) */
uint32_t manual_prio;
/** Source address of the SA(s) tied to this policy */
host_t *src;
/** Destination address of the SA(s) tied to this policy */
host_t *dst;
/** Details about the SA(s) tied to this policy */
ipsec_sa_cfg_t *sa;
};
struct ipsec_sa_cfg_t {
/** mode of SA (tunnel, transport) */
ipsec_mode_t mode;
/** unique ID */
uint32_t reqid;
/** number of policies of the same kind (in/out/fwd) attached to SA */
uint32_t policy_count;
/** details about ESP/AH */
struct {
/** TRUE if this protocol is used */
bool use;
/** SPI for ESP/AH */
uint32_t spi;
} esp, ah;
/** details about IPComp */
struct {
/** the IPComp transform used */
uint16_t transform;
/** CPI for IPComp */
uint16_t cpi;
} ipcomp;
};
6 sa的抽象模型
6.1 实现sa管理的思路
略。
6.2 sa
目的地址(dip)加 spi 唯一确定一个sa条目。
| 属性 | 取值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| id | ||
| spi | 协商过程带过来的 | |
| mode | transport/tunnel | |
| protocol | esp/ah/ipcom | 加密协议的方式 |
| sip | 另一条隧道是sip和dip互换的,故两个sa | |
| dip | ||
| life | 生存时间 | |
| enc_alg | ||
| enc_key | ||
| integrity_alg | 完整性验证 | |
| integrity_key | ||
| nat | 是否做nat |
6.3 policy
| 属性 | 取值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| id | ||
| action | drop/pass/ipsec | 命中此策略后的行为 |
| priority | 优先级 | |
| dir | in/out/fwd | 方向 |
| s_ts | source traffic selector | |
| d_ts | destination traffic selector |
6.4 traffic selector
ts就是五元组,ip使用掩码掩起来的一个段。port也可以掩,具体跟kernel学一下。
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| source ip | |
| sip_prefixlen | |
| dest ip | |
| dip_prefixlen | |
| sport | |
| sport_mask | |
| dport | |
| dport_mask | |
| protocol |
7 问题
7.1 policy与路由的关系
在我的测试虚机环境里,删掉了策略路由之后,功能正常。
目前还不清楚为什么。路由与policy之间的关系,以及路由和policy在内核包转发过程中的逻辑关系,
都需要进一步的调研。