All GUI applications are event-driven. Events are generated mainly by the user of an application. But they can be generated by other means as well: e.g. an Internet connection, a window manager, or a timer. When we call the application's exec_() method, the application enters the main loop. The main loop fetches events and sends them to the objects.
In the event model, there are three participants:
- event source
- event object
- event target
The event source is the object whose state changes. It generates events. The event object (event) encapsulates the state changes in the event source. The event target is the object that wants to be notified. Event source object delegates the task of handling an event to the event target.
PyQt4 has a unique signal and slot mechanism to deal with events. Signals and slots are used for communication between objects. A signal is emitted when a particular event occurs. A slot can be any Python callable. A slot is called when a signal connected to it is emitted.
New API
PyQt4.5 introduced a new style API for working with signals and slots.
QtCore.QObject.connect(button, QtCore.SIGNAL('clicked()'), self.onClicked)
This is the old style API.
button.clicked.connect(self.onClicked)
The new style adheres more to the Python standards.
Signals & Slots
This is a simple example demonstrating signals and slots in PyQt4.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we connect a signal
of a QtGui.QSlider to a slot
of a QtGui.QLCDNumber.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: October 2011
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
lcd = QtGui.QLCDNumber(self)
sld = QtGui.QSlider(QtCore.Qt.Horizontal, self)
vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addWidget(lcd)
vbox.addWidget(sld)
self.setLayout(vbox)
sld.valueChanged.connect(lcd.display)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Signal & slot')
self.show()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we display a QtGui.QLCDNumber and a QtGui.QSlider. We change the lcd number by dragging the slider knob.
sld.valueChanged.connect(lcd.display)
Here we connect a valueChanged signal of the slider to the display slot of the lcd number.
The sender is an object that sends a signal. The receiver is the object that receives the signal. Theslot is the method that reacts to the signal.
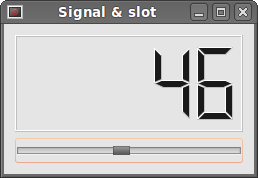 Figure: Signal & slot
Figure: Signal & slot