文章结构:
1. 基本数据类型的系统描述;
2.数据类型的包装类理解(含源码解析);
3.数据类型转换、装包拆包等一些小坑。
一、基本数据类型的系统描述:
1. 总述:
Java基本数据类型分为两大类:boolean类型和数值类型。数值类型可分为整数类型和浮点类型,而其中字符类型可单独对待。所以Java只包含8种基本数据类型。
注意!字符串不是基本数据类型,字符串是一个类,是一个引用类型。
boolean 数值只有true和false,不能用0代替。其他数值类型不能转换成boolean。包装类–Boolean
byte 内存8位,无符号位时最大存储255,表数范围:-128~127。包装类–Byte
short 内存16位,无符号位时最大存储65536,表数范围:-32768~32767。包装类–Short
int 内存32位,无符号位时最大存储2的32次方减1,表数范围:负的2的31次方到正的2的31次方减1。包装类–Integer。
long 内存64位,无符号位时最大存储2的64次方减1,表数范围:负的2的63次方到正的2的63次方减1。包装类–Long。
float 内存32位,数据范围在3.4e-45~1.4e38,直接赋值时必须在数字后加上f或F。包装类–Float。
double 内存64位,数据范围在4.9e-324~1.8e308,赋值时可以加d或D也可以不加。包装类–Double。
char:16位,存储Unicode字符集,用单引号赋值。可以参与加减乘除运算的,也可以比较大小的!!包装类–Character。
二、数据类型的包装类理解(含部分源码解析)
Java会为每一个基础数据类型都提供一个相应包装类的目的,在于将Java的所有东西都抽象成对象,可以更方便的控制和使用。这就是面向对象!
对于包装类:
主要作用是:
1.作为和基本数据类型对应的类类型存在,方便涉及到对象的操作。
2.包含每种基本数据类型的相关属性如最大值、最小值等,以及相关的操作方法。
1.深入boolean基本类型、Boolean类以及细节点:
1 //看接口是可序列化,是一个final修饰的类 2 public final class Boolean implements java.io.Serializable, 3 Comparable<Boolean>{ 4 //看这两个对应的原始对象。享元模式的使用,达到多个对象都使用一份内存。至于什么是享元,以及它与单例的区别,这里就不多说了。 5 public static final Boolean TRUE = new Boolean(true); 6 public static final Boolean FALSE = new Boolean(false); 7 private final boolean value; 8 //两个构造器,可见它是可以为null的啦,使用Boolean这个类的话 9 public Boolean(boolean value) { 10 this.value = value; 11 } 12 public Boolean(String s) { 13 this(parseBoolean(s)); 14 } 15 public static boolean parseBoolean(String s) { 16 return ((s != null) && s.equalsIgnoreCase("true")); 17 } 18 //jdk文档建议用valueOf代替new方式来创建Boolean类对象。new创建的Boolean对象是不断的新创建一个实例对象,而valueOf则是返回Boolean类里的静态成员变量,也就是使用享元模式的那个对象。 19 public static Boolean valueOf(String s) { 20 return parseBoolean(s) ? TRUE : FALSE; 21 } 22 23 //下面是令人困惑的设计了,我也是看了下stackoverflow里面讨论才有点懂。 24 //原汁原味链接:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3912303/boolean-hashcode 25 //1. 使用质素是因为假如要把Boolean指插入到hashtable中,如果不是质素的话可能会比较容易造成哈希冲突。符合对象计算hashcode的时候通常会把各个属性的hashcode相加然后再做hash,如果是比较小的质素,容易造成hash分布不均匀。 26 //2. Maps是可以包裹Boolean的,而如果map除了包含Boolean对象,还包含其他对象,那么如果不适当处理,就很容易有冲突了 27 public static int hashCode(boolean value) { 28 return value ? 1231 : 1237; 29 }
总括下:
1.boolean是基础数据类型,而Boolean是一个类。
2.boolean一般存在于桟空间中,而Boolean对象存在堆空间中。
3.boolean有true和false俩种值,Boolean除了true和false外,还有null。
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main (String []args) 3 { 4 Boolean bool1 = Boolean.valueOf(true); //这里均使用valueof创建对象,new创建的Boolean对象是不断的新创建一个实例对象,而valueOf则是返回Boolean类里的静态成员变量 5 Boolean bool2 = Boolean.valueOf("True"); //这里上一句代码验证使用String变量作为参数时,不区分大小写的。 6 Boolean bool3 = Boolean.valueOf("ASD"); 7 boolean x1 = bool1.booleanValue(); 8 boolean x2 = bool2.booleanValue(); 9 System.out.println("bool1:" + x1 + ",bool2:" + x2 + ",bool3:" + bool3); 10 boolean x3 = bool1.equals(bool2); //这个就是验证享元模式,使用的是同一个对象 11 boolean x4 = bool1.equals(bool3); //肯定不是同一对象啦。 12 System.out.println("bool1.equals(bool2):" + x3 + ",bool1.equals(bool3):" + x4); 13 String str1 = Boolean.toString(bool1); //可见Boolean对象是可以转换成字符的 14 String str2 = Boolean.toString(false); 15 String str3 = bool3.toString(); 16 System.out.println("bool1:" + str1 + ",str2:" + str2 + ",bool3:" + str3); 17 boolean x5 = Boolean.parseBoolean("ASD"); //源码是直接判断然后与true对比,因此打印为false 18 System.out.println(x5); 19 } 20 }
2.深入byte基本类型
1 //也可以看到是一个final修饰的类,只能用,不能被继承咯 2 public final class Byte extends Number implements Comparable<Byte>{ 3 public static final int SIZE = 8; //只能是一个字节咯 4 //两个构造器 5 public Byte(byte value) { 6 this.value = value; //传入的要为Byte类型的值 7 } 8 public Byte(String s) throws NumberFormatException { 9 this.value = parseByte(s, 10); //传入的要求是可转换成Byte的字符串 10 } 11 //这个Byte做了缓存 12 private static class ByteCache { 13 private ByteCache(){} 14 15 static final Byte cache[] = new Byte[-(-128) + 127 + 1];//声明缓存数组的长度为256 16 17 static { 18 for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) 19 cache[i] = new Byte((byte)(i - 128));//然后将-128~127进行缓存 20 } 21 } 22 //两个解析字符串方法 23 public static byte parseByte(String s, int radix) 24 throws NumberFormatException { 25 //radix是解析字符串时候的基数,在此方法下有个解析基数的含义。 26 int i = Integer.parseInt(s, radix);//解析字符串并返回,所以s必须是-128~127的字符,至于为什么用这个方法int的包装类方法来解析,一会我们会谈到。 27 if (i < MIN_VALUE || i > MAX_VALUE) 28 throw new NumberFormatException( 29 "Value out of range. Value:"" + s + "" Radix:" + radix); 30 return (byte)i; 31 } 32 //也是解码转码方法,将String转为Byte 33 public static Byte decode(String nm) throws NumberFormatException { 34 int i = Integer.decode(nm);//一会重点讲解Integer的系列方法 35 if (i < MIN_VALUE || i > MAX_VALUE) 36 throw new NumberFormatException( 37 "Value " + i + " out of range from input " + nm); 38 return valueOf((byte)i); 39 } 40 }
解释radix的作用
b[0] = Byte.parseByte(“11”, 2) = 3
表示 字符串11以2为基数表示为10进制的byte值是 3 ,这里的11表示的是一个2进制数
b[0] = Byte.parseByte(“11”, 3) = 4
表示 字符串11以3为基数表示为10进制的byte值是 4 ,这里的11表示的是一个3进制数
3、int和Integer
1 public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> { 2 3 public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");//原始类型int的Class实例。 4 //所有可能的将数字表示为字符串的字符集合做缓存。 5 final static char[] digits = { 6 '0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , 7 '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' , 8 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' , 9 'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' , 10 'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' , 11 'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z' 12 }; 13 //两个构造器 14 public Integer(int value) { 15 this.value = value; 16 } 17 public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException { 18 this.value = parseInt(s, 10);//涉及了String转换成int,一会仔细讨论这个。 19 } 20 //像上面Byte类型中解释的那样的方法,返回第二个参数所指定的进制数的第一个参数的字符串表示形式。处理各种进制的Integer. 21 public static String toString(int i, int radix) { 22 if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) 23 radix = 10;//默认为10进制 24 /* Use the faster version */ 25 if (radix == 10) { 26 return toString(i); 27 } 28 char buf[] = new char[33]; 29 boolean negative = (i < 0); 30 int charPos = 32; 31 //统一转为负数去处理 32 if (!negative) { 33 i = -i; 34 } 35 while (i <= -radix) { 36 buf[charPos--] = digits[-(i % radix)]; 37 i = i / radix; 38 } 39 buf[charPos] = digits[-i]; 40 if (negative) { 41 buf[--charPos] = '-'; 42 } 43 return new String(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos)); 44 } 45 //一会有事例代码演示这个,这个其实就是把int型包装成Integer然后再转化成String字符串 46 public static String toString(int i) { 47 if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE) 48 return "-2147483648"; 49 int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i); 50 char[] buf = new char[size]; 51 getChars(i, size, buf); 52 return new String(buf, true); 53 } 54 //与toString组合形成一方法去转换成字符串咯 55 static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) { 56 int q, r; 57 int charPos = index; 58 char sign = 0; 59 60 if (i < 0) { //如果i为负数,则设置i的符号字符为'-'。 61 sign = '-'; //确定正负数 62 i = -i; //将负数转化为正数处理,提高效率 63 } 64 65 // Generate two digits per iteration 66 while (i >= 65536) { //如果i大于65536,则每一次都获取十位和个位上的数字对应的字符。将值判断大小后取每个数字,较大的数字一次取两位(大数字运算消耗大) 67 q = i / 100; 68 // really: r = i - (q * 100); 69 r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2)); //利用位运算,每次获得i的最后两位数,不断循环提取处理 70 i = q;//重新赋值,准备下一次循环 71 buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r]; //存储r中在个位数集合中对应的字符 72 buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r]; //存储r中在十位数集合中对应的字符 73 } 74 75 // Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers 76 // assert(i <= 65536, i); 77 for (;;) { //i<65536的情况,小数字运算消耗较小,故一次只取一位 78 q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);//52429/(2*19)约等于1,此处这样设计是为了提高精度 79 r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ... //每次获得i的最后两位数 80 buf [--charPos] = digits [r];//取最后一位的数字 81 i = q;//重新赋值,准备下一次循环 82 if (i == 0) break; 83 } 84 if (sign != 0) { 85 buf [--charPos] = sign; //设置符号 86 } 87 } 88 //下面两个是用来确定字符串长度的。 89 //定义sizeTable表示int中每个位数中最大的数,用于简便确定int数的长度。 90 final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999, 91 99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE }; 92 //使用上面的sizeTable定义来确定int数的字符串表示长度。 93 static int stringSize(int x) { 94 for (int i=0; ; i++) 95 if (x <= sizeTable[i]) 96 return i+1; 97 } 98 //炒鸡重要的方法啦!!parseInt(String s,int radix)使用第二个参数指定的基数,将字符串参数解析为有符号的整数。 parseInt(String s)只能将数字字符串转化十进制数 99 public static int parseInt(String s, int radix) 100 throws NumberFormatException 101 { 102 /* 103 * WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization 104 * before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use 105 * the valueOf method. 106 */ 107 108 if (s == null) {//参数检验,调用方法前检查参数的正确性。 109 throw new NumberFormatException("null"); 110 } 111 112 if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) { 113 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix + 114 " less than Character.MIN_RADIX"); 115 } 116 117 if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) { 118 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix + 119 " greater than Character.MAX_RADIX"); 120 } 121 122 int result = 0; 123 boolean negative = false; 124 int i = 0, len = s.length();//i表示当前遍历的s的位数 125 int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;//设置最小值为负的Integer的最大值 126 int multmin; 127 int digit; 128 129 if (len > 0) {//如果字符串长度大于0,则进行转换 130 char firstChar = s.charAt(0);//获取第一位字符 131 if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-" 132 if (firstChar == '-') {//判断是否为负数 133 negative = true; 134 limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;//将限制转换为Integer的最小值,不能小于Integer的最小值 135 } else if (firstChar != '+') 136 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);//第一个char不为+也不为-,则抛出异常 137 138 if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-" 139 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);//若只有一个符号,则抛出异常 140 i++; 141 } 142 multmin = limit / radix;//设定不同进制下的极限值 143 while (i < len) {//进行进制的转换 144 // Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE 145 digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);//将数字字符串转换成要求的进制数,使用工具类,每次遍历对一个字符进行操作转换 146 if (digit < 0) { 147 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 148 } 149 if (result < multmin) { 150 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 151 } 152 result *= radix; 153 if (result < limit + digit) { 154 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 155 } 156 result -= digit; 157 } 158 } else { 159 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 160 } 161 return negative ? result : -result;//根据符号返回正数还是负数 162 } 163 //看吧,我们经常用的parseInt只是个帮我们制定好10进制规则的静态方法 164 public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException { 165 return parseInt(s,10); 166 } 167 //强大的内部类缓存机制吗,内部字符缓存类 168 private static class IntegerCache { 169 //缓存的下界,-128,不可变 170 static final int low = -128; 171 //缓存上界,暂为null 172 static final int high; 173 static final Integer cache[];//利用数组来缓存 174 //原理:初始化数组将一定范围的整数放到cache数组中,然后在调valueOf方法的时候首先判断范围然后从缓存数组中去抓取数据 175 176 static { 177 // high value may be configured by property 178 // 缓存上届,可以通过JVM属性来配置 179 int h = 127; 180 String integerCacheHighPropValue = 181 sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); 182 //获取,得到上界 183 if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { 184 try { 185 int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); 186 i = Math.max(i, 127); 187 // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE 188 h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); 189 } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { 190 // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. 191 } 192 } 193 high = h; 194 //获取Integer中所有能保存的数据,初始化缓存数组 195 cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; 196 int j = low; 197 //缓存所有Integer的数据 198 for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) 199 cache[k] = new Integer(j++); 200 201 // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) 202 assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; 203 } 204 205 private IntegerCache() {} 206 } 207 //还有这个我们经常用的,官方也推荐使用这个方法去创建对象的 208 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { 209 //如果i在Integer缓存中,则直接取出 210 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) 211 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; 212 //否则,直接创建一个实例 213 return new Integer(i); 214 } 215 }
使用Integer事例代码:
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Integer a1 = 1; 3 Integer a2 = 1; 4 5 Integer b1 = 200; 6 Integer b2 = 200; 7 8 Integer c1 = Integer.valueOf(1); 9 // Integer c2 = new Integer(1); 官方不推荐这种建对象的方法喔 10 Integer c2 = Integer.valueOf(1); 11 12 Integer d1 = Integer.valueOf(200); 13 Integer d2 = Integer.valueOf(200); 14 15 16 System.out.println("a1==a2?" + (a1 == a2)); 17 System.out.println("b1==b2?" + (b1 == b2)); 18 System.out.println("c1==c2?" + (c1 == c2)); 19 System.out.println("d1==d2?" + (d1 == d2)); 20 }
运行结果:
a1==a2? true b1==b2? false c1==c2? false d1==d2? false
4.Character的基本了解
Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值。Character 类型的对象包含类型为 char 的单个字段。该类提供了几种方法,以确定字符的类别(小写字母,数字,等等),并将字符从大写转换成小写,从小写转换成大写。Character 类的方法和数据是通过 UnicodeData 文件中的信息定义的。至于Unicode 大家就百度了解下就好。
5.Long类:
1 public final class Long extends Number implements Comparable<Long> { 2 @Native public static final long MIN_VALUE = 0x8000000000000000L;//最小值为2的63次方-1 3 @Native public static final long MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffffffffffffL;//最大值为-2的63次方 4 public static final Class<Long> TYPE = (Class<Long>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("long"); 5 //toString方法与Integer中的toString实现原理一样的。 6 7 //转换成对应的进制的字符串表示 8 public static String toUnsignedString(long i, int radix) { 9 if (i >= 0) 10 return toString(i, radix); 11 else { 12 switch (radix) { 13 case 2: 14 return toBinaryString(i);//将Long转为2进制 15 16 case 4: 17 return toUnsignedString0(i, 2);//将Long转为4进制 18 19 case 8: 20 return toOctalString(i);//将Long转为8进制 21 22 case 10: 23 /* 24 * We can get the effect of an unsigned division by 10 25 * on a long value by first shifting right, yielding a 26 * positive value, and then dividing by 5. This 27 * allows the last digit and preceding digits to be 28 * isolated more quickly than by an initial conversion 29 * to BigInteger. 30 */ 31 long quot = (i >>> 1) / 5;、//十进制嘛 32 long rem = i - quot * 10; 33 return toString(quot) + rem; 34 35 case 16: 36 return toHexString(i); 37 38 case 32: 39 return toUnsignedString0(i, 5); 40 41 default: 42 return toUnsignedBigInteger(i).toString(radix); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 //返回一个BigInteger等于参数的无符号值 47 private static BigInteger toUnsignedBigInteger(long i) { 48 if (i >= 0L) 49 return BigInteger.valueOf(i); 50 else { 51 int upper = (int) (i >>> 32); 52 int lower = (int) i; 53 54 // return (upper << 32) + lower 55 return (BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.toUnsignedLong(upper))).shiftLeft(32). 56 add(BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.toUnsignedLong(lower))); 57 } 58 } 59 public static String toHexString(long i) {//将Long转为16进制 60 return toUnsignedString(i, 4); 61 } 62 public static String toOctalString(long i) {//将Long转为8进制 63 return toUnsignedString(i, 3); 64 } 65 public static String toBinaryString(long i) {//将Long转为2进制 66 return toUnsignedString(i, 1); 67 static int stringSize(long x) {//展示Long的字符串长度 68 long p = 10; 69 for (int i=1; i<19; i++) {//每次乘十进行比较 70 if (x < p) 71 return i; 72 p = 10*p; 73 } 74 return 19; 75 } 76 //这个也跟Integer的实现差不多。将字符串参数解析为有符号的整数。 77 public static long parseLong(String s, int radix) 78 throws NumberFormatException 79 { 80 if (s == null) {//参数检验 81 throw new NumberFormatException("null"); 82 } 83 84 if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) { 85 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix + 86 " less than Character.MIN_RADIX"); 87 } 88 if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) { 89 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix + 90 " greater than Character.MAX_RADIX"); 91 } 92 93 long result = 0; 94 boolean negative = false;//这,,跟Integer基本一样的呀 95 int i = 0, len = s.length(); 96 long limit = -Long.MAX_VALUE; 97 long multmin; 98 int digit; 99 100 if (len > 0) { 101 char firstChar = s.charAt(0); 102 if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-" 103 if (firstChar == '-') { 104 negative = true; 105 limit = Long.MIN_VALUE; 106 } else if (firstChar != '+') 107 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 108 109 if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-" 110 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 111 i++; 112 } 113 multmin = limit / radix; 114 while (i < len) { 115 // Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE 116 digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix); 117 if (digit < 0) { 118 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 119 } 120 if (result < multmin) { 121 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);//转化为了负数进行计算,所以要用<号 122 } 123 result *= radix; 124 if (result < limit + digit) { 125 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 126 } 127 result -= digit; 128 } 129 } else { 130 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s); 131 } 132 return negative ? result : -result; 133 } 134 public static long parseLong(String s) throws NumberFormatException {//默认转成10进制 135 return parseLong(s, 10); 136 } 137 //官方推荐的创建Long对象的方法啦 138 public static Long valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException { 139 return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, radix)); 140 } 141 public static Long valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException 142 { 143 return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, 10)); 144 } 145 //Long的默认缓存,-128~127,缓存模块与Integer相同 146 private static class LongCache { 147 private LongCache(){} 148 149 static final Long cache[] = new Long[-(-128) + 127 + 1]; 150 151 static { 152 for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) 153 cache[i] = new Long(i - 128); 154 } 155 } 156 public static Long valueOf(long l) { 157 final int offset = 128; 158 //在缓存范围内则直接使用咯 159 if (l >= -128 && l <= 127) { // will cache 160 return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset]; 161 } 162 return new Long(l); 163 } 164 public int hashCode() {//重写hashcode()方法,无符号右移32位后乘value本身 165 return (int)(value ^ (value >>> 32)); 166 } 167 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 168 if (obj instanceof Long) { 169 return value == ((Long)obj).longValue();//比较的是value的地址值,所以在缓存范围内的相等,缓存范围外的不等(两个对象指向同一个Long除外) 170 } 171 return false; 172 } 173 }
6.列出一下包装类的共性:
(1)带有基本值参数并创建包装类对象的构造函数.如可以利用Integer包装类创建对象,Integer obj=new Integer(145)
Integer obj=new Integer(145);
(2)带有字符串参数并创建包装类对象的构造函数.如new Integer(“-45.36”);
(3)可生成对象基本值的typeValue方法,如obj.intValue();
int num=obj.intValue();
(4)将字符串转换为基本值的 parseType方法,如Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
(5)因为有装进Map的几率,所以java设计了包装类里的哈希值,生成哈稀表代码的hashCode方法,如obj.hasCode();
(6)对同一个类的两个对象进行比较的equals()方法,如obj1.eauqls(obj2);
(7)生成字符串表示法的toString()方法,如obj.toString().
(8)自动装包/拆包大大方便了基本类型数据和它们包装类地使用。
自动装包:基本类型自动转为包装类。例如(int >> Integer)
自动拆包:包装类自动转为基本类型。例如(Integer >> int)
三、数据类型转换、装包拆包
(1).类型转换:
基础:1.自动类型转换-系统支持把某种基本类型的值直接赋给另一种基本类型的变量。
规则:如下图,从左到右自动转换。
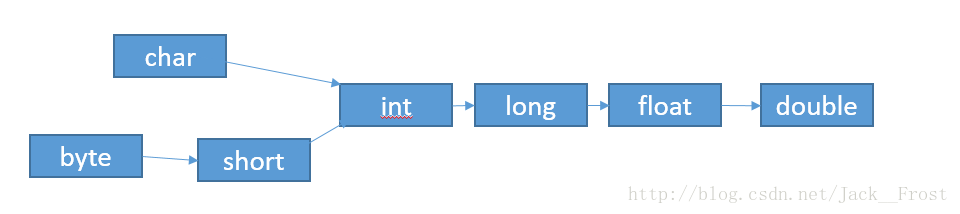
2.强制类型转换-视图把表数范围大的类型转换为表数范围小的类型时,容器引起信息丢失。
另:字符串不能直接转换为基本类型,但可通过基本类型对应的包装类实现转换成基本类型。如以下代码:
1 String a = "45"; 2 int value=Integer.parseInt(a);
3.自动提升规则:当一个算术表达式中包含多个基本类型的值时,所有的byte类、short和char类型会被提示到int类型
(2)自动装包与拆包:自动装包/拆包大大方便了基本类型数据和它们包装类地使用。
自动装包:基本类型自动转为包装类.(int >> Integer)
自动拆包:包装类自动转为基本类型.(Integer >> int)
使用装包后,我们就可以用集合去存放基本类型啦。比如:Integer先自动转换为int进行加法运算,然后int再次转换为Integer。
1 int a = 3; 2 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 3 c.add(a);//自动转换成Integer.自动装包 4 Integer b = new Integer(2); 5 c.add(b + 2);