原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 、作者信息和本声明。否则将追究法律责任。http://devbean.blog.51cto.com/448512/243546
说实话,本来我是没有打算放一个很大的例子的,一则比较复杂,二来或许需要很多次才能说得完。不过,现在已经说完了绘图部分,所以计划还是上一个这样的例子。这里我会只做出一个简单的画板程序,大体上就是能够画直线和矩形吧。这样,我计划分成两种实现,一是使用普通的QWidget作为画板,第二则是使用Graphcis View Framework来实现。因为前面有朋友说不大明白Graphics View的相关内容,所以计划如此。
好了,现在先来看看我们的主体框架。我们的框架还是使用Qt Creator创建一个Gui Application工程。
简单的main()函数就不再赘述了,这里首先来看MainWindow。顺便说一下,我一般不会使用ui文件,所以这些内容都是手写的。首先先来看看最终的运行结果:
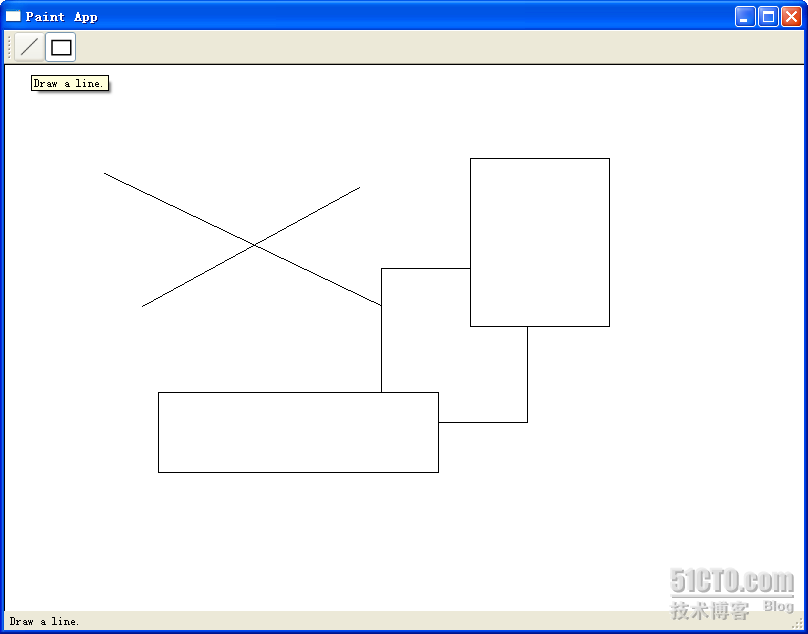
或许很简单,但是至少我们能够把前面所说的各种知识串连起来,这也就达到目的了。
现在先来看看MainWindow的代码:
mainwindow.h
 #ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H  #define MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H 
 #include <QtGui>
#include <QtGui> 
 #include "shape.h"
#include "shape.h"  #include "paintwidget.h"
#include "paintwidget.h" 
 class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow  {
{  Q_OBJECT
Q_OBJECT 
 public:
public:  MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0); 
 signals:
signals:  void changeCurrentShape(Shape::Code newShape);
void changeCurrentShape(Shape::Code newShape); 
 private slots:
private slots:  void drawLineActionTriggered();
void drawLineActionTriggered();  void drawRectActionTriggered();
void drawRectActionTriggered(); 
 };
}; 
 #endif // MAINWINDOW_H
#endif // MAINWINDOW_Hmainwindow.cpp
 #include "mainwindow.h"
#include "mainwindow.h" 
 MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)  : QMainWindow(parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)  {
{  QToolBar *bar = this->addToolBar("Tools");
QToolBar *bar = this->addToolBar("Tools");  QActionGroup *group = new QActionGroup(bar);
QActionGroup *group = new QActionGroup(bar); 
 QAction *drawLineAction = new QAction("Line",
bar);
QAction *drawLineAction = new QAction("Line",
bar);  drawLineAction->setIcon(QIcon(":/line.png"));
drawLineAction->setIcon(QIcon(":/line.png"));  drawLineAction->setToolTip(tr("Draw a line."));
drawLineAction->setToolTip(tr("Draw a line."));  drawLineAction->setStatusTip(tr("Draw a line."));
drawLineAction->setStatusTip(tr("Draw a line."));  drawLineAction->setCheckable(true);
drawLineAction->setCheckable(true);  drawLineAction->setChecked(true);
drawLineAction->setChecked(true);  group->addAction(drawLineAction);
group->addAction(drawLineAction); 
 bar->addAction(drawLineAction);
bar->addAction(drawLineAction);  QAction *drawRectAction = new QAction("Rectangle",
bar);
QAction *drawRectAction = new QAction("Rectangle",
bar);  drawRectAction->setIcon(QIcon(":/rect.png"));
drawRectAction->setIcon(QIcon(":/rect.png"));  drawRectAction->setToolTip(tr("Draw a rectangle."));
drawRectAction->setToolTip(tr("Draw a rectangle."));  drawRectAction->setStatusTip(tr("Draw a rectangle."));
drawRectAction->setStatusTip(tr("Draw a rectangle."));  drawRectAction->setCheckable(true);
drawRectAction->setCheckable(true);  group->addAction(drawRectAction);
group->addAction(drawRectAction);  bar->addAction(drawRectAction);
bar->addAction(drawRectAction); 
 QLabel *statusMsg = new QLabel;
QLabel *statusMsg = new QLabel;  statusBar()->addWidget(statusMsg);
statusBar()->addWidget(statusMsg); 
 PaintWidget *paintWidget = new PaintWidget(this);
PaintWidget *paintWidget = new PaintWidget(this);  setCentralWidget(paintWidget);
setCentralWidget(paintWidget); 
 connect(drawLineAction, SIGNAL(triggered()),
connect(drawLineAction, SIGNAL(triggered()),  this, SLOT(drawLineActionTriggered()));
this, SLOT(drawLineActionTriggered()));  connect(drawRectAction, SIGNAL(triggered()),
connect(drawRectAction, SIGNAL(triggered()),  this, SLOT(drawRectActionTriggered()));
this, SLOT(drawRectActionTriggered()));  connect(this, SIGNAL(changeCurrentShape(Shape::Code)),
connect(this, SIGNAL(changeCurrentShape(Shape::Code)),  paintWidget, SLOT(setCurrentShape(Shape::Code)));
paintWidget, SLOT(setCurrentShape(Shape::Code)));  }
} 
 void MainWindow::drawLineActionTriggered()
void MainWindow::drawLineActionTriggered()  {
{  emit changeCurrentShape(Shape::Line);
emit changeCurrentShape(Shape::Line);  }
} 
 void MainWindow::drawRectActionTriggered()
void MainWindow::drawRectActionTriggered()  {
{  emit changeCurrentShape(Shape::Rect);
emit changeCurrentShape(Shape::Rect);  }
} 应该说,从以往的学习中可以看出,这里的代码没有什么奇怪的了。我们在MainWindow类里面声明了一个信号,changeCurrentShape(Shape::Code),用于按钮按下后通知画图板。注意,QActio的triggered()信号是没有参数的,因此,我们需要在QAction的槽函数中重新emit我们自己定义的信号。构造函数里面创建了两个QAction,一个是drawLineAction,一个是drawRectAction,分别用于绘制直线和矩形。MainWindow的中心组件是PainWidget,也就是我们的画图板。下面来看看PaintWidget类:
paintwidget.h
 #ifndef PAINTWIDGET_H
#ifndef PAINTWIDGET_H  #define PAINTWIDGET_H
#define PAINTWIDGET_H 
 #include <QtGui>
#include <QtGui>  #include <QDebug>
#include <QDebug>  #include "shape.h"
#include "shape.h"  #include "line.h"
#include "line.h"  #include "rect.h"
#include "rect.h" 
 class PaintWidget : public QWidget
class PaintWidget : public QWidget  {
{  Q_OBJECT
Q_OBJECT 
 public:
public:  PaintWidget(QWidget *parent = 0);
PaintWidget(QWidget *parent = 0); 
 public slots:
public slots:  void setCurrentShape(Shape::Code s)
void setCurrentShape(Shape::Code s)  {
{  if(s != currShapeCode) {
if(s != currShapeCode) {  currShapeCode = s;
currShapeCode = s;  }
}  }
} 
 protected:
protected:  void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event);
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event);  void mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
void mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event);  void mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
void mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event);  void mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
void mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event); 
 private:
private:  Shape::Code currShapeCode;
Shape::Code currShapeCode;  Shape *shape;
Shape *shape;  bool perm;
bool perm;  QList<Shape*> shapeList;
QList<Shape*> shapeList;  };
}; 
 #endif // PAINTWIDGET_H
#endif // PAINTWIDGET_H paintwidget.cpp
 #include "paintwidget.h"
#include "paintwidget.h" 
 PaintWidget::PaintWidget(QWidget *parent)
PaintWidget::PaintWidget(QWidget *parent)  : QWidget(parent), currShapeCode(Shape::Line), shape(NULL), perm(false)
: QWidget(parent), currShapeCode(Shape::Line), shape(NULL), perm(false)  {
{  setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);
setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Expanding, QSizePolicy::Expanding);  }
} 
 void PaintWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event)
void PaintWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event)  {
{  QPainter painter(this);
QPainter painter(this);  painter.setBrush(Qt::white);
painter.setBrush(Qt::white);  painter.drawRect(0, 0, size().width(), size().height());
painter.drawRect(0, 0, size().width(), size().height());  foreach(Shape * shape, shapeList) {
foreach(Shape * shape, shapeList) {  shape->paint(painter);
shape->paint(painter);  }
}  if(shape) {
if(shape) {  shape->paint(painter);
shape->paint(painter);  }
}  }
} 
 void PaintWidget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent
*event)
void PaintWidget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent
*event)  {
{  switch(currShapeCode)
switch(currShapeCode)  {
{  case Shape::Line:
case Shape::Line:  {
{  shape = new Line;
shape = new Line;  break;
break;  }
}  case Shape::Rect:
case Shape::Rect:  {
{  shape = new Rect;
shape = new Rect;  break;
break;  }
}  }
}  if(shape != NULL) {
if(shape != NULL) {  perm = false;
perm = false;  shapeList<<shape;
shapeList<<shape;  shape->setStart(event->pos());
shape->setStart(event->pos());  shape->setEnd(event->pos());
shape->setEnd(event->pos());  }
}  }
} 
 void PaintWidget::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
void PaintWidget::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event)  {
{  if(shape && !perm) {
if(shape && !perm) {  shape->setEnd(event->pos());
shape->setEnd(event->pos());  update();
update();  }
}  }
} 
 void PaintWidget::mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent
*event)
void PaintWidget::mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent
*event)  {
{  perm = true;
perm = true;  }
} PaintWidget类定义了一个slot,用于接收改变后的新的ShapeCode。最主要的是,PaintWidget重定义了三个关于鼠标的事件:mousePressEvent,mouseMoveEvent和mouseReleaseEvent。
我们来想象一下如何绘制一个图形:图形的绘制与鼠标操作息息相关。以画直线为例,首先我们需要按下鼠标,确定直线的第一个点,所以在mousePressEvent里面,我们让shape保存下start点。然后在鼠标按下的状态下移动鼠标,此时,直线就会发生变化,实际上是直线的终止点在随着鼠标移动,所以在mouseMoveEvent中我们让shape保存下end点,然后调用update()函数,这个函数会自动调用paintEvent()函数,显示出我们绘制的内容。最后,当鼠标松开时,图形绘制完毕,我们将一个标志位置为true,此时说明这个图形绘制完毕。
为了保存我们曾经画下的图形,我们使用了一个List。每次按下鼠标时,都会把图形存入这个List。可以看到,我们在paintEvent()函数中使用了foreach遍历了这个List,绘制出历史图形。foreach是Qt提供的一个宏,用于遍历集合中的元素。
最后我们来看看Shape类。
shape.h
 #ifndef SHAPE_H
#ifndef SHAPE_H  #define SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H 
 #include <QtGui>
#include <QtGui> 
 class Shape
class Shape  {
{  public:
public: 
 enum Code {
enum Code {  Line,
Line,  Rect
Rect  };
}; 
 Shape();
Shape(); 
 void setStart(QPoint s)
void setStart(QPoint s)  {
{  start = s;
start = s;  }
} 
 void setEnd(QPoint e)
void setEnd(QPoint e)  {
{  end = e;
end = e;  }
} 
 QPoint startPoint()
QPoint startPoint()  {
{  return start;
return start;  }
} 
 QPoint endPoint()
QPoint endPoint()  {
{  return end;
return end;  }
} 
 void virtual paint(QPainter
& painter) = 0;
void virtual paint(QPainter
& painter) = 0; 
 protected:
protected:  QPoint start;
QPoint start;  QPoint end;
QPoint end;  };
}; 
 #endif // SHAPE_H
#endif // SHAPE_H shape.cpp
 #include "shape.h"
#include "shape.h" 
 Shape::Shape()
Shape::Shape()  {
{  }
} Shape类最重要的就是保存了start和end两个点。为什么只要这两个点呢?因为我们要绘制的是直线和矩形。对于直线来说,有了两个点就可以确定这条直线,对于矩形来说,有了两个点作为左上角的点和右下角的点也可以确定这个矩形,因此我们只要保存两个点,就足够保存这两种图形的位置和大小的信息。paint()函数是Shape类的一个纯虚函数,子类都必须实现这个函数。我们现在有两个子类:Line和Rect,分别定义如下:
line.h
 #ifndef LINE_H
#ifndef LINE_H  #define LINE_H
#define LINE_H 
 #include "shape.h"
#include "shape.h" 
 class Line : public Shape
class Line : public Shape  {
{  public:
public:  Line();
Line(); 
 void paint(QPainter &painter);
void paint(QPainter &painter);  };
}; 
 #endif // LINE_H
#endif // LINE_H line.cpp
 #include "line.h"
#include "line.h" 
 Line::Line()
Line::Line()  {
{  }
} 
 void Line::paint(QPainter &painter)
void Line::paint(QPainter &painter)  {
{  painter.drawLine(start, end);
painter.drawLine(start, end);  }
} rect.h
 #ifndef RECT_H
#ifndef RECT_H  #define RECT_H
#define RECT_H 
 #include "shape.h"
#include "shape.h" 
 class Rect : public Shape
class Rect : public Shape  {
{  public:
public:  Rect();
Rect(); 
 void paint(QPainter &painter);
void paint(QPainter &painter);  };
}; 
 #endif // RECT_H
#endif // RECT_H rect.cpp
 #include "rect.h"
#include "rect.h" 
 Rect::Rect()
Rect::Rect()  {
{  }
} 
 void Rect::paint(QPainter &painter)
void Rect::paint(QPainter &painter)  {
{  painter.drawRect(start.x(), start.y(),
painter.drawRect(start.x(), start.y(),  end.x() - start.x(), end.y() - start.y());
end.x() - start.x(), end.y() - start.y());  }
} 使用paint()函数,根据两个点的数据,Line和Rect都可以绘制出它们自身来。此时就可以看出,我们之所以要建立一个Shape作为父类,因为这两个类有几乎完全相似的数据对象,并且从语义上来说,Line、Rect与Shape也完全是一个is-a的关系。如果你想要添加颜色等的信息,完全可以在Shape类进行记录。这也就是类层次结构的好处。