经过前面两篇文章的介绍,相信大家对Boo的一些基本特性有所了解,本文着重介绍Boo深层次的知识以及其在AOP中的实现。
在开始之前先给大家做些准备:
一、Boo Parser
目前Boo的编译器使用C#实现,用ANTLR进行解析。
Compiler Steps
Pipelines consist of a set of steps that the compiler passes the code through. The source code for all the steps is here.
The order of steps when you compile a script is like this:
1.First the Boo Parser (and lexer): Boo.Lang.Parser.BooParsingStep.
1.The rules the Boo parser uses are defined in this ANTLR grammar file
2.The boo lexer turns the text script into a set of tokens, and the boo parser converts the tokens into an abstract syntax tree (AST). I'll show examples of this later on. Each step after the parser is basically just working on this AST and transforming it. At the end, the AST is used to produce raw .NET assembly code (IL). The steps that happen after the parser step:
2.InitializeTypeSystemServices
3.PreErrorChecking
4.InitializeNameResolutionService
5.IntroduceGlobalNamespaces
6.TransformCallableDefinitions
7.BindTypeDefinitions
8.[BindNamespaces]
9.BindBaseTypes
10.BindAndApplyAttributes
11.ExpandMacros
12.IntroduceModuleClasses
13.NormalizeStatementModifiers
14.[NormalizeTypeAndMemberDefinitions]
15.BindTypeDefinitions
16.BindBaseTypes
17.ResolveTypeReferences
18.BindTypeMembers
19.[ProcessInheritedAbstractMembers]
20.ProcessMethodBodiesWithDuckTyping
21.[ProcessAssignmentsToValueTypeMembers]
22.[ExpandProperties]
23.[StricterErrorChecking]
24.[RemoveDeadCode]
25.NormalizeIterationStatements
26.ProcessSharedLocals
27.ProcessClosures
28.ProcessGenerators
29.InjectCallableConversions
30.[ImplementICallableOnCallableDefinitions]
31.[EmitAssembly]
32.and finally [SaveAssembly] or [RunAssembly]
二、Boo.Lang.Compiler.AbstractAstAttribute与Boo.Lang.Compiler.AbstractAstMacro
继承体系如下:
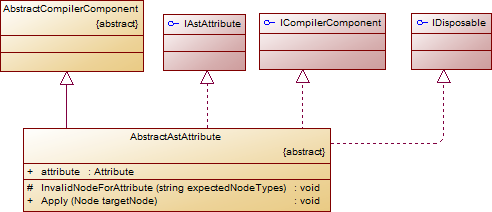
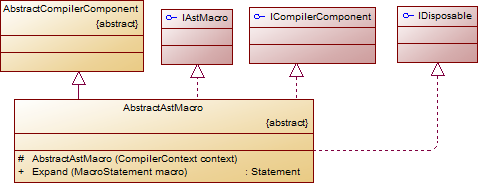
public abstract class Node : ICloneable { // Fields protected Node _parent; ...... // Mothods public abstract void Accept(IAstVisitor visitor); public abstract object Clone(); public Node CloneNode(); public TAncestor GetAncestor<TAncestor>() where TAncestor: Node; public Node GetAncestor(NodeType ancestorType); public Node GetAncestor(NodeType ancestorType, int limitDepth); public IEnumerable<TAncestor> GetAncestors<TAncestor>() where TAncestor: Node; public virtual bool Replace(Node existing, Node newNode); public int ReplaceNodes(Node pattern, Node template); public int ReplaceNodes(NodePredicate predicate, Node template); public string ToCodeString(); public override string ToString(); ...... // Properties public abstract NodeType NodeType {get;} public Node ParentNode {get;} ...... }
在前一篇文章我们看到:
class AssignFieldsMacro(AbstractAstMacro): override def Expand(macro as MacroStatement): # ctor = (macro.ParentNode.ParentNode as Constructor) ctor = macro.GetAncestor(NodeType.Constructor) as Constructor b = Block() for param in ctor.Parameters: assign = BinaryExpression(BinaryOperatorType.Assign, ReferenceExpression("_" + param.Name), ReferenceExpression(param.Name)) b.Add(assign) return b
class Customer: [property(Name)] private _name as string def constructor(name as string): AssignFields #autoAssign
上述Macro会在编译阶段将Customer构造函数的代码扩展为:
def constructor(name as string): self._name = name
[注]:
目前在Boo 0.91下可以有更简洁的写法:
macro autoAssign: ctor = autoAssign.GetAncestor(NodeType.Constructor) as Constructor b = Block() for param in ctor.Parameters: assign = BinaryExpression(BinaryOperatorType.Assign, ReferenceExpression("_" + param.Name), ReferenceExpression(param.Name)) b.Add(assign) return b
三、DepthFirstVisitor与DepthFirstTransformer
它们都继承于IAstVisitor。
1、DepthFirstVisitor访问AST中的所有节点,但是不会对AST进行修改操作。请看下面这个例子:
class CaptureReferences(DepthFirstVisitor): [getter(Found)] _found = [] def constructor(node as Node): node.Accept(self) override def OnReferenceExpression(reference as ReferenceExpression): _found.Add(reference)
上例就是通过DepthFirstVisitor提供的OnReferenceExpression方法获取所用到的ReferenceExpression,具体使用如下:
expression = BinaryExpression( BinaryOperatorType.Division, BinaryExpression( BinaryOperatorType.Subtraction, ReferenceExpression("x"), IntegerLiteralExpression(3)), ReferenceExpression("t")) print expression.ToCodeString() // (x-3)/t references = CaptureReferences(expression).Found print join(references) // x t
2、DepthFirstTransformer访问AST中的所有节点,并可以对AST进行添加与删除操作。通常在自定义的Macro与Attribute中,会需要对当前的AST进行修改以根据要求产生相应的AST,这时就会用到DepthFirstTransformer提供的RemoveCurrentNode,ReplaceCurrentNode等方法。请看下面这个例子:
class WithMacro(AbstractAstMacro): private class NameExpander(DepthFirstTransformer): _inst as ReferenceExpression def constructor(inst as ReferenceExpression): _inst = inst override def OnReferenceExpression(node as ReferenceExpression): // if the name of the reference begins with '_' // then convert the reference to a member reference // of the provided instance if node.Name.StartsWith('_'): // create the new member reference and set it up mre = MemberReferenceExpression(node.LexicalInfo) mre.Name = node.Name[1:] mre.Target = _inst.CloneNode() // replace the original reference in the AST // with the new member-reference ReplaceCurrentNode(mre) override def Expand(macro as MacroStatement) as Statement: assert 1 == macro.Arguments.Count assert macro.Arguments[0] isa ReferenceExpression inst = macro.Arguments[0] as ReferenceExpression // convert all _<ref> to inst.<ref> block = macro.Body ne = NameExpander(inst) ne.Visit(block) return block
class Example: public Name as string public Content as string def DoSomething([default('hello')]cstr as string): print cstr.ToUpper()
ex = Example() with ex: _Name = "hans" _Content = "test" _DoSomething('hello world') print ex.Name,ex.Content
[注]:
目前在Boo 0.91下可以有更简洁的写法:
macro with(target, body as Expression*): for expression in body: match expression: case BinaryExpression(Left: mre = MemberReferenceExpression(Target: OmittedExpression())): mre.Target = target case MethodInvocationExpression(Target: mre = MemberReferenceExpression(Target: OmittedExpression())): mre.Target = target yield
with ex: .Name = "hans" .Content = "test" .DoSomething('hello world')
可以看到上述的with使用方法更为大家所熟悉。
四、Boo与AOP
为了建立松散耦合的、可扩展的企业系统,AOP应用到的横切技术,通常分为动态横切和静态横切两种类型。
静态横切和动态横切的区别在于它不修改一个给定对象的执行行为。相反,它允许通过引入附加的方法字段和属性来修改对象的结构。
此外,静态横切可以把扩展和实现附加到对象的基本结构中。
通过前面的介绍,我们知道了Boo有着强大的编译器扩展功能,可以通过AbstractAstAttribute与AbstractAstMacro很容易进行AOP的静态横切。
1、<在.Net中关于AOP的实现>中的”设计一个计算器,它能提供加法和减法功能。”例子可以简单通过如下的Boo代码实现:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)] class LogAttribute(AbstractAstAttribute): def constructor(): pass override def Apply(node as Node): method as Method = node // Before expression = cast(ReturnStatement, method.Body.Statements[-1]).Expression match expression: case [| $left+$right |]: code = [| print "${$(method.Name)}(${$left},${$right})" |] case [| $left-$right |]: code = [| print "${$(method.Name)}(${$left},${$right})" |] otherwise: code = [| print "${$(method.Name)}" |] // Body tmp = AstUtil.CreateReferenceExpression("__${method.Name}__") tbody = [| block: $tmp = $expression // After print "Result is ${$tmp}" print "After ${$(method.Name)} at ${date.Now}" return $tmp |].Body method.Replace(method.Body,tbody) method.Body.Insert(0, code)
class Calculator: """ Description of Calculator 核心关注点是加法和减法,而通用业务-横切关注点则是日志功能. """ def constructor(): pass [log] def Add(x as int, y as int): return x+y [log] def Substract(x as int, y as int): return x-y calc = Calculator() calc.Add(2,10)
2、<在.Net中关于AOP的实现(补遗)>中“一个已经实现了收发邮件的类Mail。然而它并没有实现地址验证的功能。”例子,利用Boo可以将IValidatable接口织入到原有的Mail类中,这是一种非常形象的introduce功能:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)] class ValidatableAttribute(AbstractAstAttribute): def constructor(): pass override def Apply(node as Node): classDef as ClassDefinition = node classDef.BaseTypes.Add(SimpleTypeReference("Examples.IValidatable")) AddMethod(classDef) def AddMethod(classDef as ClassDefinition): validator = Method() # fields = FindField(classDef) # field as Field = fields[0] validator.Name = "ValidateAddress" code = [| if string.IsNullOrEmpty($(ReferenceExpression('_mail'))): return false return true |] validator.Body.Add(code) classDef.Members.Add(validator)
[validatable] class Mail: """Description of Mail""" [property(Email)] _mail as string def constructor(): pass def constructor(mail as string): _mail = mail def Send(): pass def Receive(): pass interface IValidatable: def ValidateAddress() as bool: pass
mail = Mail("test@gmail.com")
print mail.Email
mail.ValidateAddress()
当然,上面的两个例子还相当不完善,只是向大家展示了Boo在AOP方面的优势,更好的实现需要大家自己去学习了解。
参考:
http://boo.codehaus.org/Type+System
http://boo.codehaus.org/Compiler+Steps
http://tore.vestues.no/2008/12/27/the-boo-extensibility-tutorials/
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-aopsc/
http://www.cnblogs.com/wayfarer/articles/233212.html