2018-10-06 22:04:38
问题描述:

问题求解:
对于边没有权重的最短路径的求解,首选的方案是bfs。
本题要求是求遍历所有节点的最短路径,由于本题中是没有要求一个节点只能访问一次的,也就是说可以访问一个节点多次,但是如果表征两次节点状态呢?可以使用(curNode, VisitedNode)来进行表征,如果两次的已经访问的节点相同那么就没有必要再进行访问了,最终的状态就是所有节点都访问过了。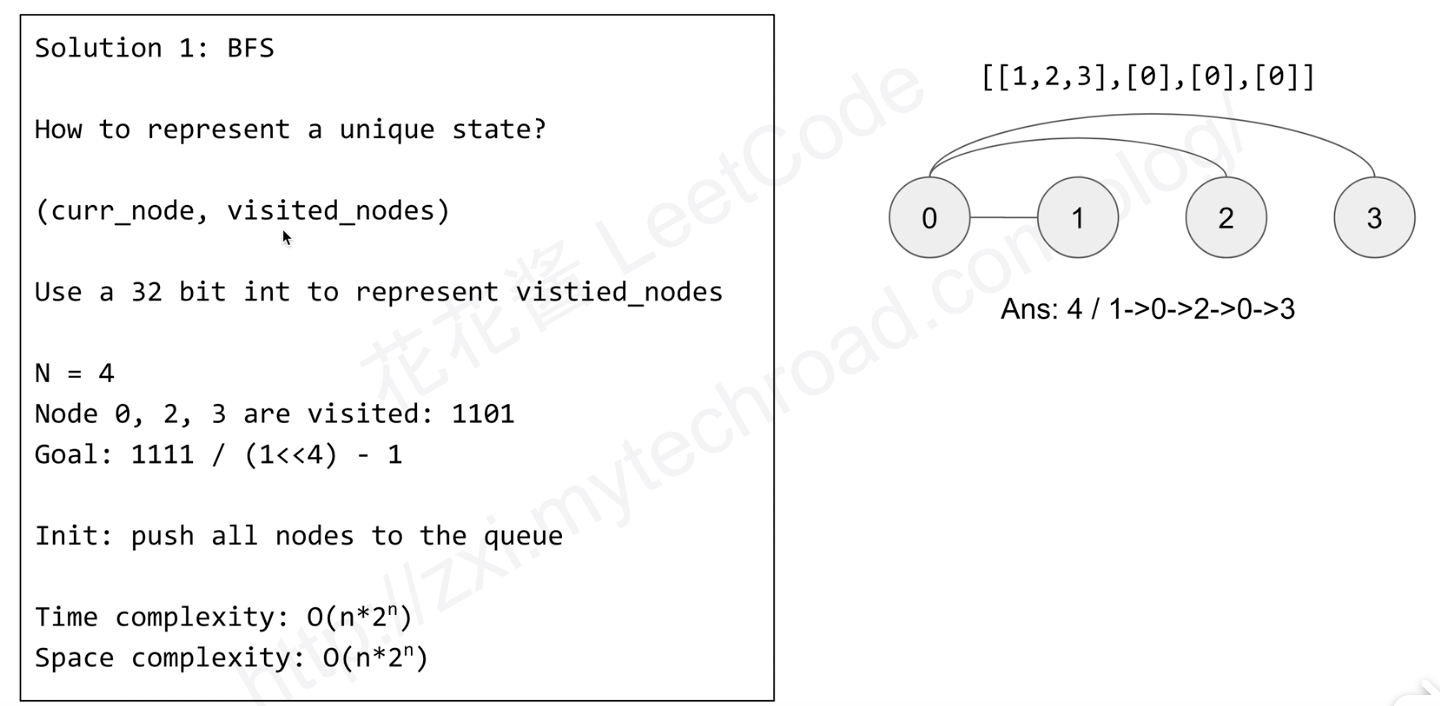
另外,由于起点对结果是有影响的,因此在最开始需要将所有的节点都压栈。
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
int target = (1 << n) - 1;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
q.add(i << 16 | 1 << i);
seen.add(i << 16 | 1 << i);
}
int step = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int cur = q.poll();
int node = cur >> 16;
int state = cur & 0xffff;
if (state == target) return step;
for (int next : graph[node]) {
int newstate = state | 1 << next;
if (seen.contains(next << 16 | newstate)) continue;
q.add(next << 16 | newstate);
seen.add(next << 16 | newstate);
}
}
step += 1;
}
return -1;
}
扩展:
- 864. Shortest Path to Get All Keys
问题描述:

问题求解:
给一个BFS模版。

public int shortestPathAllKeys(String[] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length();
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
int target = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
char c = grid[i].charAt(j);
if (c == '@') {
q.add(i << 16 | j << 8);
seen.add(i << 16 | j << 8);
}
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f') target |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
}
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int step = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int cur = q.poll();
int x = cur >> 16;
int y = cur >> 8 & 0xFF;
int key = cur & 0xFF;
if (key == target) return step;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
int nkey = key;
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
char c = grid[nx].charAt(ny);
if (c == '#') continue;
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F' && ((key & (1 << (c - 'A'))) == 0)) continue;
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f') nkey = key | (1 << (c - 'a'));
int newstate = nx << 16 | ny << 8 | nkey;
if (seen.contains(newstate)) continue;
q.add(newstate);
seen.add(newstate);
}
}
step += 1;
}
return -1;
}