大多数的 Spark 操作可以用在任意类型的 RDD 上, 但是有一些比较特殊的操作只能用在key-value类型的 RDD 上.
这些特殊操作大多都涉及到 shuffle 操作, 比如: 按照 key 分组(group), 聚集(aggregate)等.
在 Spark 中, 这些操作在包含对偶类型(Tuple2)的 RDD 上自动可用(通过隐式转换).
object RDD {
implicit def rddToPairRDDFunctions[K, V](rdd: RDD[(K, V)])
(implicit kt: ClassTag[K], vt: ClassTag[V], ord: Ordering[K] = null): PairRDDFunctions[K, V] = {
new PairRDDFunctions(rdd)
}
键值对的操作是定义在PairRDDFunctions类上, 这个类是对RDD[(K, V)]的装饰.
1、partitionBy
作用: 对pairRDD 进行分区操作,如果原有的 partionRDD 的分区器和传入的分区器相同, 则返回原pairRDD,否则会生成 ShuffleRDD,即会产生 shuffle过程
def partitionBy(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
if (self.partitioner == Some(partitioner)) {
self
} else {
new ShuffledRDD[K, V, V](self, partitioner)
}
}
scala> val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "a"), (2, "b"), (3, "c"), (4, "d")))
scala> rdd1.partitions.length
res1: Int = 2
scala> rdd1.partitionBy(new org.apache.spark.HashPartitioner(3)).partitions.length
res3: Int = 3
2、reduceByKey(func,[numTasks])
作用: 在一个(K,V)的 RDD 上调用,返回一个(K,V)的 RDD,使用指定的reduce函数,将相同key的value聚合到一起,reduce任务的个数可以通过第二个可选的参数来设置。
scala> val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(List(("female",1),("male",5),("female",5)("male",2)))
scala> rdd1.reduceByKey(_ + _)
scala> res1.collect
res2: Array[(String, Int)] = Array((female,6), (male,7))
3、groupByKey()
作用: 按照key进行分组.
scala> val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array("hello", "world", "h", "hello", "are", "go"))
scala> val rdd2 = rdd1.map((_, 1))
rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Int)] = MapPartitionsRDD[3] at map at <console>:26
scala> rdd2.groupByKey()
res3: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = ShuffledRDD[4] at groupByKey at <console>:29
scala> res3.collect
res4: Array[(String, Iterable[Int])] = Array((are,CompactBuffer(1)), (hello,CompactBuffer(1, 1)), (go,CompactBuffer(1)), (h,CompactBuffer(1)), (world,CompactBuffer(1)))
scala> res3.map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum))
res5: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Int)] = MapPartitionsRDD[5] at map at <console>:31
scala> res5.collect
res7: Array[(String, Int)] = Array((are,1), (hello,2), (go,1), (h,1), (world,1))
注意:
(1)基于当前的实现, groupByKey必须在内存中持有所有的键值对 . 如果一个key有太多的value, 则会导致内存溢出(OutOfMemoryError)
(2)所以这操作非常耗资源, 如果分组的目的是为了在每个key上执行聚合操作(比如: sum 和 average), 则应该使用PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey 或者PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey, 因为他们有更好的性能(会先在分区进行预聚合)
4、reduceByKey和groupByKey的区别
(1)reduceByKey:按照Key进行聚合,在Shuffle之前有combine(预聚合)操作,返回结果是RDD[k,v]
def reduceByKey(partitioner: Partitioner, func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => v, func, func, partitioner)
}
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true,
serializer: Serializer = null)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
require(mergeCombiners != null, "mergeCombiners must be defined") // required as of Spark 0.9.0
if (keyClass.isArray) {
if (mapSideCombine) {
throw new SparkException("Cannot use map-side combining with array keys.")
}
if (partitioner.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioner]) {
throw new SparkException("HashPartitioner cannot partition array keys.")
}
}
val aggregator = new Aggregator[K, V, C](
self.context.clean(createCombiner),
self.context.clean(mergeValue),
self.context.clean(mergeCombiners))
if (self.partitioner == Some(partitioner)) {
self.mapPartitions(iter => {
val context = TaskContext.get()
new InterruptibleIterator(context, aggregator.combineValuesByKey(iter, context))
}, preservesPartitioning = true)
} else {
new ShuffledRDD[K, V, C](self, partitioner)
.setSerializer(serializer)
.setAggregator(aggregator)
.setMapSideCombine(mapSideCombine)
}
}
(2)groupByKey:按照key进行分组,直接进行shuffle。
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}
5、aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numTasks])
函数声明:
/**
* Aggregate the values of each key, using given combine functions and a neutral "zero value".
* This function can return a different result type, U, than the type of the values in this RDD,
* V. Thus, we need one operation for merging a V into a U and one operation for merging two U's,
* as in scala.TraversableOnce. The former operation is used for merging values within a
* partition, and the latter is used for merging values between partitions. To avoid memory
* allocation, both of these functions are allowed to modify and return their first argument
* instead of creating a new U.
*/
def aggregateByKey[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U)(seqOp: (U, V) => U,
combOp: (U, U) => U): RDD[(K, U)] = self.withScope {
aggregateByKey(zeroValue, defaultPartitioner(self))(seqOp, combOp)
}
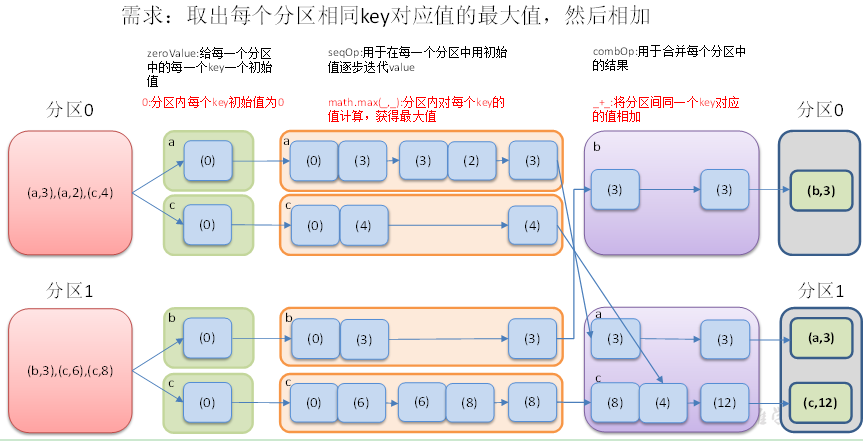
使用给定的 combine 函数和一个初始化的zero value, 对每个key的value进行聚合.
这个函数返回的类型U不同于源 RDD 中的V类型. U的类型是由初始化的zero value来定的. 所以, 我们需要两个操作: -
一个操作(seqOp)去把 1 个v变成 1 个U - 另外一个操作(combOp)来合并 2 个U
一个操作用于在一个分区进行合并, 第二个操作用在两个分区间进行合并.
为了避免内存分配, 这两个操作函数都允许返回第一个参数, 而不用创建一个新的U
(1) eroValue:给每一个分区中的每一个key一个初始值;
(2)seqOp:函数用于在每一个分区中用初始值逐步迭代value;
(3)combOp:函数用于合并每个分区中的结果。
创建一个 pairRDD,取出每个分区相同key对应值的最大值,然后相加
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Author z
* Date 2019-12-09 15:39:08
*/
object AggregateByKey {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("MySqlRead").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd = sc.parallelize(List(("a", 3), ("a", 2), ("c", 4), ("b", 3), ("c", 6), ("c", 8)), 2)
/* val rdd2 = rdd.aggregateByKey((Int.MinValue, Int.MaxValue))(
(x, y) => (x._1.max(y), x._2.min(y)),
(x, y) => (x._1 + y._1, x._2 + x._2)
)*/
val rdd2 = rdd.aggregateByKey((Int.MinValue, Int.MaxValue))(
{ //分区内相同key的(最大值,最小值)
case (kv, e) => (kv._1.max(e), kv._2.min(e))
},
{ //两个分区间数据的合并
case (kv1, kv2) => (kv1._1 + kv2._1, kv1._2 + kv2._2)
}
)
// 计算出来每个key对应的值的平均值!!
/* val rdd2=rdd.aggregateByKey((0, 0))(
{ //(sum,count)即为zero value,每个key
case ((sum, count), e) => (sum + e, count + 1)
},
{
case ((sum1,count1),(sum2,count2)) => (sum1 + sum2, count1 + count2)
}
)*/
//val rdd3 = rdd2.mapValues(kv => kv._1.toDouble / kv._2)
rdd2.collect().foreach(println)
}
}
6、foldByKey
参数: (zeroValue:V)(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
作用:aggregateByKey的简化操作,seqop和combop相同
object FoldLeft {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("FoldLeft").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd= sc.parallelize(Array(("c","3"), ("c","2"), ("c","4"), ("c","3"), ("c","6"), ("c","8")), 3)
// foldByKey来说, 0值, 每个分区内用一次. 重点: 分区间合并的时候, 零值不参与
val res = rdd.foldByKey("-")(_ + _)
res.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
7、combineByKey
def combineByKey[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners,
partitioner, mapSideCombine, serializer)(null)
}
作用: 针对每个K, 将V进行合并成C, 得到RDD[(K,C)]
参数描述:
(1)createCombiner: combineByKey会遍历分区中的每个key-value对. 如果第一次碰到这个key, 则调用createCombiner函数,传入value, 得到一个C类型的值.(如果不是第一次碰到这个 key, 则不会调用这个方法)
(2)mergeValue: 如果不是第一个遇到这个key, 则调用这个函数进行合并操作. 分区内合并
(3)mergeCombiners 跨分区合并相同的key的值(C). 跨分区合并
创建一个 pairRDD,根据 key 计算每种 key 的value的平均值。(先计算每个key出现的次数以及可以对应值的总和,再相除得到结果

object CombineByKey {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("MySqlRead").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(("a", 88), ("b", 95), ("a", 91), ("b", 93), ("a", 95), ("b", 98)), 2)
val rdd2:RDD[(String,(Int,Int))] = rdd.combineByKey(
(_, 1),
{
case ((sum: Int, count: Int), e:Int) => (sum + e, count + 1)
},
{
case ((sum1: Int, count1: Int), (sum2:Int, count2:Int)) => (sum1 + sum2, count1 + count2)
}
)
val rdd3 = rdd2.mapValues {
case (sum, count) => (sum, count, sum.toDouble / count)
}
rdd3.collect.foreach(println)
}
}
8、sortByKey
作用: 在一个(K,V)的 RDD 上调用, K必须实现 Ordered[K] 接口(或者有一个隐式值: Ordering[K]), 返回一个按照key进行排序的(K,V)的 RDD
object SorkByKey {
//1. 冥界召唤,需要样例类
/* implicit val ord = new Ordering[User]{
override def compare(x: User, y: User): Int = x.age - y.age
}
*/
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SorkByKey").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
// val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "a"), (10, "b"), (11, "c"), (4, "d"), (20, "d"), (10, "e")))
// val res: RDD[(Int, String)] = rdd.sortByKey(ascending = false, numPartitions = 10)
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(User(10, "a"), User(8, "c"), User(12, "b"))).map((_, 1))
val res: RDD[(User, Int)] = rdd.sortByKey()
res.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
//
//case class User(id:Int,name:String)
//2. 继承 Ordered
case class User(age: Int, name:String) extends Ordered[User] {
override def compare(that: User): Int = this.age - that.age
}
9、mapValues
作用: 针对(K,V)形式的类型只对V进行操作
scala> val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "a"), (10, "b"), (11, "c"), (4, "d"), (20, "d"), (10, "e")))
scala> rdd.mapValues("<" + _ + ">").collect
res29: Array[(Int, String)] = Array((1,<a>), (10,<b>), (11,<c>), (4,<d>), (20,<d>), (10,<e>))
10、join(otherDataSet,[numTasks])
内连接:在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的 RDD 上调用,返回一个相同 key 对应的所有元素对在一起的(K,(V,W))的RDD
object Join {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Join").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
var rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "a"), (1, "b"), (2, "c"), (4, "d")))
var rdd2 = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "aa"),(1, "bb"), (3, "bb"), (2, "cc")), 3)
// 内连接
// val res: RDD[(Int, (String, String))] = rdd1.join(rdd2)
// var res = rdd1.leftOuterJoin(rdd2)
// val res: RDD[(Int, (Option[String], String))] = rdd1.rightOuterJoin(rdd2)
val res = rdd1.rightOuterJoin(rdd2)
println(res.partitions.length)
res.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
(1) 如果某一个 RDD 有重复的 Key, 则会分别与另外一个 RDD 的相同的 Key进行组合.
(2)也支持外连接: leftOuterJoin,rightOuterJoin, fullOuterJoin.
11、cogroup(otherDataSet,[numTasks])
作用:在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的 RDD 上调用,返回一个(K,(Iterable<V>,Iterable<W>))类型的 RDD
object Cogroup {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Cogroup").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array((1, 10), (2, 20), (1, 100), (3, 30)), 1)
val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(Array((1, "a"), (2, "b"), (1, "aa"), (3, "c")), 1)
val res: RDD[(Int, (Iterable[Int], Iterable[String]))] = rdd1.cogroup(rdd2)
res.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
(1,(CompactBuffer(10, 100),CompactBuffer(a, aa)))
(3,(CompactBuffer(30),CompactBuffer(c)))
(2,(CompactBuffer(20),CompactBuffer(b)))