本文的学习来自技术胖大神的教程:https://jspang.com/
1第一个实例--用vuex实现数据的共享
新建一个vuextest的项目:vue init webpack 项目名
安装vuex:
npm install vuex --save
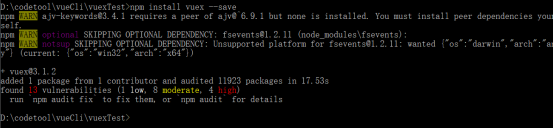
新建一个vuex文件夹,在文件夹下新建store.js文件,文件中引入vue和vuex。
增加一个常量对象。
用export default 封装代码,让外部可以引用。


在components文件夹下新建count.vue。在模板中引入store.js文件,并在模板中用$store.state.count输出count 的值。

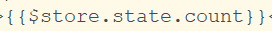
然后在store.js文件中加入两个改变state的方法。

完整代码:
router/index.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' import Count from '@/components/count' Vue.use(Router) export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: '/', name: 'HelloWorld', component: HelloWorld }, { path: '/count', name: 'count', component: Count } ] })
vuex/store.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) const state={ count:1 } const mutations={ add(state){ state.count++; }, reduce(state){ state.count--; } } export default new Vuex.Store({ state,mutations })
count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr />
<h3>{{$store.state.count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="$store.commit('add')">+</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('reduce')">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
2 state访问状态对象
const state 就是访问状态对象,它就是SPA(单页应用程序)中的共享值。
把stroe.js中的值,赋值给模板里data中的值有三种赋值方式:
1)通过computed的计算属性直接赋值
computed:{ count(){ return this.$store.state.count } }
2)通过mapState的对象来赋值
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
computed:mapState({
count:state=>state.count
})
3)通过mapState的数组来赋值
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
computed:mapState(['count'])
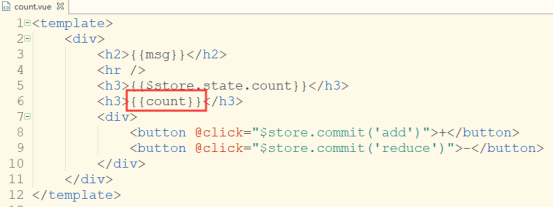
完整代码:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr />
<h3>{{$store.state.count}}</h3>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="$store.commit('add')">+</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('reduce')">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store,
//第一种方式
/*computed:{
count(){
return this.$store.state.count
}
}*/
//第二种方式
/*computed:mapState({
count:state=>state.count
})*/
//第三种方式
computed:mapState(['count'])
}
</script>
<style>
</style>

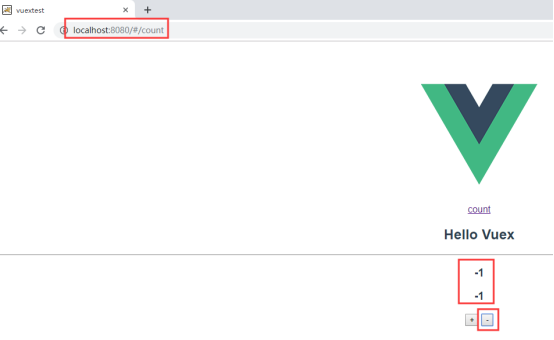
3 Mutations修改状态
上面的例子中,定义的mutations就是改变状态,

mutations这个单词的意思是“突变”。里面定义的两个方法就是为了改变state中的count的状态。
也就是说,mutations存在的意义就是要写方法来改变数据的状态。
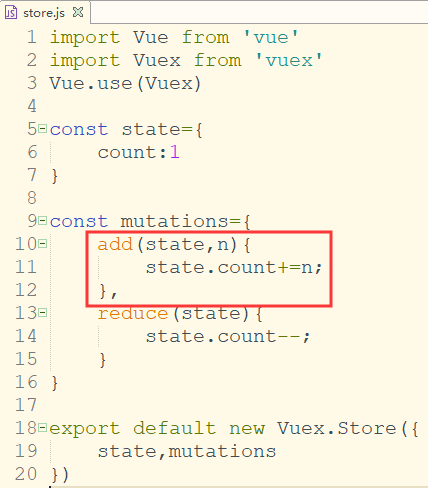
实际开发中,不会这么简单,可能会涉及到传值,
例:修改add方法,每次加10
add(state,n){ state.count+=n; },
方法调用时:
<button @click="$store.commit('add',10)">+</button>
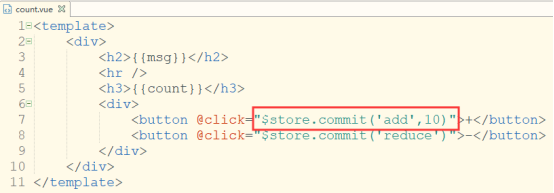
add中的参数,第一个可以理解为默认的,就是要操作的数据,后面的参数需要在方法调用时传入,
$store.commit的参数,第一个是方法名,后面的是要传入的参数。
这里有点别扭,需要特殊记一下。
$store.commit这种方式很繁琐,可以简化:
引入mapMutations,然后在methods中把add和reduce传进去。
count.vue完整代码:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr />
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="add(10)">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store,
computed:mapState(['count']),
methods:mapMutations(['add','reduce'])
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
4 getters计算过滤操作
getters相当于在vuex中的computed。每操作一次数据,都会经过getters过滤一遍,相当于一个“安检”。
例:
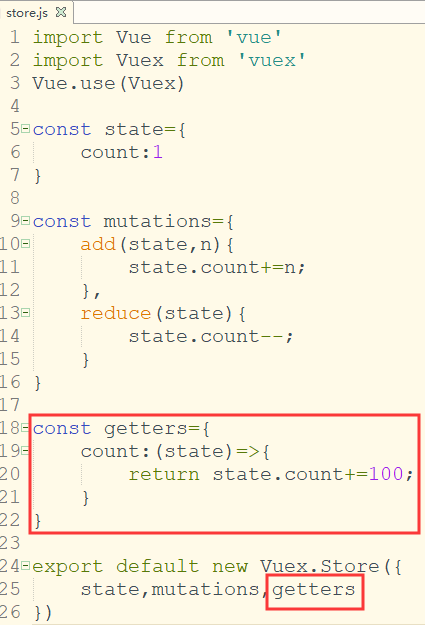
在store.js声明getters:
const getters={ count:(state)=>{ return state.count+=100; } }
并引入:
模板中也是写到computed中,但是已经有一个mapState(['count'])了,所以需要用到扩展运算符...
computed:{ ...mapState(['count']), count(){ return this.$store.getters.count; } },
最好简写:
引入mapGetters,然后...mapGetters(['count'])
完整代码:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr/>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="add(10)">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store,
computed:{
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['count'])
},
methods:mapMutations(['add','reduce'])
}
</script>
<style>
</style>

5 Actions异步状态
Mutations是同步修改状态,Actions是异步的,
在store.js中定义一个actions,写两个方法,传入的参数是context,叫上下文对象,就相当于store.js这个文件。用context调用mutations中的add方法,再写reduceAction方法,传一个commit对象,然后用commit调用reduce方法。然后在模板中写methods。
完整代码:
store.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) const state={ count:1 } const mutations={ add(state,n){ state.count+=n; }, reduce(state){ state.count--; } } const getters={ count:(state)=>{ return state.count+=100; } } const actions={ addAction(context){ context.commit('add',10); }, reduceAction({commit}){ commit('reduce'); } } export default new Vuex.Store({ state,mutations,getters,actions })
count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr/>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="add(10)">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
<div>
<button @click="addAction">+</button>
<button @click="reduceAction">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store,
computed:{
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['count'])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add','reduce']),
...mapActions(['addAction','reduceAction'])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
为了体现出异步,在actions中写一个延迟,然后在settimeout后面写一些代码,如果后面的代码先执行了,就说明是异步的。
addAction(context){ context.commit('add',10); setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('reduce'); },5000); console.log('这里打印了说明是异步的'); },

6 vuex模块组
如果项目不是特别的复杂,不建议用模块组。
声明模块组,然后修改原来 Vuex.Stroe里的值。在模板中用插值的形式写入。如果想用简单的方法引入,在计算属性中rutrun状态。
完整代码:
store.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) const state={ count:1 } const mutations={ add(state,n){ state.count+=n; }, reduce(state){ state.count--; } } const getters={ count:(state)=>{ return state.count+=100; } } const actions={ addAction(context){ context.commit('add',10); setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('reduce'); },5000); console.log('这里打印了说明是异步的'); }, reduceAction({commit}){ commit('reduce'); } } const moduleA={ state,mutations,getters,actions } export default new Vuex.Store({ modules:{a:moduleA} })
count.vue:
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr/>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<h3>{{$store.state.a.count}}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="add(10)">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<button @click="addAction">+</button>
<button @click="reduceAction">-</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/vuex/store'
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello Vuex'
}
},
store,
computed:{
count(){
return this.$store.state.a.count;
}
},
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add','reduce']),
...mapActions(['addAction','reduceAction'])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
vuex总结:
实际项目中登录状态、访问状态都需要用到vuex来管理状态。但是不要过度使用,能用参数传递时还是用参数传递。如果一个数据在很多地方都要用到,而且要管理状态,再用vuex。