题意:给定一张n*m的方格,起点在左上角,只能向下或向右走,地图中有k个地雷,人不能走到地雷上,问可能到达的点有多少。
很明显,这道题的数据很大,我们直接处理整张图肯定不行,而k很小,所以我们得从地雷入手,求哪些点走不到。
而因为我们的人只能向下向右,所以当一个点本身为地雷且(x-1,y+1)也有地雷,那说明这两点包夹的那个点也走不到,如图:
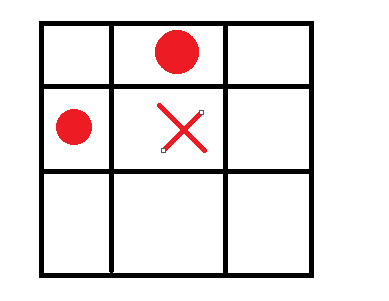
圆圈为给出的地雷位置,叉叉是实际上同样走不到的点。
那么我们不妨对地雷的位置按照行优先排序,对于每一行的地雷,我们只需要知道上一行从(x-1,y+1)开始有连续的多少个地雷,就能求出在这一行中对应的地雷会产生多少无法到达的点。这时不难想到要用线段树来维护。
注意因为x=0与y=0处默认是无法到达的,所以我们可以通过将线段树初值设为1(无法到达)来解决x=0,通过加入n-1个点(k,0)来解决m=0的点。
这里(1,0)是没有必要加入的,因为不可能与输入的地雷产生互动,记得在计算答案时减掉即可。
下附代码:

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define ll long long 3 using namespace std; 4 ll n,m,k; 5 struct seg_tree{ 6 #define p2 (p<<1) 7 #define p3 ((p<<1)|1) 8 ll tr[400005],lz[400005]; 9 void build(int l,int r,int p){ 10 if(l==r){ 11 tr[p]=1; 12 lz[p]=-1; 13 return ; 14 } 15 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 16 build(l,mid,p2); 17 build(mid+1,r,p3); 18 tr[p]=tr[p2]+tr[p3]; 19 lz[p]=-1; 20 } 21 void push_down(int l,int r,int p){ 22 if(lz[p]!=-1){ 23 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 24 tr[p2]=lz[p]*(mid-l+1); 25 tr[p3]=lz[p]*(r-mid); 26 lz[p2]=lz[p3]=lz[p]; 27 lz[p]=-1; 28 } 29 } 30 void update(int l,int r,int le,int ri,int p,int val){ 31 if (l==le && ri==r){ 32 tr[p]=val*(r-l+1); 33 lz[p]=val; 34 return ; 35 } 36 if(lz[p]!=-1) push_down(l,r,p); 37 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 38 if(ri<=mid) update(l,mid,le,ri,p2,val); 39 else if(le>mid) update(mid+1,r,le,ri,p3,val); 40 else update(l,mid,le,mid,p2,val),update(mid+1,r,mid+1,ri,p3,val); 41 tr[p]=tr[p2]+tr[p3]; 42 } 43 ll query(int l,int r,int le,int ri,int p){ 44 if(l==le && r==ri && tr[p]==r-l+1) 45 return tr[p]; 46 if (l==r) return 0; 47 if(lz[p]!=-1) push_down(l,r,p); 48 int mid=(l+r)>>1,ret=0; 49 if (ri<=mid) ret=query(l,mid,le,ri,p2); 50 else if (le>mid) ret=query(mid+1,r,le,ri,p3); 51 else { 52 int q1=query(l,mid,le,mid,p2); 53 if (q1==(mid-le+1)) ret=q1+query(mid+1,r,mid+1,ri,p3); 54 else ret=q1; 55 } 56 return ret; 57 } 58 } tr; 59 struct node{ 60 int x,y; 61 }a[200005]; 62 vector<pair<int,int>> vet; 63 bool cmp(node x,node y){ 64 if (x.x!=y.x) return x.x<y.x; 65 else return x.y<y.y; 66 } 67 int main(){ 68 // freopen("1008.in","r",stdin); 69 // freopen("1.out","w",stdout); 70 int T; 71 scanf("%d",&T); 72 while (T--){ 73 scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&k); 74 for (int i=1; i<=k; i++){ 75 scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); 76 } 77 for (int i=2; i<=n; i++){ 78 a[k+i-1].x=i,a[k+i-1].y=0; 79 } 80 k+=n-1; 81 sort(a+1,a+1+k,cmp); 82 tr.build(0,m,1); 83 ll ret=0,st=1; 84 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){ 85 int ed=-1; 86 ll sum=0; 87 vet.clear(); 88 while (a[st].x==i && st<=k){ 89 if (a[st].y<=ed) { 90 st++; 91 continue; 92 } 93 ll tmp; 94 if (a[st].y==m) tmp=0; 95 else tmp=tr.query(0,m,a[st].y+1,m,1); 96 vet.push_back({a[st].y,a[st].y+tmp}); 97 ed=a[st].y+tmp; 98 sum+=tmp+1; 99 st++; 100 } 101 ret+=sum; 102 tr.update(0,m,0,m,1,0); 103 for (auto j:vet){ 104 tr.update(0,m,j.first,j.second,1,1); 105 } 106 } 107 printf("%lld ",n*(m+1)-ret-1); 108 } 109 } 110 111 /*7 7 8 112 2 3 113 2 5 114 3 2 115 3 6 116 5 2 117 5 6 118 6 3 119 6 5 120 */
