Part 1
来说说它的构造
线段树的堆式储存
我们来转成二进制看看
小学生问题:找规律
规律是很显然的
- 一个节点的父节点是这个数左移1,这个位运算就是低位舍弃,所有数字左移一位
- 一个节点的子节点是这个数右移1,是左节点,右移1+1是右节点
- 同一层的节点是依次递增的,第n层有2^(n-1)个节点
- 最后一层有多少节点,值域就是多少(这个很重要)
有了这些规律就可以开始着手建树了
- 查询区间[1,n]
最后一层不是2的次幂怎么办?
开到2的次幂!后面的空间我不要了!就是这么任性!
Build函数就这么出来了!找到不小于n的2的次幂
直接输入叶节点的信息
1 int n,M,q;int d[N<<1];
2 inline void Build(int n){
3 for(M=1;M<n;M<<=1);
4 for(int i=M+1;i<=M+n;i++) d[i]=in();
5 }
建完了?当然没有!父节点还都是空的呢!
维护父节点信息?
倒叙访问,每个节点访问的时候它的子节点已经处理过辣!
- 维护区间和?
1 for(int i=M-1;i;--i) d[i]=d[i<<1]+d[i<<1|1];
- 维护最值?
1 for(int i=M-1;i;--i) d[i]=max/min (d[i<<1],d[i<<1|1]);
这样就构造出了一颗二叉树,也就是zkw线段树了!
如果你是压行选手的话(比如我),建树的代码只需要两行。
是不是特别Easy!
新技能Get√
Part 2
单点操作
- 单点修改
1 void Change(int x,int v){
2 d[M+x]+=v;
3 }
只是这么简单?当然不是,跟线段树一样,我们要更新它的父节点!
1 void Change(int x,int v){
2 d[x=M+x]+=v;
3 while(x) d[x>>=1]=d[x<<1]+d[x<<1|1];
4 }
没了?没了。
- 单点查询(差分思想,后面会用到)
把d维护的值修改一下,变成维护它与父节点的差值(为后面的RMQ问题做准备)
建树的过程就要修改一下咯!
1 void Build(int n){
2 for(M=1;M<=n+1;M<<=1);for(int i=M+1;i<=M+n;i++) d[i]=in();
3 for(int i=M-1;i;--i) d[i]=min(d[i<<1],d[i<<1|1]),d[i<<1]-=d[i],d[i<<1|1]-=d[i];
4 }
在当前情况下的查询
1 void Sum(int x,int res=0){
2 while(x) res+=d[x],x>>=1;return res;
3 }
Part 3
区间操作
询问区间和,把[s,t]闭区间换成(s,t)开区间来计算
1 int Sum(int s,int t,int Ans=0){
2 for (s=s+M-1,t=t+M+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1){
3 if(~s&1) Ans+=d[s^1];
4 if( t&1) Ans+=d[t^1];
5 }return Ans;
6 }
- 为什么
~s&1? -
为什么
t&1? 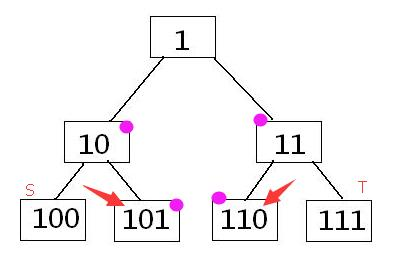
-
变成开区间了以后,如果s是左儿子,那么它的兄弟节点一定在区间内,同理,如果t是右儿子,那么它的兄弟节点也一定在区间内!
-
这样计算不会重复吗?
答案是会的!所以注意迭代的出口s^t^1
如果s,t就是兄弟节点,那么也就迭代完成了。
代码简单,即使背过也不难QuQ
- 区间最小值
1 void Sum(int s,int t,int L=0,int R=0){
2 for(s=s+M-1,t=t+M+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1){
3 L+=d[s],R+=d[t];
4 if(~s&1) L=min(L,d[s^1]);
5 if(t&1) R=min(R,d[t^1]);
6 }
7 int res=min(L,R);while(s) res+=d[s>>=1];
8 }
差分!
不要忘记最后的统计!
还有就是建树的时候是用的最大值还是最小值,这个一定要注意,影响到差分。
- 区间最大值
1 void Sum(int s,int t,int L=0,int R=0){
2 for(s=s+M-1,t=t+M+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1){
3 L+=d[s],R+=d[t];
4 if(~s&1) L=max(L,d[s^1]);
5 if(t&1) R=max(R,d[t^1]);
6 }
7 int res=max(L,R);while(s) res+=d[s>>=1];
8 }
同理。
- 区间加法
1 void Add(int s,int t,int v,int A=0){
2 for(s=s+M-1,t=t+M+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1){
3 if(~s&1) d[s^1]+=v;if(t&1) d[t^1]+=v;
4 A=min(d[s],d[s^1]);d[s]-=A,d[s^1]-=A,d[s>>1]+=A;
5 A=min(d[t],d[t^1]);d[t]-=A,d[t^1]-=A,d[t>>1]+=A;
6 }
7 while(s) A=min(d[s],d[s^1]),d[s]-=A,d[s^1]-=A,d[s>>=1]+=A;
8 }
同样是差分!差分就是厉害QuQ
zkw线段树小试牛刀(code来自hzwer.com)

1 #include<cstdio>
2 #include<iostream>
3 #define M 261244
4 using namespace std;
5 int tr[524289];
6 void query(int s,int t)
7 {
8 int ans=0;
9 for(s=s+M-1,t=t+M+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1)
10 {
11 if(~s&1)ans+=tr[s^1];
12 if(t&1)ans+=tr[t^1];
13 }
14 printf("%d
",ans);
15 }
16 void change(int x,int y)
17 {
18 for(tr[x+=M]+=y,x>>=1;x;x>>=1)
19 tr[x]=tr[x<<1]+tr[x<<1|1];
20 }
21 int main()
22 {
23 int n,m,f,x,y;
24 scanf("%d",&n);
25 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%d",&x);change(i,x);}
26 scanf("%d",&m);
27 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
28 {
29 scanf("%d%d%d",&f,&x,&y);
30 if(f==1)change(x,y);
31 else query(x,y);
32 }
33 return 0;
34 }
POJ3468(code来自网络)

1 #include <cstdio>
2 #include <cstring>
3 #include <cctype>
4 #define N ((131072 << 1) + 10) //表示节点个数->不小于区间长度+2的最小2的正整数次幂*2+10
5 typedef long long LL;
6 inline int getc() {
7 static const int L = 1 << 15;
8 static char buf[L] , *S = buf , *T = buf;
9 if (S == T) {
10 T = (S = buf) + fread(buf , 1 , L , stdin);
11 if (S == T)
12 return EOF;
13 }
14 return *S++;
15 }
16 inline int getint() {
17 static char c;
18 while(!isdigit(c = getc()) && c != '-');
19 bool sign = (c == '-');
20 int tmp = sign ? 0 : c - '0';
21 while(isdigit(c = getc()))
22 tmp = (tmp << 1) + (tmp << 3) + c - '0';
23 return sign ? -tmp : tmp;
24 }
25 inline char getch() {
26 char c;
27 while((c = getc()) != 'Q' && c != 'C');
28 return c;
29 }
30 int M; //底层的节点数
31 int dl[N] , dr[N]; //节点的左右端点
32 LL sum[N]; //节点的区间和
33 LL add[N]; //节点的区间加上一个数的标记
34 #define l(x) (x<<1) //x的左儿子,利用堆的性质
35 #define r(x) ((x<<1)|1) //x的右儿子,利用堆的性质
36 void pushdown(int x) { //下传标记
37 if (add[x]&&x<M) {//如果是叶子节点,显然不用下传标记(别忘了)
38 add[l(x)] += add[x];
39 sum[l(x)] += add[x] * (dr[l(x)] - dl[l(x)] + 1);
40 add[r(x)] += add[x];
41 sum[r(x)] += add[x] * (dr[r(x)] - dl[r(x)] + 1);
42 add[x] = 0;
43 }
44 }
45 int stack[20] , top;//栈
46 void upd(int x) { //下传x至根节点路径上节点的标记(自上而下,用栈实现)
47 top = 0;
48 int tmp = x;
49 for(; tmp ; tmp >>= 1)
50 stack[++top] = tmp;
51 while(top--)
52 pushdown(stack[top]);
53 }
54 LL query(int tl , int tr) { //求和
55 LL res=0;
56 int insl = 0, insr = 0; //两侧第一个有用节点
57 for(tl=tl+M-1,tr=tr+M+1;tl^tr^1;tl>>=1,tr>>=1) {
58 if (~tl&1) {
59 if (!insl)
60 upd(insl=tl^1);
61 res+=sum[tl^1];
62 }
63 if (tr&1) {
64 if(!insr)
65 upd(insr=tl^1)
66 res+=sum[tr^1];
67 }
68 }
69 return res;
70 }
71 void modify(int tl , int tr , int val) { //修改
72 int insl = 0, insr = 0;
73 for(tl=tl+M-1,tr=tr+M+1;tl^tr^1;tl>>=1,tr>>=1) {
74 if (~tl&1) {
75 if (!insl)
76 upd(insl=tl^1);
77 add[tl^1]+=val;
78 sum[tl^1]+=(LL)val*(dr[tl^1]-dl[tl^1]+1);
79 }
80 if (tr&1) {
81 if (!insr)
82 upd(insr=tr^1);
83 add[tr^1]+=val;
84 sum[tr^1]+=(LL)val*(dr[tr^1]-dl[tr^1]+1);
85 }
86 }
87 for(insl=insl>>1;insl;insl>>=1) //一路update
88 sum[insl]=sum[l(insl)]+sum[r(insl)];
89 for(insr=insr>>1;insr;insr>>=1)
90 sum[insr]=sum[l(insr)]+sum[r(insr)];
91
92
93 }
94 inline void swap(int &a , int &b) {
95 int tmp = a;
96 a = b;
97 b = tmp;
98 }
99 int main() {
100 //freopen("tt.in" , "r" , stdin);
101 int n , ask;
102 n = getint();
103 ask = getint();
104 int i;
105 for(M = 1 ; M < (n + 2) ; M <<= 1);
106 for(i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i)
107 sum[M + i] = getint() , dl[M + i] = dr[M + i] = i; //建树
108 for(i = M - 1; i >= 1 ; --i) { //预处理节点左右端点
109 sum[i] = sum[l(i)] + sum[r(i)];
110 dl[i] = dl[l(i)];
111 dr[i] = dr[r(i)];
112 }
113 char s;
114 int a , b , x;
115 while(ask--) {
116 s = getch();
117 if (s == 'Q') {
118 a = getint();
119 b = getint();
120 if (a > b)
121 swap(a , b);
122 printf("%lld
" , query(a , b));
123 }
124 else {
125 a = getint();
126 b = getint();
127 x = getint();
128 if (a > b)
129 swap(a , b);
130 modify(a , b , x);
131 }
132 }
133 return 0;
134 }
可持久化线段树版本(来自http://blog.csdn.net/forget311300/article/details/44306265)

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <cmath>
5 #include <algorithm>
6 #include <vector>
7 #define mp(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
8
9 using namespace std;
10
11 const int N = 100000;
12 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
13
14 int a[N + 10];
15 int b[N + 10];
16 int M;
17 int lq, rq;
18 vector<pair<int, int> > s[N * 22];
19
20 void add(int id, int cur)
21 {
22 cur += M;
23 int lat = 0;
24 if (s[cur].size())
25 lat = s[cur][s[cur].size() - 1].second;
26 s[cur].push_back(mp(id, ++lat));
27 for (cur >>= 1; cur; cur >>= 1)
28 {
29 int l = 0;
30 if (s[cur << 1].size())
31 l = s[cur << 1][s[cur << 1].size() - 1].second;
32 int r = 0;
33 if (s[cur << 1 | 1].size())
34 r = s[cur << 1 | 1][s[cur << 1 | 1].size() - 1].second;
35 s[cur].push_back(mp(id, l + r));
36 }
37 }
38
39 int Q(int id, int k)
40 {
41 if (id >= M) return id - M;
42 int l = id << 1, r = l ^ 1;
43 int ll = lower_bound(s[l].begin(), s[l].end(), mp(lq, inf)) - s[l].begin() - 1;
44 int rr = lower_bound(s[l].begin(), s[l].end(), mp(rq, inf)) - s[l].begin() - 1;
45 int kk = 0;
46 if (rr >= 0)kk = s[l][rr].second;
47 if (ll >= 0)kk = s[l][rr].second - s[l][ll].second;
48 if (kk < k)return Q(r, k - kk);
49 return Q(l, k);
50 }
51
52 int main()
53 {
54 int n, m;
55 while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m))
56 {
57 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
58 {
59 scanf("%d", a + i);
60 b[i] = a[i];
61 }
62 sort(b, b + n);
63 int nn = unique(b, b + n) - b;
64 for (M = 1; M < nn; M <<= 1);
65 for (int i = 1; i < M + M; i++)
66 {
67 s[i].clear();
68 //s[i].push_back(mp(0, 0));
69 }
70 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
71 {
72 int id = lower_bound(b, b + nn, a[i]) - b;
73 add(i + 1, id);
74 }
75 while (m--)
76 {
77 int k;
78 scanf("%d %d %d", &lq, &rq, &k);
79 lq--;
80 int x = Q(1, k);
81 printf("%d
", b[x]);
82 }
83 }
84 return 0;
85 }
完全模板(来自http://blog.csdn.net/forget311300/article/details/44306265)

1 const int N = 1e5;
2
3 struct node
4 {
5 int sum, d, v;
6 int l, r;
7 void init()
8 {
9 d = 0;
10 v = -1;
11 }
12 void cb(node ls, node rs)
13 {
14 sum = ls.sum + rs.sum;
15 l = ls.l, r = rs.r;
16 }
17 int len()
18 {
19 return r - l + 1;
20 }
21 void V(int x)
22 {
23 sum = len() * x;
24 d = 0;
25 v = x;
26 }
27 void D(int x)
28 {
29 sum += len() * x;
30 d += x;
31 }
32 };
33
34 struct tree
35 {
36 int m, h;
37 node g[N << 2];
38 void init(int n)
39 {
40 for (m = h = 1; m < n + 2; m <<= 1, h++);
41 int i = 0;
42 for (; i <= m; i++)
43 {
44 g[i].init();
45 g[i].sum = 0;
46 }
47 for (; i <= m + n; i++)
48 {
49 g[i].init();
50 scanf("%d", &g[i].sum);
51 g[i].l = g[i].r = i - m;
52 }
53 for (; i < m + m; i++)
54 {
55 g[i].init();
56 g[i].sum = 0;
57 g[i].l = g[i].r = i - m;
58 }
59 for (i = m - 1; i > 0; i--)
60 g[i].cb(g[i << 1], g[i << 1 | 1]);
61 }
62 void dn(int x)
63 {
64 for (int i = h - 1; i > 0; i--)
65 {
66 int f = x >> i;
67 if (g[f].v != -1)
68 {
69 g[f << 1].V(g[f].v);
70 g[f << 1 | 1].V(g[f].v);
71 }
72 if (g[f].d)
73 {
74 g[f << 1].D(g[f].d);
75 g[f << 1 | 1].D(g[f].d);
76 }
77 g[f].v = -1;
78 g[f].d = 0;
79 }
80 }
81 void up(int x)
82 {
83 for (x >>= 1; x; x >>= 1)
84 {
85 if (g[x].v != -1)continue;
86 int d = g[x].d;
87 g[x].d = 0;
88 g[x].cb(g[x << 1], g[x << 1 | 1]);
89 g[x].D(d);
90 }
91 }
92 void update(int l, int r, int x, int o)
93 {
94 l += m - 1, r += m + 1;
95 dn(l), dn(r);
96 for (int s = l, t = r; s ^ t ^ 1; s >>= 1, t >>= 1)
97 {
98 if (~s & 1)
99 {
100 if (o)
101 g[s ^ 1].V(x);
102 else
103 g[s ^ 1].D(x);
104 }
105 if (t & 1)
106 {
107 if (o)
108 g[t ^ 1].V(x);
109 else
110 g[t ^ 1].D(x);
111 }
112 }
113 up(l), up(r);
114 }
115 int Q(int l, int r)
116 {
117 int ans = 0;
118 l += m - 1, r += m + 1;
119 dn(l), dn(r);
120 for (int s = l, t = r; s ^ t ^ 1; s >>= 1, t >>= 1)
121 {
122 if (~s & 1)ans += g[s ^ 1].sum;
123 if (t & 1)ans += g[t ^ 1].sum;
124 }
125 return ans;
126 }
127 };
二维情况(来自http://blog.csdn.net/forget311300/article/details/44306265)

1 #include <cstdio>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <cmath>
5 #include <vector>
6 #include <iostream>
7
8 using namespace std;
9
10 const int W = 1000;
11
12 int m;
13
14 struct tree
15 {
16 int d[W << 2];
17 void o()
18 {
19 for (int i = 1; i < m + m; i++)d[i] = 0;
20 }
21 void Xor(int l, int r)
22 {
23 l += m - 1, r += m + 1;
24 for (int s = l, t = r; s ^ t ^ 1; s >>= 1, t >>= 1)
25 {
26 if (~s & 1)d[s ^ 1] ^= 1;
27 if (t & 1)d[t ^ 1] ^= 1;
28 }
29 }
30
31 } g[W << 2];
32
33 void chu()
34 {
35 for (int i = 1; i < m + m; i++)
36 g[i].o();
37 }
38
39
40 void Xor(int lx, int ly, int rx, int ry)
41 {
42 lx += m - 1, rx += m + 1;
43 for (int s = lx, t = rx; s ^ t ^ 1; s >>= 1, t >>= 1)
44 {
45 if (~s & 1)g[s ^ 1].Xor(ly, ry);
46 if (t & 1)g[t ^ 1].Xor(ly, ry);
47 }
48 }
49
50 int Q(int x, int y)
51 {
52 int ans = 0;
53 for (int xx = x + m; xx; xx >>= 1)
54 {
55 for (int yy = y + m; yy; yy >>= 1)
56 {
57 ans ^= g[xx].d[yy];
58 }
59 }
60 return ans;
61 }
62
63 int main()
64 {
65 int T;
66 cin >> T;
67 int fl = 0;
68 while (T--)
69 {
70 if (fl)
71 {
72 printf("
");
73 }
74 fl = 1;
75 int N, M;
76 cin >> N >> M;
77 for (m = 1; m < N + 2; m <<= 1);
78 chu();
79 while (M--)
80 {
81 char o[4];
82 scanf("%s", o);
83 if (*o == 'Q')
84 {
85 int x, y;
86 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
87 printf("%d
", Q(x, y));
88 }
89 else
90 {
91 int lx, ly, rx, ry;
92 scanf("%d%d%d%d", &lx, &ly, &rx, &ry);
93 Xor(lx, ly, rx, ry);
94 }
95 }
96 }
97 return 0;
98 }
非递归扫描线+离散化(来自http://blog.csdn.net/forget311300/article/details/44306265)

1 #include <algorithm>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #include <cmath>
7
8 using namespace std;
9
10 const int N = 111;
11
12 int n;
13 vector<double> y;
14
15 struct node
16 {
17 double s;
18 int c;
19 int l, r;
20 void chu(double ss, int cc, int ll, int rr)
21 {
22 s = ss;
23 c = cc;
24 l = ll, r = rr;
25 }
26 double len()
27 {
28 return y[r] - y[l - 1];
29 }
30 } g[N << 4];
31 int M;
32
33 void init(int n)
34 {
35 for (M = 1; M < n + 2; M <<= 1);
36 g[M].chu(0, 0, 1, 1);
37 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
38 g[i + M].chu(0, 0, i, i);
39 for (int i = n + 1; i < M; i++)
40 g[i + M].chu(0, 0, n, n);
41 for (int i = M - 1; i > 0; i--)
42 g[i].chu(0, 0, g[i << 1].l, g[i << 1 | 1].r);
43 }
44
45 struct line
46 {
47 double x, yl, yr;
48 int d;
49 line() {}
50 line(double x, double yl, double yr, int dd): x(x), yl(yl), yr(yr), d(dd) {}
51 bool operator < (const line &cc)const
52 {
53 return x < cc.x || (x == cc.x && d > cc.d);
54 }
55 };
56
57 vector<line>L;
58
59 void one(int x)
60 {
61 if (x >= M)
62 {
63 g[x].s = g[x].c ? g[x].len() : 0;
64 return;
65 }
66 g[x].s = g[x].c ? g[x].len() : g[x << 1].s + g[x << 1 | 1].s;
67 }
68
69 void up(int x)
70 {
71 for (; x; x >>= 1)
72 one(x);
73 }
74
75 void add(int l, int r, int d)
76 {
77 if (l > r)return;
78 l += M - 1, r += M + 1;
79 for (int s = l, t = r; s ^ t ^ 1; s >>= 1, t >>= 1)
80 {
81 if (~s & 1)
82 {
83 g[s ^ 1].c += d;
84 one(s ^ 1);
85 }
86 if (t & 1)
87 {
88 g[t ^ 1].c += d;
89 one(t ^ 1);
90 }
91 }
92 up(l);
93 up(r);
94 }
95
96 double sol()
97 {
98 y.clear();
99 L.clear();
100 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
101 {
102 double lx, ly, rx, ry;
103 scanf("%lf %lf %lf %lf", &lx, &ly, &rx, &ry);
104 L.push_back(line(lx, ly, ry, 1));
105 L.push_back(line(rx, ly, ry, -1));
106 y.push_back(ly);
107 y.push_back(ry);
108 }
109 sort(y.begin(), y.end());
110 y.erase(unique(y.begin(), y.end()), y.end());
111 init(y.size());
112 sort(L.begin(), L.end());
113 n = L.size() - 1;
114 double ans = 0;
115 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
116 {
117 int l = upper_bound(y.begin(), y.end(), L[i].yl + 1e-8) - y.begin();
118 int r = upper_bound(y.begin(), y.end(), L[i].yr + 1e-8) - y.begin() - 1;
119 add(l, r, L[i].d);
120 ans += g[1].s * (L[i + 1].x - L[i].x);
121 }
122 return ans;
123 }
124
125 int main()
126 {
127 int ca = 1;
128 while (cin >> n && n)
129 {
130 printf("Test case #%d
Total explored area: %.2f
", ca++, sol());
131 }
132 return 0;
133 }


