老年代TenuredGeneration所使用的垃圾回收算法是标记-压缩-清理算法。在回收阶段,将标记对象越过堆的空闲区移动到堆的另一端,所有被移动的对象的引用也会被更新指向新的位置。看起来像是把杂陈的箱子一股脑推到房间的一侧一样。 下面,从TenuredGeneration的collect()开始,分析TenuredGeneration的GC过程。
void TenuredGeneration::collect(bool full, bool clear_all_soft_refs, size_t size, bool is_tlab) { retire_alloc_buffers_before_full_gc(); OneContigSpaceCardGeneration::collect(full, clear_all_soft_refs, size, is_tlab); }
转而调用了父类OneContigSpaceCardGeneration的collect():
void OneContigSpaceCardGeneration::collect(bool full, bool clear_all_soft_refs, size_t size, bool is_tlab) { SpecializationStats::clear(); // Temporarily expand the span of our ref processor, so // refs discovery is over the entire heap, not just this generation ReferenceProcessorSpanMutator x(ref_processor(), GenCollectedHeap::heap()->reserved_region()); GenMarkSweep::invoke_at_safepoint(_level, ref_processor(), clear_all_soft_refs); SpecializationStats::print(); }
接着看GenMarkSweep的invoke_at_safepoint():
1.前面的实现都是进行一些gc前的初始化工作和统计工作
(1).设置引用处理器和引用处理策略为clear_all_softrefs
_ref_processor = rp;
rp->setup_policy(clear_all_softrefs);
(2).增加调用计数,并统计gc前的堆的使用大小
gch->perm_gen()->stat_record()->invocations++; // Capture heap size before collection for printing. size_t gch_prev_used = gch->used();
(3).保存当前内存代和更低的内存代、以及永久代的已使用区域
gch->save_used_regions(level, true /* perm */);
(4).创建遍历栈
allocate_stacks();
2.接下来就是MarkSweepCompact算法的实现了,算法的实现分为四个阶段:
mark_sweep_phase1-4,其中:
mark_sweep_phase1:递归标记所有活跃对象
mark_sweep_phase2:计算所有活跃对象在压缩后的偏移地址
mark_sweep_phase3:更新对象的引用地址
mark_sweep_phase4:移动所有活跃/存活对象到新的位置
mark_sweep_phase1(level, clear_all_softrefs); mark_sweep_phase2(); //... mark_sweep_phase3(level); //... mark_sweep_phase4();
3.在将对象标记入栈的时候,会将原MarkWord保存在_preserved_marks,MarkWord被设置为转发指针,当四个处理阶段结束后,恢复这些”废弃”对象的MarkWord,以防止下次GC时干扰标记,虽然没有真正“清空”死亡对象的内存空间,但由于对象引用将指向新的位置,原来的这些对象所占用内存空间将会被看作是空闲空间。
restore_marks();
保存各内存代的mark指针为当前空闲分配指针
gch->save_marks();
4.一些gc后的处理工作,例如清空所有遍历栈、更新堆的一些使用信息和最近一次gc发生的时间等
mark_sweep_phase1:递归标记所有活跃对象
1.与新生代类似,标记根集对象。
follow_root_closure.set_orig_generation(gch->get_gen(level)); gch->gen_process_strong_roots(level, false, // Younger gens are not roots. true, // activate StrongRootsScope true, // Collecting permanent generation. SharedHeap::SO_SystemClasses, &follow_root_closure, true, // walk code active on stacks &follow_root_closure);
follow_root_closure的工作函数如下:
void MarkSweep::FollowRootClosure::do_oop(oop* p) { follow_root(p); } void MarkSweep::FollowRootClosure::do_oop(narrowOop* p) { follow_root(p); }
不考虑压缩指针的解压,follow_root()实现如下:
template <class T> inline void MarkSweep::follow_root(T* p) { assert(!Universe::heap()->is_in_reserved(p), "roots shouldn't be things within the heap"); //... T heap_oop = oopDesc::load_heap_oop(p); if (!oopDesc::is_null(heap_oop)) { oop obj = oopDesc::decode_heap_oop_not_null(heap_oop); if (!obj->mark()->is_marked()) { mark_object(obj); obj->follow_contents(); } } follow_stack(); }
对于没有被标记的活跃对象,follow_root()会调用mark_object()标记该对象(设置转发指针),随后调用follow_contents()和follow_stack()处理该对象,根据借助栈进行递归标记的思想,递归标记的过程就是遍历根集对象,把根集对象进行标记后,将其所引用的对象压入栈,然后遍历栈中元素,递归标记活跃对象及其所引用的对象,直至栈空为止。
oop_follow_contents()就应该是将当前活跃对象所引用的对象标记并压入栈的过程:
void instanceKlass::oop_follow_contents(oop obj) { assert(obj != NULL, "can't follow the content of NULL object"); obj->follow_header(); InstanceKlass_OOP_MAP_ITERATE( obj, MarkSweep::mark_and_push(p), assert_is_in_closed_subset) }
InstanceKlass_OOP_MAP_ITERATE()语句块在”源码分析HotSpot GC过程(二):DefNewGeneration的GC过程“一文中已经分析过了,其作用就是遍历对象的引用域,使用OopClosure进行处理。
故follow_contents()处理活跃对象就是将该对象标记后,将该对象所引用的对象标记后压入_marking_stack。那么,可以预见,follow_stack()的处理必然就是遍历栈中的对象,并递归地将其引用对象标记和入栈直到栈空为止,那么下面看看follow_stack()的具体实现:
void MarkSweep::follow_stack() { do { while (!_marking_stack.is_empty()) { oop obj = _marking_stack.pop(); assert (obj->is_gc_marked(), "p must be marked"); obj->follow_contents(); } // Process ObjArrays one at a time to avoid marking stack bloat. if (!_objarray_stack.is_empty()) { ObjArrayTask task = _objarray_stack.pop(); objArrayKlass* const k = (objArrayKlass*)task.obj()->blueprint(); k->oop_follow_contents(task.obj(), task.index()); } } while (!_marking_stack.is_empty() || !_objarray_stack.is_empty()); }
那么结果如何呢?好消息是,follow_stack()的前半段确实如此,坏消息是栈空了并不一定会结束,因为,光有一个_marking_stack栈是不够的,对于数组对象的引用如果全都放在标记栈中时,当数组非常大时,就会出现爆栈的问题,这里就需要一个_objArrayKlass和一个ObjArrayTask用来处理数组对象的引用问题。具体的实现这里就不再深入下去了。
分析完活跃对象的处理过程,我们回到mark_sweep_phase1()中:
注意gen_process_strong_roots()传入的younger_gens_as_roots参数为false,即不会对更低的内存代进行处理,因为在SharedHeap::process_strong_roots的处理过程中,就已经标记了所有的活跃对象。但是,如果存在更高内存代,那么更低内存代是无法将更高内存代的没有被引用的对象当做垃圾对象处理的,所以虽然不会再处理更低的内存代,但仍要将更高内存代的对象当做根集对象递归遍历。(Hotspot中TenuredGeneration没有更高的内存代了)
2.递归标记发现的引用
// Process reference objects found during marking { ref_processor()->setup_policy(clear_all_softrefs); ref_processor()->process_discovered_references( &is_alive, &keep_alive, &follow_stack_closure, NULL); }
3.卸载不再使用的类
// Follow system dictionary roots and unload classes bool purged_class = SystemDictionary::do_unloading(&is_alive);
4.部分类卸载后,需要清理CodeCache,此外,需要清空标记栈
// Follow code cache roots CodeCache::do_unloading(&is_alive, &keep_alive, purged_class); follow_stack(); // Flush marking stack
5.部分类卸载后,更新存活类的子类、兄弟类、实现类的引用关系
follow_weak_klass_links();
6.清理未被标记的软引用和弱引用
follow_mdo_weak_refs();
7.删除拘留字符串表中未被标记的字符串对象
StringTable::unlink(&is_alive);
8.清理符号表中没有被引用的符号
SymbolTable::unlink();
mark_sweep_phase2:计算所有活跃对象在压缩后的偏移地址
void GenMarkSweep::mark_sweep_phase2() { GenCollectedHeap* gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap(); Generation* pg = gch->perm_gen(); //... VALIDATE_MARK_SWEEP_ONLY(reset_live_oop_tracking(false)); gch->prepare_for_compaction(); VALIDATE_MARK_SWEEP_ONLY(_live_oops_index_at_perm = _live_oops_index); CompactPoint perm_cp(pg, NULL, NULL); pg->prepare_for_compaction(&perm_cp); }
GenCollectedHeap的prepare_for_compaction()如下:
void GenCollectedHeap::prepare_for_compaction() { Generation* scanning_gen = _gens[_n_gens-1]; // Start by compacting into same gen. CompactPoint cp(scanning_gen, NULL, NULL); while (scanning_gen != NULL) { scanning_gen->prepare_for_compaction(&cp); scanning_gen = prev_gen(scanning_gen); } }
看到还记得在DefNewGeneration的GC分析中下一片压缩区域的设置么? 根据内存代的不同实现,如DefNewGeneration分为Eden区(EdenSpace,ContiguousSpace的子类)、From/To区(ContiguousSpace),TenuredGeneration只有一个_the_space区(ContiguousSpace),这里直接看ContiguousSpace对prepare_for_compaction的实现:
// Faster object search. void ContiguousSpace::prepare_for_compaction(CompactPoint* cp) { SCAN_AND_FORWARD(cp, top, block_is_always_obj, obj_size); }
SCAN_AND_FORWARD(),该函数定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/memory/space.hpp中
1.compact_top为压缩指针,指向压缩的目标内存空间的起始地址,在压缩地址计算的开始,指向当前内存区域的起始位置
HeapWord* compact_top; /* This is where we are currently compacting to. */ /* We're sure to be here before any objects are compacted into this * space, so this is a good time to initialize this: */ set_compaction_top(bottom());
2.初始化CompactPoint,若CompactPoint的压缩区域为空,即这是内存代的第一片区域,那么初始化CompactPoint的压缩区域为内存代的第一片区域,初始化压缩指针为区域的起始地址,初始化区域的压缩的目标区域起始地址为该区域的起始地址,初始化压缩边界为区域边界(默认实现),若CompactPoint的压缩区域不为空,那么之前继续进行该区域的压缩工作,即初始化压缩指针为原压缩指针的值。
if (cp->space == NULL) { //assert cp->space = cp->gen->first_compaction_space(); compact_top = cp->space->bottom(); cp->space->set_compaction_top(compact_top); cp->threshold = cp->space->initialize_threshold(); } else { compact_top = cp->space->compaction_top(); }
3.每经过MarkSweepAlwaysCompactCount次GC,就允许当前区域空间的MarkSweepDeadRatio%(TenuredSpace)/PermMarkSweepDeadRatio%(ContigPermSpace)大小被用来将死亡对象当做存活对象处理,这里姑且将这些对象称为弥留对象,把这片空间称为弥留空间好了(实际上并没有这样的明确定义)。
nt invocations = SharedHeap::heap()->perm_gen()->stat_record()->invocations; bool skip_dead = ((invocations % MarkSweepAlwaysCompactCount) != 0); size_t allowed_deadspace = 0; if (skip_dead) { const size_t ratio = allowed_dead_ratio(); allowed_deadspace = (capacity() * ratio / 100) / HeapWordSize; }
4.q为遍历指针,t为扫描边界,end_of_live为最后一个活跃对象的地址,LiveRange保存着死亡对象后面存活对象的地址范围,first_dead为第一个死亡对象的地址
HeapWord* q = bottom(); HeapWord* t = scan_limit(); HeapWord* end_of_live= q; /* One byte beyond the last byte of the last live object. */ HeapWord* first_dead = end();/* The first dead object. */ LiveRange* liveRange = NULL; /* The current live range, recorded in the first header of preceding free area. */ _first_dead = first_dead;
在边界内遍历,若当前遍历的对象被标记过,即这是一个活跃对象,那么为该对象计算压缩后的地址,设置转发指针,并更新压缩指针和最后一个活跃对象的地址,并继续遍历
while (q < t) { if (block_is_obj(q) && oop(q)->is_gc_marked()) { /* prefetch beyond q */ Prefetch::write(q, interval); /* size_t size = oop(q)->size(); changing this for cms for perm gen */ size_t size = block_size(q); compact_top = cp->space->forward(oop(q), size, cp, compact_top); q += size; end_of_live = q; }
否则,跳过死亡对象,遍历直到遇到一个活跃对象为止
else { /* run over all the contiguous dead objects */ HeapWord* end = q; do { /* prefetch beyond end */ Prefetch::write(end, interval); end += block_size(end); } while (end < t && (!block_is_obj(end) || !oop(end)->is_gc_marked()));
若仍有弥留空间可以用,那么在这片空间上调用insert_deadspace()构造弥留对象,当做活跃对象进行压缩的计算处理
if (allowed_deadspace > 0 && q == compact_top) { size_t sz = pointer_delta(end, q); if (insert_deadspace(allowed_deadspace, q, sz)) { compact_top = cp->space->forward(oop(q), sz, cp, compact_top); q = end; end_of_live = end; continue; } }
更新上一个LiveRange的活跃对象结束地址,这个活跃范围对象设置在死亡对象的MarkWord上,由于在死亡对象后遇到了一个新的活跃对象,于是需要重新构造一个LiveRange对象来记录下一片活跃对象的地址范围。
if (liveRange) { liveRange->set_end(q); } liveRange = (LiveRange*)q; liveRange->set_start(end); liveRange->set_end(end);
保存首个死亡对象的地址,并继续遍历
/* see if this is the first dead region. */ if (q < first_dead) { first_dead = q; } /* move on to the next object */ q = end; }
循环结束,更新最后一个死亡对象的活跃对象范围、最后一个活跃对象的地址、第一个死亡对象的地址
if (liveRange != NULL) { liveRange->set_end(q); } _end_of_live = end_of_live; if (end_of_live < first_dead) { first_dead = end_of_live; } _first_dead = first_dead;
保存当前空间的压缩指针
cp->space->set_compaction_top(compact_top);
mark_sweep_phase3:更新对象的引用地址
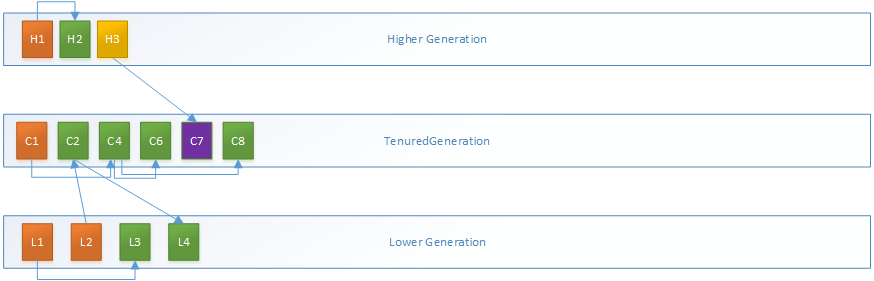
1.adjust_root_pointer_closure和adjust_pointer_closure都是静态创建的对象引用地址调整函数的封装对象,这里将调用gen_process_strong_roots()并使用这两个处理函数调整根集对象指针的引用地址。
adjust_root_pointer_closure.set_orig_generation(gch->get_gen(level)); adjust_pointer_closure.set_orig_generation(gch->get_gen(level)); gch->gen_process_strong_roots(level, false, // Younger gens are not roots. true, // activate StrongRootsScope true, // Collecting permanent generation. SharedHeap::SO_AllClasses, &adjust_root_pointer_closure, false, // do not walk code &adjust_root_pointer_closure);
adjust_root_pointer_closure()的工作函数如下:
void MarkSweep::AdjustPointerClosure::do_oop(oop* p) { adjust_pointer(p, _is_root); } void MarkSweep::AdjustPointerClosure::do_oop(narrowOop* p) { adjust_pointer(p, _is_root); }
MarkSweep的adjust_pointer将会解析引用对象的MarkWord,若该引用对象已经被标记,就会解析转发指针,并设置引用地址为引用对象新的地址。
template <class T> inline void MarkSweep::adjust_pointer(T* p, bool isroot) { T heap_oop = oopDesc::load_heap_oop(p); if (!oopDesc::is_null(heap_oop)) { oop obj = oopDesc::decode_heap_oop_not_null(heap_oop); oop new_obj = oop(obj->mark()->decode_pointer()); //...assert if (new_obj != NULL) { //...assert oopDesc::encode_store_heap_oop_not_null(p, new_obj); } } VALIDATE_MARK_SWEEP_ONLY(track_adjusted_pointer(p, isroot)); }
所以对引用地址的更新就是遍历各内存代对象/引用,若对象所引用的对象已经被标记,则更新其引用地址为转发指针所转向的新地址。
gen_process_strong_roots()完成了对初始根对象的引用地址更新
2.调整引用指针的引用地址
CodeBlobToOopClosure adjust_code_pointer_closure(&adjust_pointer_closure, /*do_marking=*/ false); gch->gen_process_weak_roots(&adjust_root_pointer_closure, &adjust_code_pointer_closure, &adjust_pointer_closure);
3.使用GenAdjustPointersClosure遍历各内存代,以更新引用对象的引用地址
GenAdjustPointersClosure blk; gch->generation_iterate(&blk, true); pg->adjust_pointers();
其基本思想如图所示:
mark_sweep_phase4:移动所有active对象到新的位置
1.永久代对象压缩,只有在永久代对象压缩后,实例才能获得正确的类数据地址
pg->compact();
2.使用GenCompactClosure遍历堆上的对象
GenCompactClosure blk; gch->generation_iterate(&blk, true);
GenCollectedHeap的generation_iterate()将调用GenCompactClosure的do_generation()遍历各个内存代
void GenCollectedHeap::generation_iterate(GenClosure* cl, bool old_to_young) { if (old_to_young) { for (int i = _n_gens-1; i >= 0; i--) { cl->do_generation(_gens[i]); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < _n_gens; i++) { cl->do_generation(_gens[i]); }
do_generation()实际上是调用各个内存代的compact()进行处理(因为各个内存代的区域组织形式不同,比如新生代有Eden和From/To区,而老年代只有一个区域存在)
class GenCompactClosure: public GenCollectedHeap::GenClosure { public: void do_generation(Generation* gen) { gen->compact(); } };
compact()调用了CompactibleSpace(ContiguousSpace的父类)的SCAN_AND_COMPACT()完成对象内容的复制
void CompactibleSpace::compact() { SCAN_AND_COMPACT(obj_size); }
SCAN_AND_COMPACT()定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/memory/space.hpp中
(1).q是遍历指针,t是最后一个活跃对象的位置,记录最后一个活跃对象的位置,就不必再遍历全部内存区域,否则当gc后剩余的活跃对象较少时,将会进行很多不必要的遍历
HeapWord* q = bottom(); HeapWord* const t = _end_of_live;
(2).跳过死亡对象区域
if (q < t && _first_dead > q && !oop(q)->is_gc_marked()) { //... HeapWord* const end = _first_dead; while (q < end) { size_t size = obj_size(q); //...assert q += size; }
当第一个死亡对象的地址与最后一个活跃对象的地址不相同时,即有连续多个死亡对象存在,那么第一个死亡对象的MarkWord就是之前保存的LiveRange,通过LiveRange可以获取下一个活跃对象的地址
if (_first_dead == t) { q = t; } else { /* $$$ Funky */ q = (HeapWord*) oop(_first_dead)->mark()->decode_pointer(); }
(3).开始遍历,对于死亡对象,同样通过LiveRange获取下一个存活对象的地址
const intx scan_interval = PrefetchScanIntervalInBytes; const intx copy_interval = PrefetchCopyIntervalInBytes; while (q < t) { if (!oop(q)->is_gc_marked()) { /* mark is pointer to next marked oop */ q = (HeapWord*) oop(q)->mark()->decode_pointer(); }
(4).复制原对象的数据内容到压缩后的地址,并初始化新的位置的对象的MarkWord
else { /* prefetch beyond q */ Prefetch::read(q, scan_interval); /* size and destination */ size_t size = obj_size(q); HeapWord* compaction_top = (HeapWord*)oop(q)->forwardee(); /* prefetch beyond compaction_top */ Prefetch::write(compaction_top, copy_interval); //... Copy::aligned_conjoint_words(q, compaction_top, size); oop(compaction_top)->init_mark(); //... q += size; }
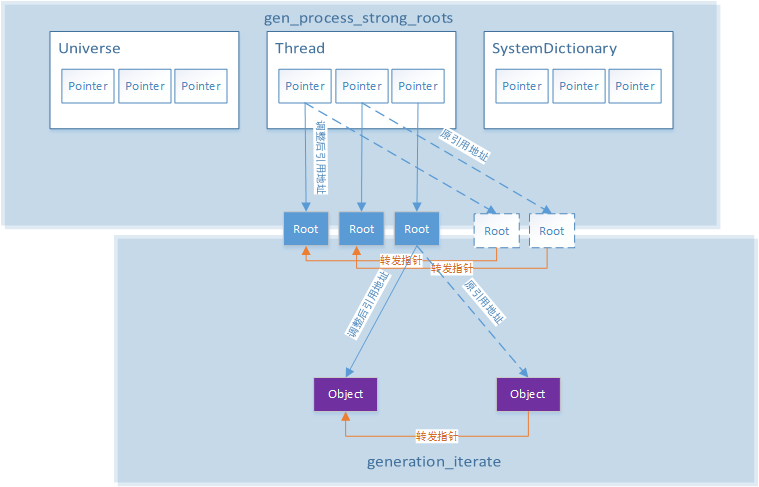
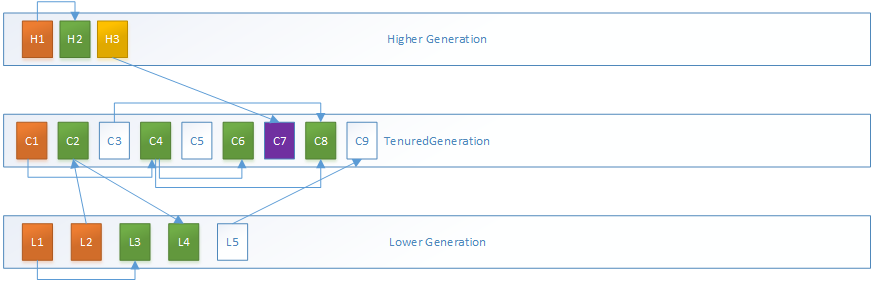
我们以如下分代和引用模型为基础进行TenuredGeneration的GC分析:
其中蓝色对象为正常的根对象,箭头代表引用关系。
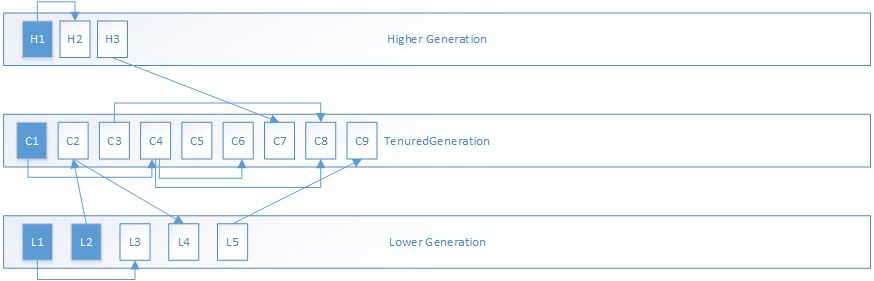
1.MarkSweepPhase1过程分为两步,第一步是递归标记所有根对象:
以根集对象C1为例,借助标记栈的标记过程如下,其中橙色对象为被标记的正常的根对象,绿色为被标记的其他对象:
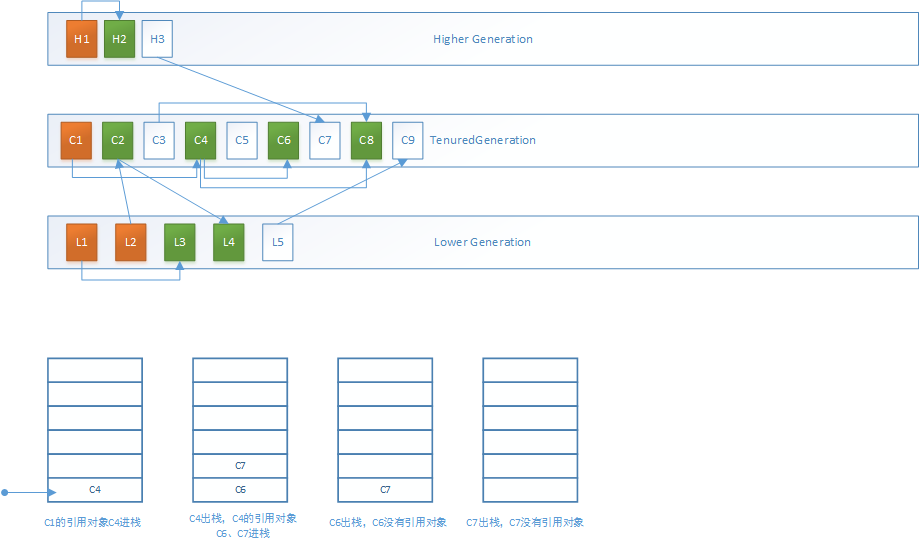
第二步是递归标记作为更高内存代的对象,这里即为H3,和其所引用的C7对象:
2.MarkSweepPhase2过程,以TenuredGeneration为代表进行分析:
C3、C5、C9对象均为垃圾对象,由于前面没有垃圾对象,C1、C2的转发指针均指向自身所在地址
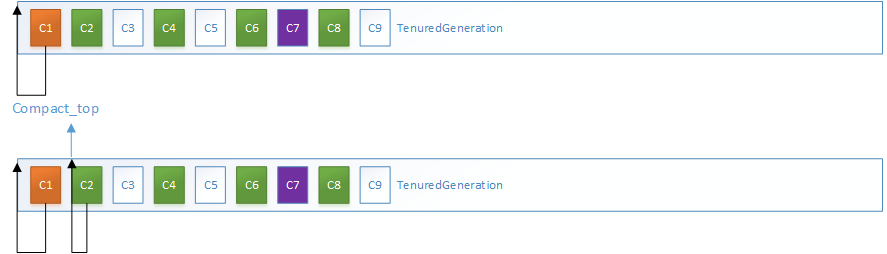
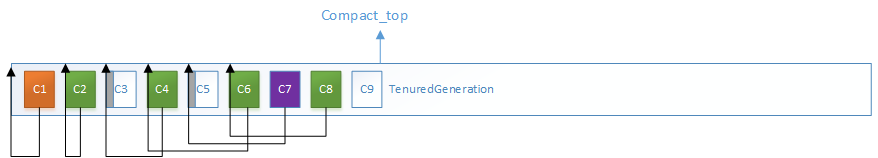
而C3是垃圾对象,C3的MarkWord被设置为LiveRange,指向前一块活跃对象的范围,而C4的转发指针将压缩到C3的起始地址

以此类推,计算所有活跃对象的转发地址和活跃范围,注意这里压缩指针位置是根据前一次的指针位置和前一个活跃对象的大小计算的
3.MarkSweepPhase3过程,这里C4、C6、C7、C8的压缩后地址均已发生变化,但对象内容尚未复制到新地址,所以以虚线边框浅色来代表这个”名义上存在的”新对象,并更新引用这些对象的指针地址:
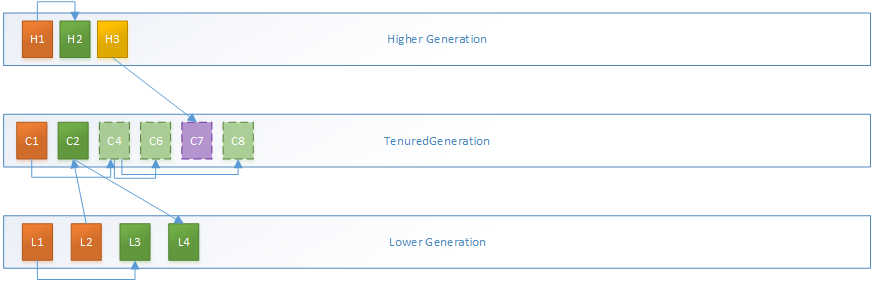
4.MarkSweepPhase3过程,C4、C6、C7、C8的对象内容复制到新地址。