用Python处理文本文件是极方便的,当文本文件中有较多的重复的行的时候,将那些重复的行数去掉并打印诸如"...<repeats X times>..."有助于更好的浏览文本文件的内容。下面将通过Python打造一个双向链表来实现这一功能。如果你对在Python中实现双向链表感兴趣,不妨花五分钟读一读。Have fun :-)
01 - 定义链表结点
1 struct node { 2 int lineno; 3 char *line; 4 char *md5; 5 char *dupcnt; /* duplicated counter */ 6 struct node *prev; 7 struct node *next; 8 };
在Python3中,可以使用字典定义这样的结点。例如:
1 node = {} 2 node['lineno'] = index + 1 3 node['line'] = line.strip().rstrip() 4 node['md5'] = md5txt 5 node['dupcnt'] = 0 6 node['prev'] = index - 1 7 node['next'] = index + 1
由于Python的list本身就是可变数组,这就省力多了,我们不需要从C的角度去考虑链表的建立。
02 - 初始化双向链表
1 def init_doubly_linked_list(l_in): 2 l_out = [] 3 index = 0 4 for text in l_in: 5 data = text.strip().rstrip() 6 md5 = hashlib.md5(data.encode(encoding='UTF-8')).hexdigest() 7 8 d_node = {} 9 d_node['lineno'] = index + 1 10 d_node['line'] = data 11 d_node['md5'] = md5 12 d_node['dupcnt'] = 0 13 d_node['prev'] = index - 1 14 d_node['next'] = index + 1 15 if index == 0: 16 d_node['prev'] = None 17 if index == len(l_in) - 1: 18 d_node['next'] = None 19 l_out.append(d_node) 20 21 index += 1 22 return l_out
很简单,直接采用尾插法搞定。
03 - 将双向链表中的包含有重复行的结点处理掉
1 def omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll): 2 for curr_node in l_dll: 3 prev_node_index = curr_node['prev'] 4 next_node_index = curr_node['next'] 5 6 if prev_node_index is None: # the head node 7 prev_node = None 8 continue 9 else: 10 prev_node = l_dll[prev_node_index] 11 12 if next_node_index is None: # the tail node 13 next_node = None 14 else: 15 next_node = l_dll[next_node_index] 16 17 if curr_node['md5'] != prev_node['md5']: 18 continue 19 20 # Update dupcnt of previous node 21 prev_node['dupcnt'] += 1 22 23 # Remove current node 24 if next_node is not None: 25 next_node['prev'] = curr_node['prev'] 26 if prev_node is not None: 27 prev_node['next'] = curr_node['next']
如果当前行的md5跟前一行一样,那说明就重复了。处理的方法如下:
- 将前一个结点的重复计数器(dupcnt)加1;
- 把当前结点从双向链表上摘掉(这里我们只修改前驱结点的next和后继结点的prev, 不做实际的删除,因为没必要)。
也许你会问为什么采用md5比较而不采用直接的文本行比较,个人觉得先把文本行的md5算出后,再使用md5比较会更好一些,尤其是文本行很长的时候,因为md5(占128位)的输出总是32个字符。
04 - 遍历处理后的双向链表
1 def traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll): 2 l_out = [] 3 4 node_index = None 5 if len(l_dll) > 0: 6 node_index = 0 7 8 while (node_index is not None): # <==> p != NULL 9 curr_node = l_dll[node_index] 10 11 msg = '%6d %s' % (curr_node['lineno'], curr_node['line']) 12 l_out.append(msg) 13 14 # 15 # 1) If dupcnt is 0, it means subsequent lines don't repeat current 16 # line, just go to visit the next node 17 # 2) If dupcnt >= 1, it means subsequent lines repeat the current line 18 # a) If dupcnt is 1, i.e. only one line repeats, just pick it up 19 # b) else save message like '...<repeats X times>...' 20 # 21 if curr_node['dupcnt'] == 0: 22 node_index = curr_node['next'] 23 continue 24 elif curr_node['dupcnt'] == 1: 25 msg = '%6d %s' % (curr_node['lineno'] + 1, curr_node['line']) 26 else: # i.e. curr_node['dupcnt'] > 1 27 msg = '%s ...<repeats %d times>...' % (' ' * 6, 28 curr_node['dupcnt']) 29 l_out.append(msg) 30 31 node_index = curr_node['next'] 32 33 return l_out
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为0,说明它后面的行与之不同,直接打印;
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为1,说明它后面的行与之相同,那么打印当前行,再打印下一行,注意行号得加一;
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为N(>1),说明它后面有N行与之重复了,那么打印当前行并再打印...<repeates N times>...。
注意:头结点的prev和尾结点的next都被定义为None。我们因此可以做类C的遍历。典型的C遍历链表是这样的:
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) /* print p->data */
到此为止,在Python中实现一个简单的双向链表就搞定了。其特点是:
- 用None代表NULL;
- 头结点的prev指针的值和尾结点的next指针的值均为None;
- 中间结点的prev指针的值是其前趋结点的下标;
- 中间结点的next指针的值是其后继结点的下标。
完整的代码实现如下:
1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 import sys 4 import hashlib 5 import getopt 6 7 TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW = False 8 9 10 def init_doubly_linked_list(l_in): 11 # 12 # Here is the node definition of the doubly linked list 13 # 14 # struct node { 15 # int lineno; 16 # char *text; 17 # char *md5; 18 # char *dupcnt; /* duplicated counter */ 19 # struct node *prev; 20 # struct node *next; 21 # } 22 # 23 l_out = [] 24 index = 0 25 for text in l_in: 26 data = text.strip().rstrip() 27 md5 = hashlib.md5(data.encode(encoding='UTF-8')).hexdigest() 28 29 d_node = {} 30 d_node['lineno'] = index + 1 31 d_node['line'] = data 32 d_node['md5'] = md5 33 d_node['dupcnt'] = 0 34 d_node['prev'] = index - 1 35 d_node['next'] = index + 1 36 if index == 0: 37 d_node['prev'] = None 38 if index == len(l_in) - 1: 39 d_node['next'] = None 40 l_out.append(d_node) 41 42 index += 1 43 return l_out 44 45 46 def omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll): 47 # 48 # Core algorithm to omit repeated lines saved in the doubly linked list 49 # 50 # prev_node = curr_node->prev; 51 # next_node = curr_node->next; 52 # 53 # if (curr_node->md5 == prev_node.md5) { 54 # prev_node.dupcnt++; 55 # 56 # /* remove current node */ 57 # next_node->prev = curr_node->prev; 58 # prev_node->next = curr_node->next; 59 # } 60 # 61 for curr_node in l_dll: 62 prev_node_index = curr_node['prev'] 63 next_node_index = curr_node['next'] 64 65 if prev_node_index is None: # the head node 66 prev_node = None 67 continue 68 else: 69 prev_node = l_dll[prev_node_index] 70 71 if next_node_index is None: # the tail node 72 next_node = None 73 else: 74 next_node = l_dll[next_node_index] 75 76 if curr_node['md5'] != prev_node['md5']: 77 continue 78 79 # Update dupcnt of previous node 80 prev_node['dupcnt'] += 1 81 82 # Remove current node 83 if next_node is not None: 84 next_node['prev'] = curr_node['prev'] 85 if prev_node is not None: 86 prev_node['next'] = curr_node['next'] 87 88 89 def traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll): 90 # 91 # Core algorithm to traverse the doubly linked list 92 # 93 # p = l_dll; 94 # while (p != NULL) { 95 # /* print p->lineno and p->text */ 96 # 97 # if (p->dupcnt == 0) { 98 # p = p->next; 99 # continue; 100 # } 101 # 102 # if (p->dupcnt == 1) 103 # /* print p->lineno + 1 and p->text */ 104 # else /* i.e. > 1 */ 105 # printf("...<repeats %d times>...", p->dupcnt); 106 # 107 # p = p->next; 108 # } 109 # 110 l_out = [] 111 112 node_index = None 113 if len(l_dll) > 0: 114 node_index = 0 115 116 while (node_index is not None): # <==> p != NULL 117 curr_node = l_dll[node_index] 118 119 msg = '%6d %s' % (curr_node['lineno'], curr_node['line']) 120 l_out.append(msg) 121 122 # 123 # 1) If dupcnt is 0, it means subsequent lines don't repeat current 124 # line, just go to visit the next node 125 # 2) If dupcnt >= 1, it means subsequent lines repeat the current line 126 # a) If dupcnt is 1, i.e. only one line repeats, just pick it up 127 # b) else save message like '...<repeats X times>...' 128 # 129 if curr_node['dupcnt'] == 0: 130 node_index = curr_node['next'] 131 continue 132 elif curr_node['dupcnt'] == 1: 133 msg = '%6d %s' % (curr_node['lineno'] + 1, curr_node['line']) 134 else: # i.e. curr_node['dupcnt'] > 1 135 msg = '%s ...<repeats %d times>...' % (' ' * 6, 136 curr_node['dupcnt']) 137 l_out.append(msg) 138 139 node_index = curr_node['next'] 140 141 return l_out 142 143 144 def print_refined_text(l_lines): 145 l_dll = init_doubly_linked_list(l_lines) 146 omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll) 147 l_out = traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll) 148 for line in l_out: 149 print(line) 150 151 152 def print_raw_text(l_lines): 153 lineno = 0 154 for line in l_lines: 155 lineno += 1 156 line = line.strip().rstrip() 157 print('%6d %s' % (lineno, line)) 158 159 160 def usage(prog): 161 sys.stderr.write('Usage: %s [-r] <logfile> ' % prog) 162 163 164 def main(argc, argv): 165 shortargs = ":r" 166 longargs = ["raw"] 167 try: 168 options, rargv = getopt.getopt(argv[1:], shortargs, longargs) 169 except getopt.GetoptError as err: 170 sys.stderr.write("%s " % str(err)) 171 usage(argv[0]) 172 return 1 173 174 for opt, arg in options: 175 if opt in ('-r', '--raw'): 176 global TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW 177 TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW = True 178 else: 179 usage(argv[0]) 180 return 1 181 182 rargc = len(rargv) 183 if rargc < 1: 184 usage(argv[0]) 185 return 1 186 187 logfile = rargv[0] 188 with open(logfile, 'r') as file_handle: 189 if TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW: 190 print_raw_text(file_handle.readlines()) 191 else: 192 print_refined_text(file_handle.readlines()) 193 194 return 0 195 196 if __name__ == '__main__': 197 sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
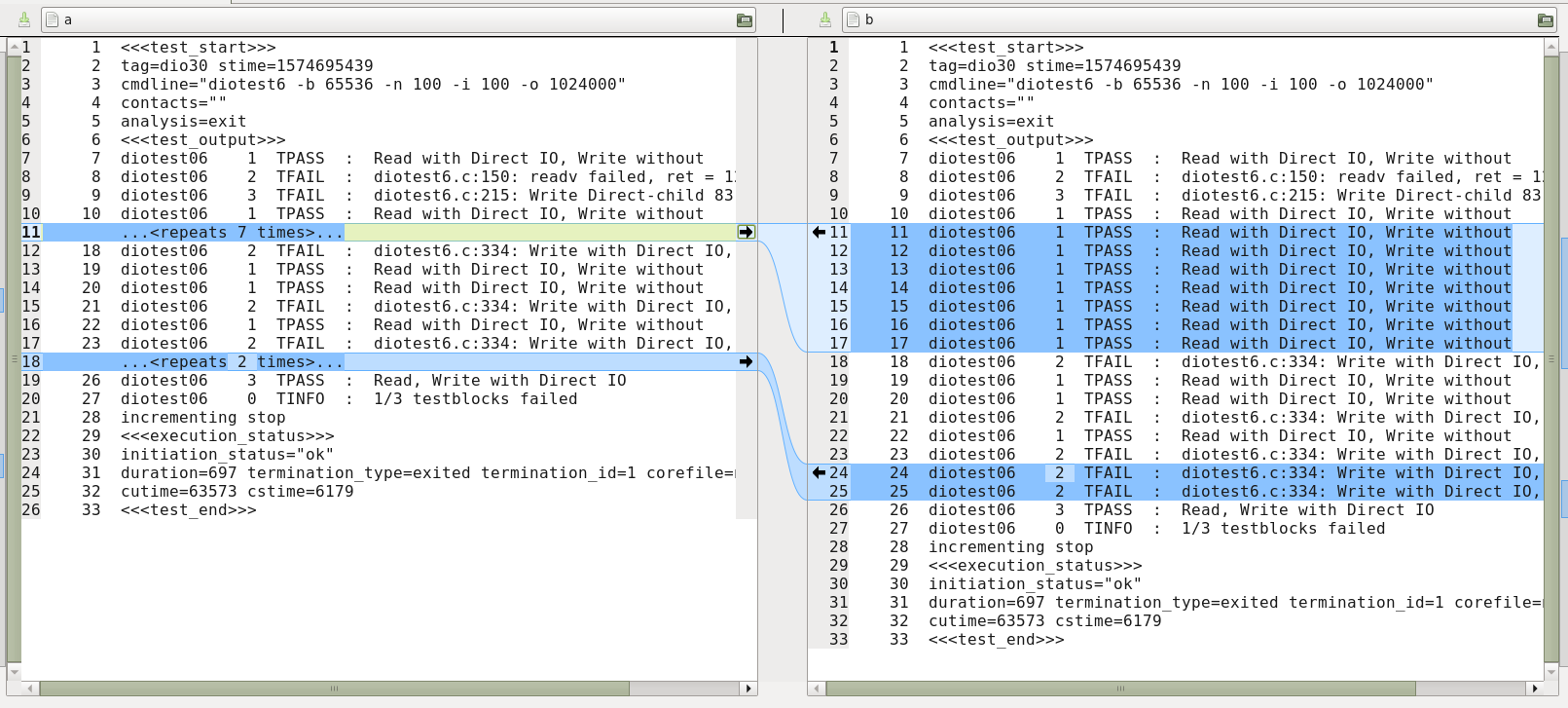
测试运行如下:
$ ./foo.py /tmp/a.log > /tmp/a && cat /tmp/a 1 <<<test_start>>> 2 tag=dio30 stime=1574695439 3 cmdline="diotest6 -b 65536 -n 100 -i 100 -o 1024000" 4 contacts="" 5 analysis=exit 6 <<<test_output>>> 7 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 8 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:150: readv failed, ret = 1269760 9 diotest06 3 TFAIL : diotest6.c:215: Write Direct-child 83 failed 10 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without ...<repeats 7 times>... 18 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 19 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 20 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 21 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 22 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 23 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without ...<repeats 2 times>... 26 diotest06 3 TPASS : Read, Write with Direct IO 27 diotest06 0 TINFO : 1/3 testblocks failed 28 incrementing stop 29 <<<execution_status>>> 30 initiation_status="ok" 31 duration=697 termination_type=exited termination_id=1 corefile=no 32 cutime=63573 cstime=6179 33 <<<test_end>>> $ ./foo.py -r /tmp/a.log > /tmp/b && cat /tmp/b 1 <<<test_start>>> 2 tag=dio30 stime=1574695439 3 cmdline="diotest6 -b 65536 -n 100 -i 100 -o 1024000" 4 contacts="" 5 analysis=exit 6 <<<test_output>>> 7 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 8 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:150: readv failed, ret = 1269760 9 diotest06 3 TFAIL : diotest6.c:215: Write Direct-child 83 failed 10 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 11 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 12 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 13 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 14 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 15 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 16 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 17 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 18 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 19 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 20 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 21 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 22 diotest06 1 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without 23 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 24 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 25 diotest06 2 TFAIL : diotest6.c:334: Write with Direct IO, Read without 26 diotest06 3 TPASS : Read, Write with Direct IO 27 diotest06 0 TINFO : 1/3 testblocks failed 28 incrementing stop 29 <<<execution_status>>> 30 initiation_status="ok" 31 duration=697 termination_type=exited termination_id=1 corefile=no 32 cutime=63573 cstime=6179 33 <<<test_end>>>
用meld对照/tmp/a和/tmp/b截图如下: