出处: http://www.erlang.org/course/concurrent_programming.html
1. 定义
a. process 一个concurrent activity, 【线程,进程,whatever】,erlang的虚拟机环境会负责将所有的process并发
b. Message 一种activity之间交换传达message的方法
c. Timeout 一种等待一定时间的机制,方法
d. registered process 一个注册的 concurrent process, 有名字
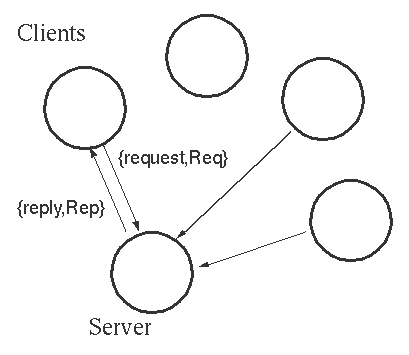
e. Server/client Model 服务端/客户端模型 并发环境下的标准模型
2. 创建一个新的process
使用spawn函数,创建新的process【感觉很像fork~~~~】
Pid2 = spawn(Mod, Func, Args)
3. process间的消息传播
self() 返回当前process的id
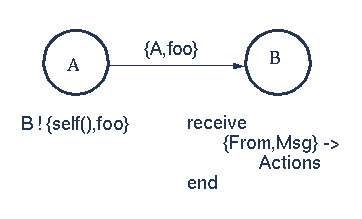
上图中的From和Msg在被接收的时候,会被bound,Msg中可以包含数据
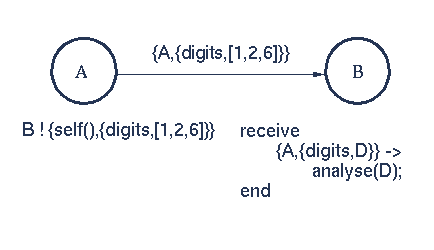
变量只能绑定一次,如果A之前被绑定过,则只有D会被绑定上【1,2,6】,A维持之前的绑定不变
4. 一个echo程序
-module(echo).
-export([go/0, loop/0]).
go() ->
Pid2 = spawn(echo, loop, []), %创建一个process,其pid与Pid2绑定
Pid2 ! {self(), hello}, %向pid2 的process发送一个消息
receive %接收消息
{Pid2, Msg} -> %如果收到这个,执行下边的东东
io:format("P1 ~w~n",[Msg])
end,
Pid2 ! stop. %向pid2的process发送stop消息
loop() ->
receive %接收消息
{From, Msg} -> %收到{From, Msg}pattern的message
From ! {self(), Msg}, %向发送者回复消息,echo
loop(); %【这里是??递归?或者是?不懂】
stop ->
true
end.
5. Selective Mesage Reception 【选择性接收消息】
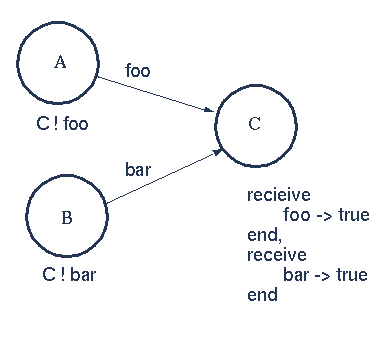
The message foo is received - then the message bar - irrespective of the order in which they were sent.
---
【process C中的两个receive依次接收,先接收foo,再接收bar,与发送顺序无关,会hang住?】
6. Selection of any message 【接收任何消息】
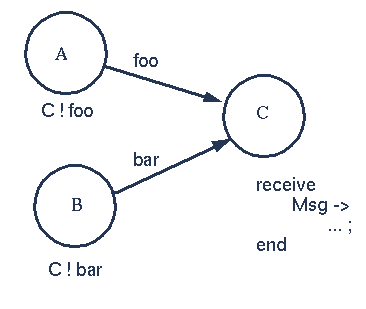
The first message to arrive at the process C will be processed - the variable Msg in the process C will be bound to one of the atoms foo or bar depending on which arrives first.
---
C 会接收任何消息,处理顺序和发送顺序相同
7. A Telephony Example
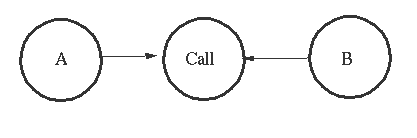
ringing_a(A, B) ->
receive
{A, on_hook} ->
A ! {stop_tone, ring},
B ! terminate,
idle(A);
{B, answered} ->
A ! {stop_tone, ring},
switch ! {connect, A, B},
conversation_a(A, B)
end.
This is the code in the process `Call. A and B are local bound variables in the process Call.
8. 消息中可以包含pid
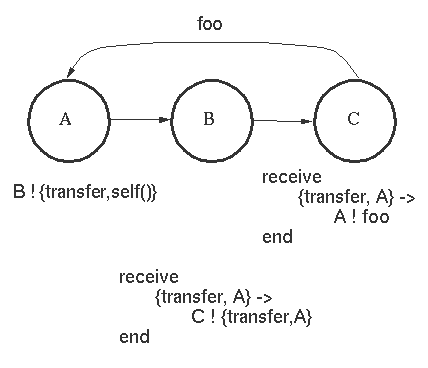
A sends a message to B containing the Pid of A.
B sends a transfer message to C.
C replies directly to A.
9. registered process
register(Alias, Pid) Registers the process Pid with the name Alias.
start() ->
Pid = spawn(num_anal, server, [])
register(analyser, Pid).
analyse(Seq) ->
analyser ! {self(),{analyse,Seq}},
receive
{analysis_result,R} ->
R
end.
Any process can send a message to a registered process.
---
可以通过process注册的名字向其发送消息
10. Server client model
Protocol 【通信协议】
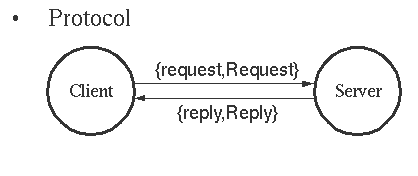
Server code
-module(myserver)
server(data)->
receive
{From, {request, X}} ->
{R, Data1} = fn(X, Data),
From ! {myserver,{reply, R}},
server(Data1)
end.
client code
-export([request/1]).
request(Req) ->
myserver ! {self(),{request,Req}},
receive
{myserver,{reply,Rep}} ->
Rep
end.
11. Timeouts 【超时】
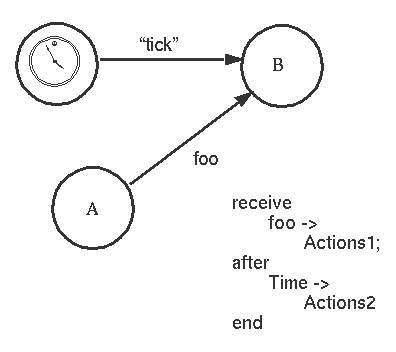
如果B在Time内接收到foo,执行Actions1,否则执行actions2
Uses of Timeouts
sleep(T)- process suspends for T ms.
sleep(T) ->
receive
after
T ->
true
end.
suspend() - process suspends indefinitely.
suspend() ->
receive
after
infinity ->
true
end.
alarm(T, What) - The message What is sent to the current process iin T miliseconds from now
set_alarm(T, What) ->
spawn(timer, set, [self(),T,What]).
set(Pid, T, Alarm) ->
receive
after
T ->
Pid ! Alarm
end.
receive
Msg ->
... ;
end
flush() - flushes the message buffer
flush() ->
receive
Any ->
flush()
after
0 ->
true
end.
A value of 0 in the timeout means check the message buffer first and if it is empty execute the following code.