Error Handling
出处:http://www.erlang.org/course/error_handling.html
1. 定义
a. Link 一个exit信号的双线扩散管道
b. Exit Signal process的exit信息
c. Error Trapping 如果接到相linked的其他process的exit signal,可以像接受消息一样对其进行处理
2. Exit Signals are Sent when Processes Crash
当一个process退出的时候,exit signal会被发送给与其相link的其他process
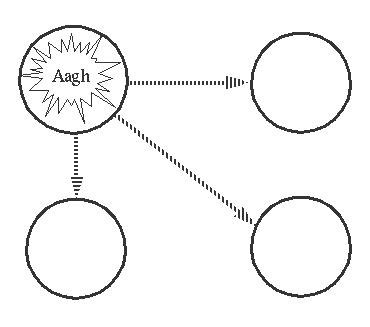
3. Exit Signals propagate through Links
如果Process A异常结束,发送了异常exit signal,那么b-f都会终止~
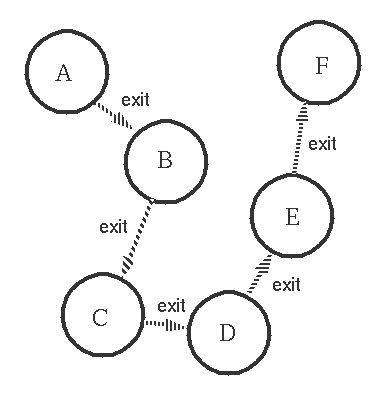
4. Processes can trap exit signals
如果p1,p2,p3三个process的link关系如下,当p1异常退出的时候,异常的exit signal会被发送到p2,p2可以处理这个exit signal,使异常不会扩散
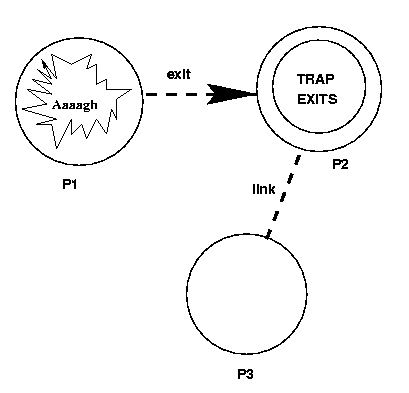
P2 has the following code:
receive
{'EXIT', P1, Why} ->
... exit signals ...
{P3, Msg} ->
... normal messages ...
end
5. complex exit signal propagation
假设我们的process的link关系如下
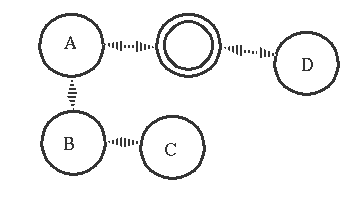
如果一个process发生异常
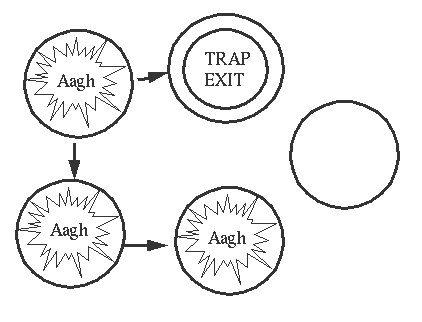
6. exit signal propagation semantics
a. 当一个process结束的的时候,它发送一个normal或者non-normal的信号给他所有的linked的process
b. 一个process如果不trap非正常的exit signal的话,它就会die,并且向它所有的linked的process发送non-normal的exit signal
c. BIFs 或者pattern matching出了问题,就会向其linked的process发送automatic exit signals
7. robust system can be made by layering
分层可以帮助构建一个健壮的系统,level1的process负责traplevel2中的异常,level2的process负责app层的异常
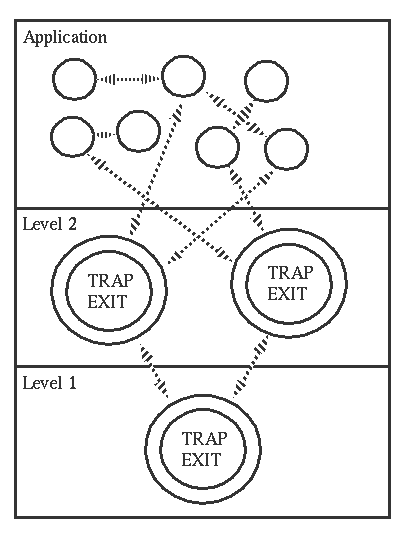
8. primitives for exit signal handling
a. link(Pid) 简历当前process和Pid之间的一个双向的link
b. process_flag(trap_exit, true) 将exit signal转成exit message,这些message可以被正常的receive捕获
c. exit(Reason) 结束process并生成一个exit signal
9. A robust server
top(Free, Allocated) ->
receive
{Pid, alloc} ->
top_alloc(Free, Allocated, Pid);
{Pid ,{release, Resource}} ->
Allocated1 = delete({Resource,Pid},�Allocated),
top([Resource|Free], Allocated1)
end.
top_alloc([], Allocated, Pid) ->
Pid ! no,
top([], Allocated);
top_alloc([Resource|Free], Allocated, Pid) ->
Pid ! {yes, Resource},
top(Free, [{Resource,Pid}|Allocated]).
This is the top loop of an allocator with no error recovery. Free is a list of unreserved resources. Allocated is a list of pairs {Resource, Pid} - showing which resource has been allocated to which process.
10. Allocator with error recovery
The following is a reliable server. If a client craches after it has allocated a resource and before it has released the resource, then the server will automatically release the resource.
The server is linked to the client during the time interval when the resource is allocted. If an exit message comes from the client during this time the resource is released.
top_recover_alloc([], Allocated, Pid) ->
Pid ! no,
top_recover([], Allocated);
top_recover_alloc([Resource|Free], Allocated, Pid) ->
%% No need to unlink.
Pid ! {yes, Resource},
link(Pid),
top_recover(Free, [{Resource,Pid}|Allocated]).
top_recover(Free, Allocated) ->
receive
{Pid , alloc}�->
top_recover_alloc(Free, Allocated, Pid);
{Pid, {release, Resource}}�->
unlink(Pid),
Allocated1 = delete({Resource, Pid}, Allocated),
top_recover([Resource|Free], Allocated1);
{'EXIT', Pid, Reason}�->
%% No need to unlink.
Resource = lookup(Pid, Allocated),
Allocated1 = delete({Resource, Pid}, Allocated),
top_recover([Resource|Free], Allocated1)
end.
Not done -- multiple allocation to same process. i.e. before doing the unlink(Pid) we should check to see that the process has not allocated more than one device.
11. Allocator Utilities
delete(H, [H|T]) ->
T;
delete(X, [H|T]) ->
[H|delete(X, T)].
lookup(Pid, [{Resource,Pid}|_]) ->
Resource;
lookup(Pid, [_|Allocated]) ->
lookup(Pid, Allocated).