Layering & Contract Philosophy With additional indirection
class CSingleton { Protect: CSingleton(); Protect: CSingleton(const CSingleton&); Protect: CSingleton& operator=(const CSingleton& rhs); Private: ~CSingleton(); Private: static CSingleton *pInstance; Public: static CSingleton * GetInstance() { if ( pInstance != NULL ) pInstance = new CSingleton; return pInstance; } } CSingleton::pInstance = NULL;
The Singleton pattern is different from Mono-state pattern which has several static variables shared by all objects of class.
Applicability
Use the Singleton pattern when:
- there must be exactly one instance of a class, and it must be accessible to clients from a well-known access point.
- when the sole instance should be extensible by subclass, and clients should be able to use an extended instance without modifying their code.
Participants
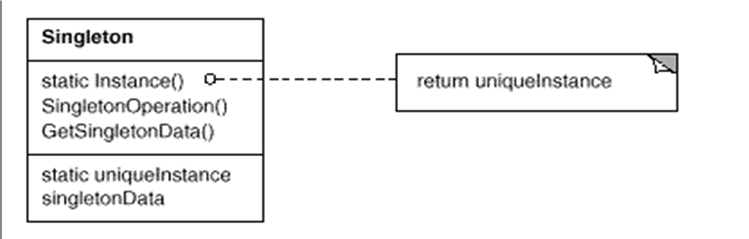
- defines an Instance operation that lets clients access its unique instance. Instance is a class operation (that is, a class method in Smalltalk and a static member function with a return values which also is static member and the constructor must be declared as private for preventing from creating a object with class type in C++).It may be responsible for creating its own unique instance.
Collaborations
- Clients access a Singleton instance solely through Singleton's Instance operation.
One Reference:http://www.cnblogs.com/Leo_wl/archive/2012/07/19/2599063.html