最近在搞容器的监控,遇到influxdb这个库,搞了两天,些许明白了些套路,做个记录,备忘....
小结如下:
influxdb go语言编写
默认情况influxdb创建的库关联autogen的RP(存储策略),即数据会保留永久
监控和日志的区别
最近搞监控,所谓监控就是监控服务肉体是否健康(还活着/生病? 各项指标是否正常?)
区分日志搜集: 分析服务的精神状态是健康(服务的一个履历/日记)
如何做一个监控
参考: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011082379
回想到如果是你自己去做一个监控, 能够做到记录每分钟 CPU 的空闲率是多少, 要怎么做?
搞一个数据库, 用来放数据的
写一个脚本, 用来获取 CPU 的相关数据, 加上时间戳, 然后保存到数据库
创建一个定时任务, 一分钟运行一次脚本
写一个简单的程序, 从数据库查到数据, 然后根据时间戳, 绘制成图表.
telegraf搜集器 + influxdb(存储) + grafana(展示)
grafana 的套路基本上跟 kibana 差不多,都是根据查询条件设置聚合规则,在合适的图表上进行展示,多个图表共同组建成一个 dashboard,熟悉 kibana 的用户应该可以非常容易上手。另外 grafana 的可视化功能比 kibana 强得多,而且 4 以上版本将集成报警功能。
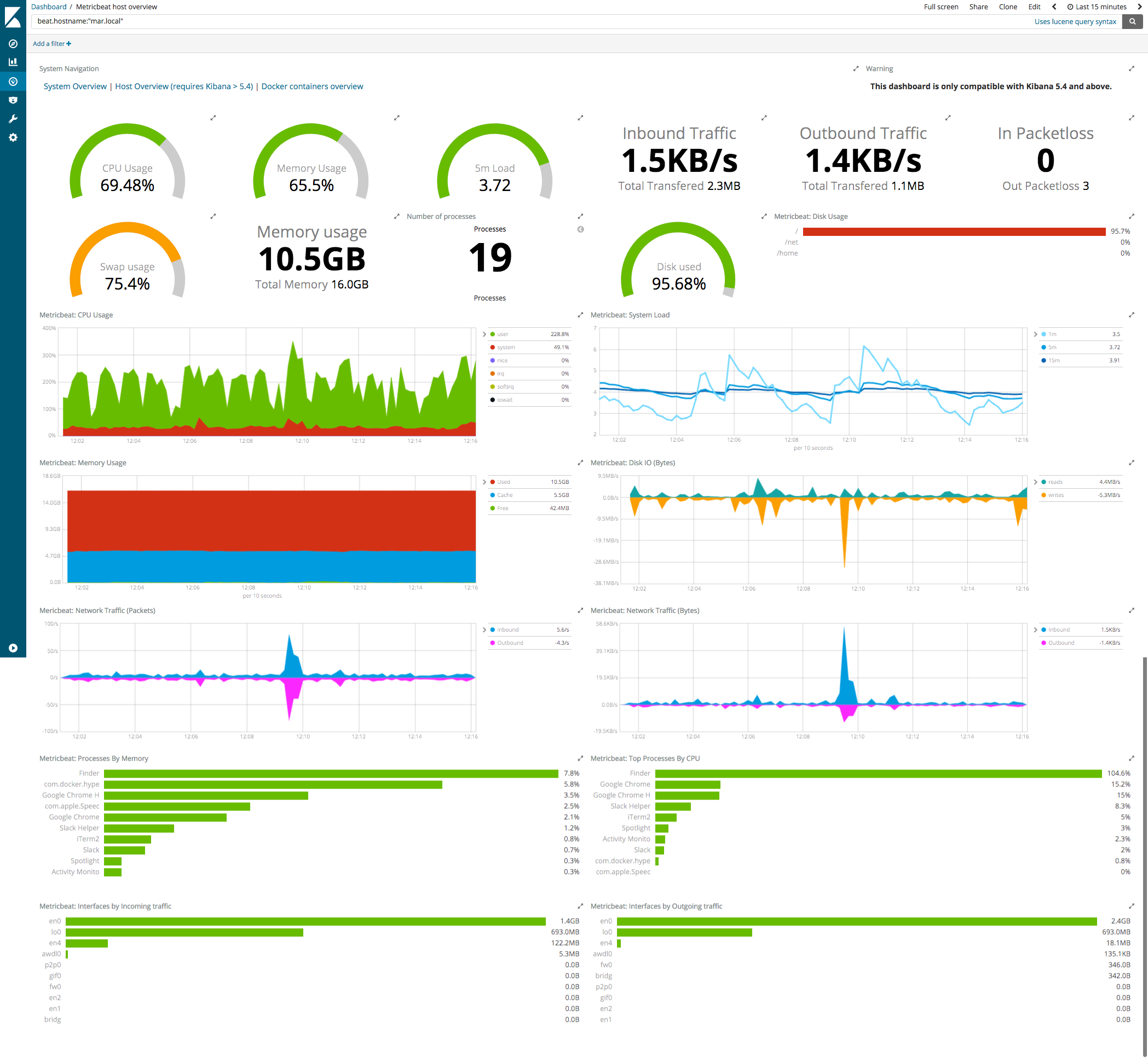
grafana主机监控效果图:

监控的对比influxdb vs 普罗

参考: http://gitbook.cn/books/59395d3d5863cf478e6b50ba/index.html
influxdb集成已有的概念,比如查询语法类似sql,引擎从LSM优化而来,学习成本相对低。
influxdb支持的类型有float,integers,strings,booleans,prometheus目前只支持float。
influxdb的时间精度是纳秒,prometheus的则是毫秒。
influxdb仅仅是个数据库,而prometheus提供的是整套监控解决方案,当然influxdb也提供了整套监控解决方案。
influxdb支持的math function比较少,prometheus相对来说更多,influxdb就目前使用上已经满足功能。
influxdb支持event log,prometheus不支持。
注: 已上对比的是普罗v1 ,现在普罗有v2版本了,听说比influxdb更强悍了. 而且influxdb集群方案已闭源.
influxdb的特性和特点
influxdb中文翻译官方的文档,感觉很棒
https://jasper-zhang1.gitbooks.io/influxdb/content/
https://jasper-zhang1.gitbooks.io/influxdb/content/Concepts/key_concepts.html
参考: http://www.ttlsa.com/monitor-safe/monitor/distributed-time-series-database-influxdb/
- influxdb 它的特性
它有三大特性:
1. Time Series (时间序列):你可以使用与时间有关的相关函数(如最大,最小,求和等)
2. Metrics(度量):你可以实时对大量数据进行计算
3. Eevents(事件):它支持任意的事件数据
时序性(Time Series):与时间相关的函数的灵活使用(例如最大、最小、求和等);
度量(Metrics):对实时大量数据进行计算;
事件(Event):支持任意的事件数据,换句话说,任意事件的数据我们都可以做操作。
- influxdb 它的特点
参考: http://dbaplus.cn/news-73-1291-1.html
schemaless(无结构),可以是任意数量的列
无特殊依赖,几乎开箱即用(如ElasticSearch需要Java)
自带数据过期功能;
自带权限管理,精细到“表”级别;
原生的HTTP支持,内置HTTP API
强大的类SQL语法,支持min, max, sum, count, mean, median 等一系列函数,方便统计。
influxdb最佳实践
1.登录 建库 查询
参考: https://jasper-zhang1.gitbooks.io/influxdb/content/Introduction/getting_start.html
influx -precision rfc3339 # -precision参数表明了任何返回的时间戳的格式和精度,针对查询时候显示的时间格式
CREATE DATABASE mydb
SHOW DATABASES
USE mydb
INSERT cpu,host=serverA,region=us_west value=0.64
SELECT "host", "region", "value" FROM "cpu"
INSERT temperature,machine=unit42,type=assembly external=25,internal=37
SELECT * FROM "temperature"
> SELECT * FROM /.*/ LIMIT 1
> SELECT * FROM "cpu_load_short"
> SELECT * FROM "cpu_load_short" WHERE "value" > 0.9
2.了解influxdb基本概念
参考: http://dbaplus.cn/news-73-1291-1.html
| InfluxDB中的名词 | 传统数据库中的概念 |
|---|---|
| database | 数据库 |
| measurement | 数据库中的表 |
| points | 表里面的一行数据 |
InfluxDB中特有的概念
Point相当于传统数据库里的一行数据,如下表所示:
Point由时间戳(time)、数据(field)、标签(tags)组成。
line-protocol格式
<measurement>[,<tag-key>=<tag-value>...] <field-key>=<field-value>[,<field2-key>=<field2-value>...] [unix-nano-timestamp]
INSERT temperature,machine=unit42,type=assembly external=25,internal=37

更多如:
cpu,host=serverA,region=us_west value=0.64
payment,device=mobile,product=Notepad,method=credit billed=33,licenses=3i 1434067467100293230
stock,symbol=AAPL bid=127.46,ask=127.48
temperature,machine=unit42,type=assembly external=25,internal=37 1434067467000000000
Tag: 被索引
上面的location和server就是tag key,us和host1是tag value,tag是可选的。不过写入数据时最好加上tag,因为它可以被索引。tag的类型只能是字符串。
Field: value支持的类型floats,integers,strings,booleans
上面的temperature是field key,82是field value。field value会用于展示,value支持的类型有floats,integers,strings,booleans。
Timestamp
格式是:RFC3339 UTC。默认精确到纳秒,可选。
Series:
measurement, tag set, retention policy相同的数据集合算做一个 series。理解这个概念至关重要,因为这些数据存储在内存中,如果series太多,会导致OOM
Retention Policy:
保留策略包括设置数据保存的时间以及在集群中的副本个数。默认配置是:RP是autogen,保留时间是永久,副本为1。这些配置在创建数据库时可以修改。
Continuous Query:
CQ是预先配置好的一些查询命令,定期自动执行这些命令并将查询结果写入指定的measurement中,这个功能主要用于数据聚合。具体参考:CQ。
Shard:
存储一定时间间隔的数据,每个目录对应一个shard,目录的名字就是shard id。每一个shard都有自己的cache、wal、tsm file以及compactor,目的就是通过时间来快速定位到要查询数据的相关资源,加速查询的过程,并且也让之后的批量删除数据的操作变得非常简单且高效。
2.实操如下: 理解 point&measurement&series(field set)(被索引的tag set)
向库中插入如下数据:
| 属性 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 库名 | my_database |
| measurement | census |
| field key | butterflies和honeybees |
| tag key | location和scientist |
name: census
-————————————
time butterflies honeybees location scientist
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 12 23 1 langstroth
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 1 30 1 perpetua
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 11 28 1 langstroth
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 3 28 1 perpetua
2015-08-18T05:54:00Z 2 11 2 langstroth
2015-08-18T06:00:00Z 1 10 2 langstroth
2015-08-18T06:06:00Z 8 23 2 perpetua
2015-08-18T06:12:00Z 7 22 2 perpetua
sql语句如下
'INSERT census,location=1,scientist=langstroth butterflies=12,honeybees=23'
'INSERT census,location=1,scientist=perpetua butterflies=1,honeybees=30'
'INSERT census,location=1,scientist=langstroth butterflies=11,honeybees=28'
'INSERT census,location=1,scientist=perpetua butterflies=3,honeybees=28'
'INSERT census,location=2,scientist=langstroth butterflies=2,honeybees=11'
'INSERT census,location=2,scientist=langstroth butterflies=1,honeybees=10'
'INSERT census,location=2,scientist=perpetua butterflies=8,honeybees=23'
'INSERT census,location=2,scientist=perpetua butterflies=7,honeybees=22'
- 造数据用到的2个脚本
为了模拟隔多久插入数据
模拟插入数据时,随机赋值
$ cat fake_data.sh
arr=(
'INSERT orders,website=30 phone=10'
'INSERT orders,website=39 phone=12'
'INSERT orders,website=56 phone=11'
)
#while :;do
for((i=0;i<${#arr[*]};i++));do
/usr/bin/influx -database 'my_food' -execute "${arr[i]}"
sleep 10
# echo "${arr[i]}"
done
#done
$ cat data.sh
#!/bin/bash
function rand(){
min=$1
max=$(($2-$min+1))
num=$(date +%s%N)
echo $(($num%$max+$min))
}
while :;do
/usr/bin/influx -database 'my_database' -execute "INSERT census,location=2,scientist=perpetua butterflies=$(rand 1 50),honeybees=$(rand 1 50)"
sleep 2;
# echo "INSERT orders,website=$(rand 1 50) phone=$(rand 1 50)"
# break
done
field value就是你的数据,它们可以是字符串、浮点数、整数、布尔值,因为InfluxDB是时间序列数据库,所以field value总是和时间戳相关联。
在示例中,field value如下:
12 23
1 30
11 28
3 28
2 11
1 10
8 23
7 22
在上面的数据中,每组field key和field value的集合组成了field set,在示例数据中,有八个field set:
butterflies = 12 honeybees = 23
butterflies = 1 honeybees = 30
butterflies = 11 honeybees = 28
butterflies = 3 honeybees = 28
butterflies = 2 honeybees = 11
butterflies = 1 honeybees = 10
butterflies = 8 honeybees = 23
butterflies = 7 honeybees = 22
注意,field是没有索引的。如果使用field value作为过滤条件来查询,则必须扫描其他条件匹配后的所有值。因此,这些查询相对于tag上的查询(下文会介绍tag的查询)性能会低很多。
在上面的数据中,tag set是不同的每组tag key和tag value的集合,示例数据里有四个tag set:
location = 1, scientist = langstroth
location = 2, scientist = langstroth
location = 1, scientist = perpetua
location = 2, scientist = perpetua
现在你已经熟悉了measurement,tag set和retention policy,那么现在是讨论series的时候了。 在InfluxDB中,series是共同retention policy,measurement和tag set的集合。 以上数据由四个series组成:

理解series对于设计数据schema以及对于处理InfluxDB里面的数据都是很有必要的。
最后,point就是具有相同timestamp的相同series的field集合。例如,这就是一个point:
name: census
-----------------
time butterflies honeybees location scientist
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 1 30 1 perpetua
例子里的series的retention policy为autogen,measurement为census,tag set为location = 1, scientist = perpetua。point的timestamp为2015-08-18T00:00:00Z。
wal(Write Ahead Log)
参考: https://jasper-zhang1.gitbooks.io/influxdb/content/Concepts/glossary.html
最近写的点数的临时缓存。为了减少访问永久存储文件的频率,InfluxDB将最新的数据点缓冲进WAL中,直到其总大小或时间触发然后flush到长久的存储空间。这样可以有效地将写入batch处理到TSM中。
可以查询WAL中的点,并且系统重启后仍然保留。在进程开始时,在系统接受新的写入之前,WAL中的所有点都必须flushed。
目录结构
参考: http://gitbook.cn/books/59395d3d5863cf478e6b50ba/index.html
InfluxDB的数据存储有三个目录,分别是meta、wal、data。meta用于存储数据库的一些元数据,meta目录下有一个meta.db文件。wal目录存放预写日志文件,以.wal结尾。data目录存放实际存储的数据文件,以.tsm结尾。基本结构如下:
-- wal
-- test
-- autogen
-- 1
-- _00001.wal
-- 2
-- _00002.wal
-- data
-- test
-- autogen
-- 1
-- 000000001-000000001.tsm
-- 2
-- 000000001-000000010.tsm
-- meta
-- meta.db
数据采样--> 理解cq和rp
Continuous Query (CQ)是在数据库内部自动周期性跑着的一个InfluxQL的查询,CQs需要在SELECT语句中使用一个函数,并且一定包括一个GROUP BY time()语句。+
Retention Policy (RP)是InfluxDB数据架构的一部分,它描述了InfluxDB保存数据的时间。InfluxDB会比较服务器本地的时间戳和你数据的时间戳,并删除比你在RPs里面用DURATION设置的更老的数据。单个数据库中可以有多个RPs但是每个数据的RPs是唯一的。
实例数据:
db: food_data
mesurement: orders
name: orders
------------
time phone website
2016-05-10T23:18:00Z 10 30
2016-05-10T23:18:10Z 12 39
2016-05-10T23:18:20Z 11 56
目标:
自动删除1h以上的原始2秒间隔数据 --> rp实现
自动删除超过5min的30s间隔数据 --> rp实现
自动将2秒间隔数据聚合到30s的间隔数据 ---> cq实现
2s中插入一次数据:(脚本参考上面fake数据)
create databaes food_data
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "a_hour" ON "food_data" DURATION 1h REPLICATION 1 DEFAULT
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "a_week" ON "food_data" DURATION 1w REPLICATION 1
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY "cq_10s" ON "food_data" BEGIN SELECT mean("website") AS "mean_website",mean("phone") AS "mean_phone" INTO "a_week"."downsampled_orders" FROM "orders" GROUP BY time(10s) END
在步骤1里面创建数据库时,InfluxDB会自动生成一个叫做autogen的RP,并作为数据库的默认RP,autogen这个RP会永远保留数据。在输入上面的命令之后,a_hours会取代autogen作为food_data的默认RP。
验证:
select * from "a_week"."downsampled_orders";
select * from "orders";
influxdb数据聚合
表名都可以正则
select * from /.*/ limit 1
查询一个表里面的所有数据
select * from cpu_idle
查询数据大于200的。
select * from response_times where value > 200
查询数据里面含有下面字符串的。
select * from user_events where url_base = ‘friends#show’
约等于
select line from log_lines where line =~ /paul@influx.com/
按照30m分钟进行聚合,时间范围是大于昨天的 主机名是server1的。
select mean(value) from cpu_idle group by time(30m) where time > now() – 1d and hostName = ‘server1′
select column_one from foo where time > now() – 1h limit 1000;
select reqtime, url from web9999.httpd where reqtime > 2.5;
select reqtime, url from web9999.httpd where time > now() – 1h limit 1000;
url搜索里面含有login的字眼,还以login开头
select reqtime, url from web9999.httpd where url =~ /^/login//;
还可以做数据的merge
select reqtime, url from web9999.httpd merge web0001.httpd;
influxdb备份恢复
参考
参考: http://stedolan.github.io/jq/
#!/bin/bash
function parse_options {
function usage() {
echo -e >&2 "Usage: $0 dump DATABASE [options...]
-u USERNAME (default: root)
-p PASSWORD (default: root)
-h HOST (default: localhost:8086)
-s (use HTTPS)"
}
if [ "$#" -lt 2 ]; then
usage; exit 1;
fi
username=root
password=root
host=localhost:8086
https=0
shift
database=$1
shift
while getopts u:p:h:s opts
do case "${opts}" in
u) username="${OPTARG}";;
p) password="${OPTARG}";;
h) host="${OPTARG}";;
s) https=1;;
?) usage; exit 1;;
esac
done
if [ "${https}" -eq 1 ]; then
scheme="https"
else
scheme="http"
fi
}
function dump {
parse_options $@
curl -s -k -G "${scheme}://${host}/db/${database}/series?u=${username}&p=${password}&chunked=true" --data-urlencode "q=select * from /.*/"
| jq . -c -M
exit
}
function restore {
parse_options $@
while read -r line
do
echo >&2 "Writing..."
curl -X POST -d "[${line}]" "${scheme}://${host}/db/${database}/series?u=${username}&p=${password}"
done
exit
}
case "$1" in
dump) dump $@;;
restore) restore $@;;
*) echo >&2 "Usage: $0 [dump|restore] ..."
exit 1;;
esac
python调用influxdb实现数据增删

utils/db.py
# - * - coding: utf-8 - * -
from influxdb import InfluxDBClient
def get_db_connection():
db_conn = InfluxDBClient(host="192.168.x.x", database="pachongdb")
return db_conn
main.py
#!/home/ansible/.venv/bin/python
# - * - coding: utf-8 - * -
from influxdb.exceptions import InfluxDBClientError, InfluxDBServerError
from utils import db
def insert_success_point_2db():
db_conn = db.get_db_connection()
# 写入成功记录,success字段值约定为1
success_point = [{
"measurement": "wake",
"tags": {
"isp": "mobile",
"region": "上海",
},
"fields": {
"mobile": 159123456xx,
"success": 1,
}
}]
try:
db_conn.write_points(success_point)
except InfluxDBClientError as e:
print("influxdb db client error: {0}".format(e))
except InfluxDBServerError as e:
print("influxdb db server error: {0}".format(e))
except Exception as e:
print("influxdb error: {0}".format(e))
finally:
if db_conn is not None:
db_conn.close()
def insert_fail_point_2db():
db_conn = db.get_db_connection()
# 写入失败记录,fail字段值约定为0
fail_point = [{
"measurement": "wake",
"tags": {
"isp": "mobile",
"region": "上海",
},
"fields": {
"mobile": 1591234xxxx,
"fail": 0,
}
}]
try:
db_conn.write_points(fail_point)
except InfluxDBClientError as e:
print("influxdb db client error: {0}".format(e))
except InfluxDBServerError as e:
print("influxdb db server error: {0}".format(e))
except Exception as e:
print("influxdb error: {0}".format(e))
finally:
if db_conn is not None:
db_conn.close()
def main():
insert_success_point_2db()
insert_fail_point_2db()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
requirements.txt
certifi==2017.11.5
influxdb==5.0.0