什么是Netty?
Netty 是一个利用 Java 的高级网络的能力,隐藏其背后的复杂性而提供一个易于使用的 API 的客户端/服务器框架。
Tomcat和Netty有什么区别?
Netty有什么优点?
并发高
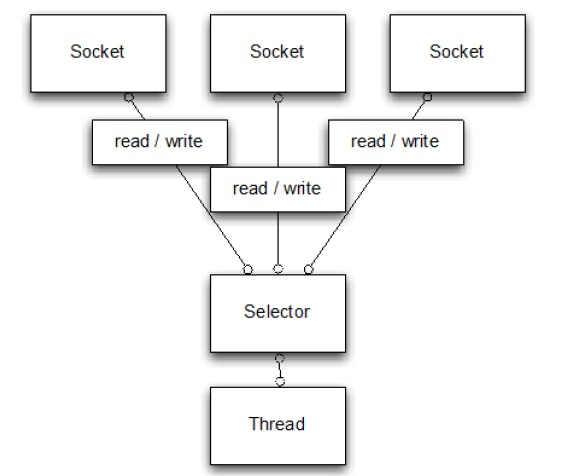
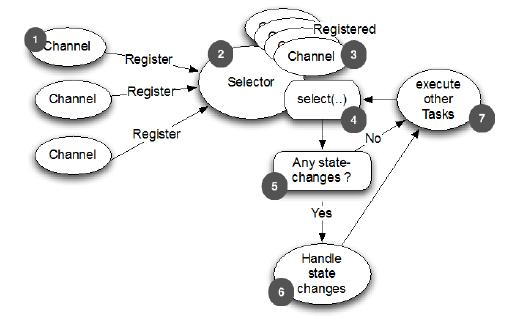
传输快
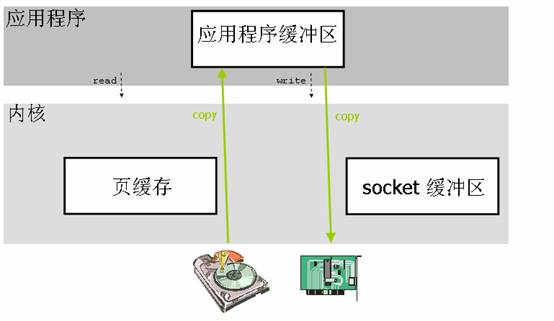
Java的内存有堆内存、栈内存和字符串常量池等等,其中堆内存是占用内存空间最大的一块,也是Java对象存放的地方,一般我们的数据如果需要从IO读取到堆内存,中间需要经过Socket缓冲区,也就是说一个数据会被拷贝两次才能到达他的的终点,如果数据量大,就会造成不必要的资源浪费。Netty针对这种情况,使用了NIO中的另一大特性——零拷贝,当他需要接收数据的时候,他会在堆内存之外开辟一块内存,数据就直接从IO读到了那块内存中去,在netty里面通过ByteBuf可以直接对这些数据进行直接操作,从而加快了传输速度。
public class NettyNioServer { public void server(int port) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer( Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi! ", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(group) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } }); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } }
相关概念
Channel,表示一个连接,可以理解为每一个请求,就是一个Channel。
ChannelHandler,核心处理业务就在这里,用于处理业务请求。
ChannelHandlerContext,用于传输业务数据。
ChannelPipeline,用于保存处理过程需要用到的ChannelHandler和ChannelHandlerContext。
ByteBuf,是一个存储字节的容器,最大特点就是使用方便,它既有自己的读索引和写索引,方便你对整段字节缓存进行读写,也支持get/set,方便你对其中每一个字节进行读写,他的数据结构如下图所示:

Heap Buffer 堆缓冲区
堆缓冲区是ByteBuf最常用的模式,他将数据存储在堆空间。
Direct Buffer 直接缓冲区
直接缓冲区是ByteBuf的另外一种常用模式,他的内存分配都不发生在堆,jdk1.4引入的nio的ByteBuffer类允许jvm通过本地方法调用分配内存,这样做有两个好处
通过免去中间交换的内存拷贝, 提升IO处理速度; 直接缓冲区的内容可以驻留在垃圾回收扫描的堆区以外。
DirectBuffer 在 -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=xxM大小限制下, 使用 Heap 之外的内存, GC对此”无能为力”,也就意味着规避了在高负载下频繁的GC过程对应用线程的中断影响.
Composite Buffer 复合缓冲区
复合缓冲区相当于多个不同ByteBuf的视图,这是netty提供的,jdk不提供这样的功能。
Codec,Netty中的编码/解码器,通过他你能完成字节与pojo、pojo与pojo的相互转换,从而达到自定义协议的目的。在Netty里面最有名的就是HttpRequestDecoder和HttpResponseEncoder了。
下面用一个简单的例子来入门:
核心业务开发:
package io.netty.example.discard; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; /** * Handles a server-side channel. */ public class DiscardServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { // (1) @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { // (2) // Discard the received data silently. ((ByteBuf) msg).release(); // (3) } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { // (4) // Close the connection when an exception is raised. cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
注意,Bytebuf是一个引用计数的对象,使用完后需要finally块手动释放,如:
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
或者
((ByteBuf) msg).release();
启动Server:
package io.netty.example.discard; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; /** * Discards any incoming data. */ public class DiscardServer { private int port; public DiscardServer(int port) { this.port = port; } public void run() throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // (1) EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); // (2) b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // (4) @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new DiscardServerHandler()); } }) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6) // Bind and start to accept incoming connections. ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7) // Wait until the server socket is closed. // In this example, this does not happen, but you can do that to gracefully // shut down your server. f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int port; if (args.length > 0) { port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); } else { port = 8080; } new DiscardServer(port).run(); } }
option() is for the NioServerSocketChannel that accepts incoming connections.
childOption() is for the Channels accepted by the parent ServerChannel, which is NioServerSocketChannel in this case.
我们来打印一下内容:
public class BussinessHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { super.channelRead(ctx, msg); try { ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(in.toString(CharsetUtil.US_ASCII)); } finally { ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); } ((ByteBuf) msg).release(); // ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause); cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
回应消息:
@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ctx.write(msg); // (1) ctx.flush(); // (2)
// ctx.writeAndFlush(msg); }
package io.netty.example.time;
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { // (1)
final ByteBuf time = ctx.alloc().buffer(4); // (2)
time.writeInt((int) (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000L + 2208988800L));
final ChannelFuture f = ctx.writeAndFlush(time); // (3)
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
assert f == future;
ctx.close(); // it returns a ChannelFuture.
}
}); // (4)
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
写一个客户端:
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ByteBuf m = (ByteBuf) msg; // (1)
try {
long currentTimeMillis = (m.readUnsignedInt() - 2208988800L) * 1000L;
System.out.println(new Date(currentTimeMillis));
ctx.close();
} finally {
m.release();
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
public class TimeClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String host = args[0]; int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); // (1) b.group(workerGroup); // (2) b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); // (3) b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (4) b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler()); } }); // Start the client. ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync(); // (5) // Wait until the connection is closed. f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
关于拆包和黏包的解决:
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private ByteBuf buf; @Override public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(4); // (1) } @Override public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { buf.release(); // (1) buf = null; } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf m = (ByteBuf) msg; buf.writeBytes(m); // (2) m.release(); if (buf.readableBytes() >= 4) { // (3) long currentTimeMillis = (buf.readUnsignedInt() - 2208988800L) * 1000L; System.out.println(new Date(currentTimeMillis)); ctx.close(); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
package io.netty.example.time; public class TimeDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { // (1) @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) { // (2) if (in.readableBytes() < 4) { return; // (3) } out.add(in.readBytes(4)); // (4) } }
public class TimeDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> { @Override protected void decode( ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) { out.add(in.readBytes(4)); } }
传输POJO对象:
定义对象
public class UnixTime { private final long value; public UnixTime() { this(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000L + 2208988800L); } public UnixTime(long value) { this.value = value; } public long value() { return value; } @Override public String toString() { return new Date((value() - 2208988800L) * 1000L).toString(); } }
client定义decoder:
@Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) { if (in.readableBytes() < 4) { return; } out.add(new UnixTime(in.readUnsignedInt())); }
client定义handler:
@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { UnixTime m = (UnixTime) msg; System.out.println(m); ctx.close(); }
server定义handler:
@Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ChannelFuture f = ctx.writeAndFlush(new UnixTime()); f.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); }
server定义encoder:
public class TimeEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<UnixTime> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, UnixTime msg, ByteBuf out) { out.writeInt((int)msg.value()); } }
停止应用:
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // (1) EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); // (2) b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // (4) @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new DiscardServerHandler()); } }) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6) // Bind and start to accept incoming connections. ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7) // Wait until the server socket is closed. // In this example, this does not happen, but you can do that to gracefully // shut down your server. f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally {
// 异步的,返回future workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); }