写在前面
新增了一行内容。
整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
查找更方便的版本见:https://alg4.ikesnowy.com/
这一节内容可能会用到的库文件有 SymbolTable,同样在 Github 上可以找到。
善用 Ctrl + F 查找题目。
习题&题解
3.1.1
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/GPA.java.html
ST.java:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/ST.java.html
建立一个符号表,然后把键值放进去,读取计算即可。
和上一章节用过的方法类似,先定义了一个接口 IST<Key, Value> ,包含书中提到的基本 API。
然后定义类 ST ,用标准库里面的 Dictionary 实现了 IST 。
代码
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary> 利用库函数实现的标准符号表。 </summary>
public class ST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>, IEnumerable<Key>
{
private Dictionary<Key, Value> st;
/// <summary> 新建一个符号表。 </summary>
public ST() => this.st = new Dictionary<Key, Value>();
/// <summary> 检查符号表中是否存在与键 <paramref name="key"/> 对应的值。 </summary>
public virtual bool Contains(Key key) => this.st.ContainsKey(key);
/// <summary> 从符号表中删除键 <paramref name="key"/> 及对应的值。 </summary>
public virtual void Delete(Key key) => this.st.Remove(key);
/// <summary> 获取键 <paramref name="key"/> 对应的值,不存在时返回 null。 </summary>
public virtual Value Get(Key key) => this.st[key];
/// <summary> 获取枚举器。 </summary>
public IEnumerator<Key> GetEnumerator() => this.st.Keys.GetEnumerator();
/// <summary> 检查符号表是否为空。 </summary>
public virtual bool IsEmpty() => this.st.Count == 0;
/// <summary> 获得符号表中所有键的集合。 </summary>
public virtual IEnumerable<Key> Keys() => this.st.Keys;
/// <summary> 向符号表中插入新的键值对。 </summary>
public virtual void Put(Key key, Value value) => this.st.Add(key, value);
/// <summary> 获取符号表中键值对的数量。 </summary>
public virtual int Size() => this.st.Count;
/// <summary> 获取枚举器。 </summary>
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() => GetEnumerator();
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.2
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/ArrayST.java.html
建立两个数组,分别存放键和值,一一对应。
添加时直接将新键值对放到数组最后即可。
删除时将待删除的键值对和位于最后的键值对交换,然后将其置空即可。
代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary>
/// 符号表(数组实现)。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="Key">键类型。</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="Value">值类型。</typeparam>
public class ArrayST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>
{
private Key[] keys; // 键数组
private Value[] values; // 值数组
private int n = 0; // 键值对数目
/// <summary>
/// 建立基于数组实现的符号表。
/// </summary>
public ArrayST() : this(8) { }
/// <summary>
/// 建立基于数组实现的符号表。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="initCapacity">初始大小。</param>
public ArrayST(int initCapacity)
{
this.keys = new Key[initCapacity];
this.values = new Value[initCapacity];
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查键 <typeparamref name="Key"/> 是否存在。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要检查是否存在的键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(Key key) => Get(key).Equals(default(Key));
/// <summary>
/// 删除键 <paramref name="key"/> 及对应的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要删除的键。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
{
if (key.Equals(this.keys[i]))
{
this.keys[i] = this.keys[this.n - 1];
this.values[i] = this.values[this.n - 1];
this.keys[this.n - 1] = default(Key);
this.values[this.n - 1] = default(Value);
this.n--;
if (this.n > 0 && this.n == this.keys.Length / 4)
Resize(this.keys.Length / 2);
return;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取键对应的值,若键不存在则返回 null。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要查找的键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Value Get(Key key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
if (this.keys[i].Equals(key))
return this.values[i];
return default(Value);
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查符号表是否为空。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool IsEmpty() => this.n == 0;
/// <summary>
/// 获得包含全部键的集合。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys()
{
Key[] result = new Key[this.n];
Array.Copy(this.keys, result, this.n);
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 向符号表中插入新元素,若键存在将被替换。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">键。</param>
/// <param name="value">值。</param>
public void Put(Key key, Value value)
{
Delete(key);
if (this.n >= this.values.Length)
Resize(this.n * 2);
this.keys[this.n] = key;
this.values[this.n] = value;
this.n++;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回符号表中键值对的数量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>键值对数量。</returns>
public int Size() => this.n;
/// <summary>
/// 为符号表重新分配空间。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="capacity">新分配的空间大小。</param>
private void Resize(int capacity)
{
Key[] tempKey = new Key[capacity];
Value[] tempValue = new Value[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
tempKey[i] = this.keys[i];
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
tempValue[i] = this.values[i];
this.keys = tempKey;
this.values = tempValue;
}
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.3
解答
基于无序链表的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/SequentialSearchST.java.html
有序符号表的 API 见书中表 3.1.4(中文版 P230,英文版 P366)。
在官方实现的基础上修改 Put 方法,先找到合适位置再插入新的键值对,保证链表有序。
为方便插入操作,可以使用双向链表作为基础进行实现。
表中同时维护开头和末尾引用,加快获得最值的速度。
代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary>
/// 基于有序链表的有序符号表实现。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="Key">符号表键类型。</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="Value">符号表值类型。</typeparam>
public class OrderedSequentialSearchST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>, IOrderedST<Key, Value>
where Key : IComparable<Key>
{
/// <summary>
/// 符号表结点。
/// </summary>
private class Node
{
public Key Key { get; set; } // 键。
public Value Value { get; set; } // 值。
public Node Next { get; set; } // 后继。
public Node Prev { get; set; } // 前驱。
}
private Node first = null; // 起始结点。
private Node tail = null; // 末尾结点。
private int n = 0; // 键值对数量。
/// <summary>
/// 构造基于有序链表的有序符号表。
/// </summary>
public OrderedSequentialSearchST() { }
/// <summary>
/// 大于等于 key 的最小值。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Ceiling(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.tail;
while (pointer != null && Greater(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Prev;
return pointer == null ? default(Key) : pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 键 <paramref name="key"/> 在表中是否存在对应的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(Key key) => Floor(key).Equals(key);
/// <summary>
/// 从表中删去键 <paramref name="key"/> 对应的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">键。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && !pointer.Key.Equals(key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
if (pointer == null)
return;
Delete(pointer);
}
/// <summary>
/// 从链表中删除结点 <paramref name="node"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node">待删除的结点。</param>
private void Delete(Node node)
{
Node prev = node.Prev;
Node next = node.Next;
if (prev == null)
this.first = next;
else
prev.Next = next;
if (next == null)
this.tail = prev;
this.n--;
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除最大的键。
/// </summary>
public void DeleteMax()
{
if (this.n == 0)
throw new Exception("ST Underflow");
Delete(this.tail);
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除最小的键。
/// </summary>
public void DeleteMin()
{
if (this.n == 0)
throw new Exception("ST Underflow");
Delete(this.first);
}
/// <summary>
/// 小于等于 Key 的最大值。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Floor(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
return pointer == null ? default(Key) : pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取键 <paramref name="key"/> 对应的值,不存在则返回 null。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Value Get(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Greater(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
if (pointer == null)
return default(Value);
else if (pointer.Key.Equals(key))
return pointer.Value;
else
return default(Value);
}
/// <summary>
/// 符号表是否为空。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool IsEmpty() => this.n == 0;
/// <summary>
/// 获得符号表中所有键的集合。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys() => this.n == 0 ? new List<Key>() : Keys(this.first.Key, this.tail.Key);
/// <summary>
/// 获得符号表中 [<paramref name="lo"/>, <paramref name="hi"/>] 之间的键。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="lo">范围起点。</param>
/// <param name="hi">范围终点。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys(Key lo, Key hi)
{
List<Key> list = new List<Key>();
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, lo))
pointer = pointer.Next;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, hi))
{
list.Add(pointer.Key);
pointer = pointer.Next;
}
if (pointer.Key.Equals(hi))
list.Add(pointer.Key);
return list;
}
/// <summary>
/// 最大的键。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Max() => this.tail == null ? default(Key) : this.tail.Key;
/// <summary>
/// 最小的键。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Min() => this.first == null ? default(Key) : this.first.Key;
/// <summary>
/// 向符号表插入键值对,重复值将被替换。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">键。</param>
/// <param name="value">值。</param>
public void Put(Key key, Value value)
{
Delete(key);
Node temp = new Node()
{
Key = key,
Value = value,
Prev = null,
Next = null
};
Node left = null, right = this.first;
while (right != null && Less(right.Key, temp.Key))
{
left = right;
right = right.Next;
}
Insert(left, right, temp);
if (left == null)
this.first = temp;
if (right == null)
this.tail = temp;
this.n++;
}
/// <summary>
/// 小于 Key 的键的数量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Rank(Key key)
{
int counter = 0;
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, key))
{
pointer = pointer.Next;
counter++;
}
return counter;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获得排名为 k 的键(从 0 开始)。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="k">排名</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Select(int k)
{
if (k >= this.n)
throw new Exception("k must less than ST size!");
Node pointer = this.first;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
pointer = pointer.Next;
return pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获得符号表中键值对的数量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Size() => this.n;
/// <summary>
/// [<paramref name="lo"/>, <paramref name="hi"/>] 之间键的数量。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="lo">范围起点。</param>
/// <param name="hi">范围终点。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Size(Key lo, Key hi)
{
int counter = 0;
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, lo))
pointer = pointer.Next;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, hi))
{
pointer = pointer.Next;
counter++;
}
return counter;
}
/// <summary>
/// 键 <paramref name="a"/> 是否小于 <paramref name="b"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">检查是否较小的键。</param>
/// <param name="b">检查是否较大的键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool Less(Key a, Key b) => a.CompareTo(b) < 0;
/// <summary>
/// 键 <paramref name="a"/> 是否大于 <paramref name="b"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">检查是否较大的键。</param>
/// <param name="b">检查是否较小的键。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool Greater(Key a, Key b) => a.CompareTo(b) > 0;
/// <summary>
/// 将结点 <paramref name="k"/> 插入到 <paramref name="left"/> 和 <paramref name="right"/> 之间。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left">作为前驱的结点。</param>
/// <param name="right">作为后继的结点。</param>
/// <param name="insert">待插入的结点。</param>
private void Insert(Node left, Node right, Node k)
{
k.Prev = left;
k.Next = right;
if (left != null)
left.Next = k;
if (right != null)
right.Prev = k;
}
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.4
解答
利用 Time 类型记录时间,用 Event 来记录事件内容。
Time 类型包含时分秒三个 int 变量,同时实现 IComparable 接口。
Event 类型只包含事件的名称,相当于对 string 做了一个封装。
随后以 Time 为键类型,Event 为值类型,利用上一题编写的有序符号表进行操作。
代码
Time 类
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace _3._1._4
{
/// <summary>
/// 时间类。
/// </summary>
public class Time : IComparable<Time>
{
public int Hour { get; set; }
public int Minute { get; set; }
public int Second { get; set; }
public Time() : this(0, 0, 0) { }
public Time(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
this.Hour = hour;
this.Minute = minute;
this.Second = second;
}
public int CompareTo(Time other)
{
int result = this.Hour.CompareTo(other.Hour);
if (result == 0)
result = this.Minute.CompareTo(other.Minute);
if (result == 0)
result = this.Second.CompareTo(other.Second);
return result;
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (this == obj)
return true;
return CompareTo((Time)obj) == 0;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
int result = 1;
result += this.Hour;
result *= 31;
result += this.Minute;
result *= 31;
result += this.Second;
return result;
}
public override string ToString()
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.Append(this.Hour < 10 ? "0" + this.Hour : this.Hour.ToString());
sb.Append(":");
sb.Append(this.Minute < 10 ? "0" + this.Minute : this.Minute.ToString());
sb.Append(":");
sb.Append(this.Second < 10 ? "0" + this.Second : this.Second.ToString());
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
Event 类
namespace _3._1._4
{
public class Event
{
public string EventMessage { get; set; }
public Event() : this(null) { }
public Event(string message)
{
this.EventMessage = message;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.EventMessage;
}
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.5
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/SequentialSearchST.java.html
size() 方法只需要直接返回当前的 n 值即可。
delete() 方法需要遍历链表,找到对应结点并删除。
keys() 方法只需要根据当前的 n 新建一个数组,把链表中的键值存入即可。
代码
/// <summary>
/// 从表中删去键 <paramref name="key"/> 及其对应的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">要删除的键。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
Node before = null, target = this.first;
while (target != null && !target.Key.Equals(key))
{
before = target;
target = target.Next;
}
if (target != null)
Delete(before, target);
}
/// <summary>
/// 从链表中删除指定的结点。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="before"><paramref name="target"/> 的前驱。</param>
/// <param name="target">准备删除的结点。</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">当 <paramref name="target"/> 为 <c>null</c> 时抛出此异常。</exception>
private void Delete(Node before, Node target)
{
if (target == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("target can't be null");
if (before == null)
this.first = target.Next;
else
before.Next = target.Next;
this.n--;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获得所有的键。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>包含所有键的集合。</returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys()
{
Key[] keys = new Key[this.n];
Node pointer = this.first;
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
{
keys[i] = pointer.Key;
pointer = pointer.Next;
}
return keys;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取符号表中的键值对数量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>当前符号表中的键值对数量。</returns>
public int Size() => this.n;
另请参阅
3.1.6
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
每个单词都会被放进符号表一次,
因此 Put 的调用次数就等于单词总数 W +1(注意寻找最大值的时候有一次 Put 调用)
对于重复的单词,输入时会先调用 Get 获得当前计数之后再 Put 回去。
寻找最大值时,对于符号表中的每个键值都会调用两次 Get。
重复的单词数量 = (W - D)。
因此 Get 方法的调用次数 = (W - D) + 2D
3.1.7
解答
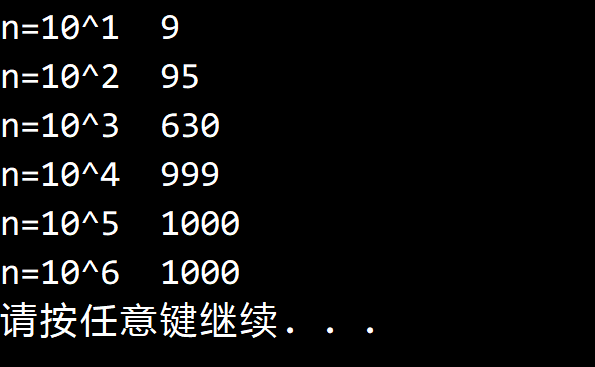
在 FrequencyCounter 中添加一个 CountDistinct 方法,计算不重复的键数。
public static int CountDistinct<TKey>(TKey[] keys, IST<TKey, int> st)
{
int distinct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < keys.Length; i++)
{
if (!st.Contains(keys[i]))
st.Put(keys[i], distinct++);
}
return distinct;
}
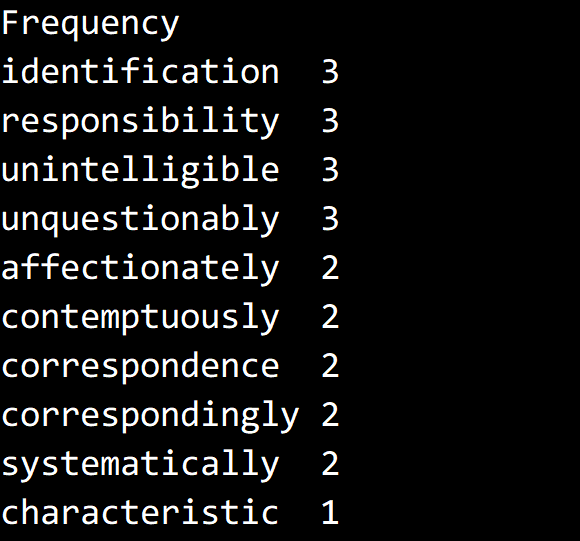
结果如下:
另请参阅
3.1.8
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
《双城记》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
官网给出的数据末尾有完整的版权说明,因此使用频率最高的单词变成了版权方的名字 Gutenberg-tm。
去掉末尾的版权声明之后,获得的单词是:Monseigneur
另请参阅
3.1.9
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
《双城记》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
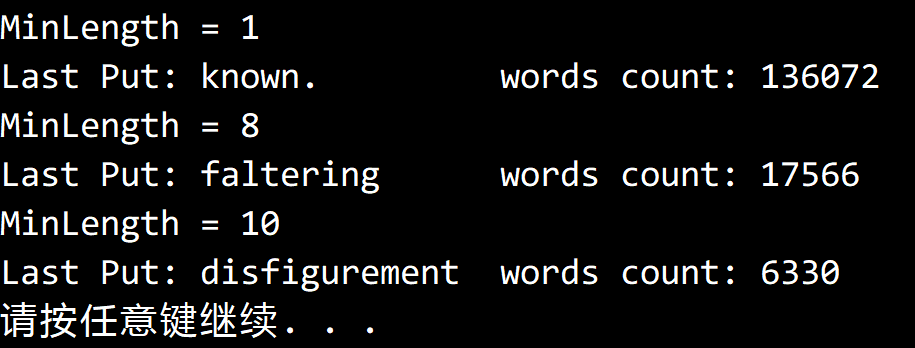
对 FrequencyCounter 做修改,在调用 Put 方法之前,将单词记录在字符串变量 lastPut 中。
在读入单词结束之后输出 lastPut 和 words 变量。
将末尾的版权信息删除后,得到的结果如下:
代码
public static string MostFrequentlyWord(string filename, int minLength, IST<string, int> st)
{
int distinct = 0, words = 0;
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(filename));
string[] inputs =
sr
.ReadToEnd()
.Split(new char[] { ' ', '
', '
' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string lastPut = "";
foreach (string s in inputs)
{
if (s.Length < minLength)
continue;
words++;
if (st.Contains(s))
{
lastPut = s;
st.Put(s, st.Get(s) + 1);
}
else
{
lastPut = s;
st.Put(s, 1);
distinct++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Last Put: " + lastPut + " words count: " + words);
string max = "";
st.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
max = s;
return max;
}
另请参阅
3.1.10
解答
如图所示:

插入新的键值对需要遍历整个链表,比较次数等于链表在插入前的键值对数目。
修改已有的键值对则需要遍历链表直到找到该键值对,比较次数等于该键值对以及它之前所有键值对的数目。
共比较 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 55 次。
3.1.11
解答
键的轨迹如下图所示:
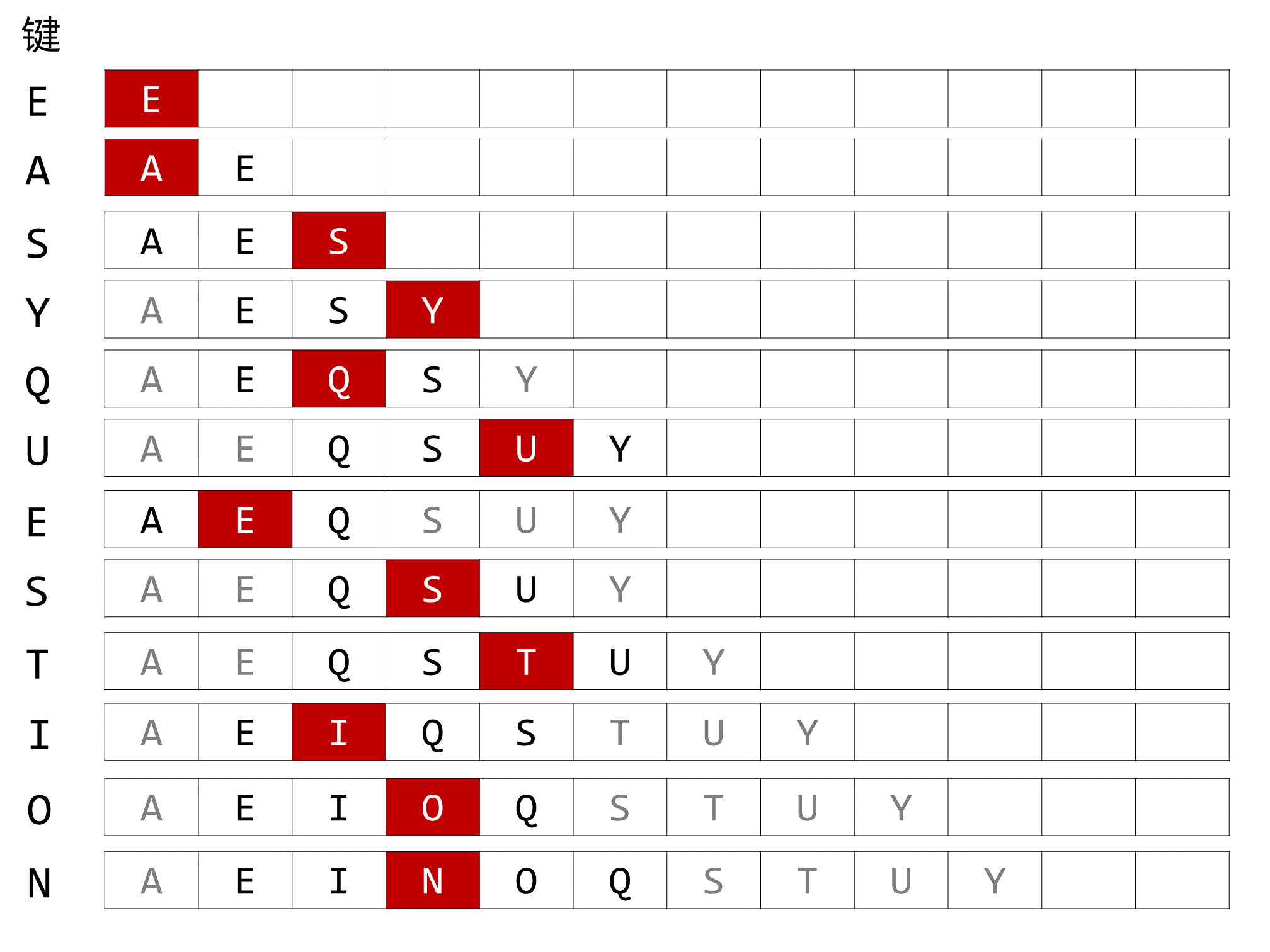
键查找使用二分查找优化,插入新的键时不必与每个键都进行比较。
共进行了 0 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 29 次比较。
3.1.12
解答
建立类 Item:
public class Item<TKey, TValue> : IComparable<Item<TKey, TValue>>
where TKey : IComparable<TKey>
{
public TKey Key { get; set; }
public TValue Value { get; set; }
public int CompareTo(Item<TKey, TValue> other)
{
return this.Key.CompareTo(other.Key);
}
}
之后修改 BinarySearchST,将其中的 TKey[] keys 和 TValue[] values 数组用 Item[] items 数组代替。
例如 keys[i] 变为 items[i].Key,values[i] 变为 items[i].Value。
添加一个构造函数,调用之前编写的归并排序实现。
/// <summary>
/// 根据已有的键值对构造一个符号表。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="items">已有的键值对。</param>
public ItemBinarySearchST(Item<TKey, TValue>[] items)
{
this.items = new Item<TKey, TValue>[items.Length];
Array.Copy(items, this.items, items.Length);
this.n = items.Length;
MergeSort merge = new MergeSort();
merge.Sort(this.items);
}
另请参阅
3.1.13
解答
Get() 调用次数比 Put() 调用次数多了三个数量级,
BinarySearchST 和 SequentialSearchST 的平均 Put() 开销是一样的,
因此选择平均 Get() 开销更小的 BinarySearchST。
3.1.14
解答
根据上题给出的结论,选择 BinarySearchST。
由于 BinarySearchST 和 SequentialSearchST 执行 Put() 的开销相同
因此选择 Get() 开销更低的 BinarySearchST。
3.1.15
解答
假设先全部 Put(),再进行查找操作。
即分别进行 $ 1 $, $ 10 ^ 3 $, $ 10 ^ 6 $ 次插入
$ N = 1 $ 时,可以直接得出比例 $ 0.1 % (。
) N = 10 ^ 3 $ 时,
插入耗时 $ = 1 + 2 + ... + 10 ^ 3 = 500500 $,
查询耗时 $ = 10 ^ 6 * lg(10 ^ 3) = 9965784 $,
比例为 $ 4.782 % (。
) N = 10 ^ 6 $ 时
插入耗时 $ = 1 + 2 + ... + 10 ^ 6 = 500000500000 $,
查询耗时 $ = 10 ^ 9 * lg(10 ^ 6) = 19931568569 $,
比例为 $ 96.17 % $。
3.1.16
解答
官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html
先通过二分查找获得下标,然后后面的元素依次向前移动一位。
public void Delete(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Delete() is null");
if (IsEmpty())
return;
int i = Rank(key);
if (i == this.n && this.keys[i].CompareTo(key) != 0)
return;
for (int j = i; j < this.n - 1; j++)
{
this.keys[j] = this.keys[j + 1];
this.values[j] = this.values[j + 1];
}
this.n--;
this.keys[this.n] = default(TKey);
this.values[this.n] = default(TValue);
if (this.n > 0 && this.n == this.keys.Length / 4)
Resize(this.n / 2);
}
另请参阅
3.1.17
解答
官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html
先通过二分查找大于等于 key 的键下标 i,
如果 keys[i] 和 key 相等则直接返回 keys[i],
否则返回 keys[i-1]。
public TKey Floor(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Floor() is null");
int i = Rank(key);
if (i < this.n && this.keys[i].CompareTo(key) == 0)
return this.keys[i];
if (i == 0)
return default(TKey);
else
return this.keys[i - 1];
}
另请参阅
3.1.18
解答
设 key 为目标键。
算法初始时 lo = 0, hi = n - 1,数组已排序。
当找到目标键时,返回的下标 mid 显然是正确的。
(0...a[mid - 1] 都小于 a[mid],同时 a[mid] = key)
接下来证明:当目标键不存在时,lo 可以代表小于 key 的键的个数。
由算法内容,当循环退出时,一定有 lo 和 hi 交叉,即 lo > hi。
考虑最后一次循环,必然执行了 lo = mid + 1 或者 hi = mid - 1。
即最后一次循环之后 lo = mid + 1 > hi 或 hi = mid - 1 < lo。
又由于 mid = (lo + hi) / 2,代入有:
即(lo + hi) / 2 + 1 > hi 或(lo + hi) / 2 - 1 < lo
(lo - hi) / 2 + 1 > 0 或(hi - lo) / 2 - 1 < 0
(hi - lo) / 2 < 1
hi - lo < 2
由于 hi 和 lo 都是整数,故有 hi -lo <= 1
由算法的内容可以得出,最后一次循环时,
下标小于 lo 的元素都小于 key,下标大于 hi 的元素都大于 key
且下标小于 lo 的元素正好有 lo 个 (0...lo - 1)。
当 lo = hi 时,mid = lo
若 key > lo,则 lo = lo + 1,即 a[lo] 本身也小于 key。
若 key < lo,lo 不变,即 a[lo] 就是大于 key 的第一个元素。
当 lo = hi - 1 时,mid = lo
若 key > lo,则 lo = lo + 1 = hi,变为上一种情况。
若 key < lo,则 hi = lo - 1,a[lo] 是大于 key 的第一个元素。
综上,Rank() 是正确的。
3.1.19
解答
将频率和当前最大频率相同的单词都放到一个队列里即可。
string max = "";
Queue<string> queue = new Queue<string>();
st.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
{
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
{
max = s;
queue.Clear();
queue.Enqueue(s);
}
else if (st.Get(s) == st.Get(max))
{
queue.Enqueue(s);
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.20
解答
国内的书中关于命题 B 的证明有错误,新版的证明如下:

虽然新版还是有个小错误,$ n-2 $ 应该改为 $ k-2 $。
勘误见:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/errata/errata-printing11.php。
先证单调性,利用数学归纳法:
已知对于 $ N=0 $,满足 $ C(0) le C(1) $。
假设对于 $ N=n $,满足 $ C(n) le C(n+1) $。
根据递归式,有:
又 $ C(n) le C(n+1) $ ,推出 $ C(lfloor n/2
floor) + 1 le C(lfloor n/2
floor + 1) + 1 $。
故 $ C(n+1) le C(n+2) (,由数学归纳法,) C(n) le C(n+1) $ 成立。
已知当 $ N = 2^k - 1 $ 时,有 $ C(N) le k = lg(N+1) le lg N + 1$。
接下来证明在 $ (2^k - 1, 2^{k + 1} -1) $ 范围内上式仍然成立。
不妨设 $ 0 < M < 2^k $ ,则有 $ 2^k - 1 < N + M < 2^{k + 1} -1 (。
转变为证:) C(N+M) le lg (N+M) + 1 $ 。
由于 $ C(N+M) $ 是一个整数,则 $ lfloor lg(N+M) +1
floor = k+1 $。
即求证: $ C(N+M) le k+1 $。
由单调性可得 $ C(N+M) le C(2^{k+1} - 1) le k+1 $,得证。
3.1.21
解答
BinarySearchST
包含一个键数组和一个值数组,以及一个 int 变量。
数组长度变化范围为 N~4N ,故总大小:
从 2 × (24 + 8N) +4 = 52 + 16N 字节 (100 %),
到 2 × (24 + 32N) +4 = 52 + 64N 字节(25 %)之间变动。
SequentialSearchST
包含 N 个结点以及一个 int 变量
(16 + 8 + 8 + 8)N + 4 = 4 + 40N 字节
3.1.22
解答
对 Get() 做修改,得到 MoveToFrontArrayST。
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
if (this.keys[i].Equals(key))
break;
if (i == this.n)
return default(TValue);
TKey toFrontKey = this.keys[i];
TValue toFrontValue = this.values[i];
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
this.keys[j] = this.keys[j - 1];
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
this.values[j] = this.values[j - 1];
this.keys[0] = toFrontKey;
this.values[0] = toFrontValue;
return this.values[0];
}
另请参阅
3.1.23
解答
这里的右移操作可以理解为 「小数点前移一位」
即数字依次向右退一位,个位上的数字被舍弃。
对于十进制,小数点前移一位会使 $ n $ 变为 $ lfloor n / 10
floor $。
同样对于二进制就会使 $ n $ 变为 $ lfloor n / 2
floor $。
当需要除以 $ 2 $ 的 $ k $ 次幂的时候,可以用右移 $ k $ 位代替并减少时间开销。
同理可以用左移 $ k $ 位来代替乘以 $ 2 $ 的 $ k $ 次幂。
注:
这样会降低程序可读性,
并且某些语言(C / C++)的编译器已经可以自动执行这项优化了。
请充分考虑你的代码受众之后再决定是否采用这种写法。
二分查找的最大查找次数 = $ lg N + 1$ (见 3.1.20 的证明)
一个数最多被左移的次数也正好等于 $ lfloor lg N
floor + 1 $
(任意正整数都能被表示为 $ 2 ^ k + m $ 的形式,即 $ k +1 $ 位二进制数)
因此一次二分查找所需的最大比较次数正好是 $ N $ 的二进制表示的位数。
3.1.24
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
二分查找总是与中间值进行比较,现在改为与数组中第 x% 位置上的元素比较。
具体而言,$ frac{k_x-k_{lo}}{k_{hi}-k_{lo}} $ 代表数组在均匀情况下目标值 $ k_x $ 的相对位置(一个比率,在数组第 x% 的位置上)。
那么相对应的下标就等于 $ lo+frac{k_x-k_{lo}}{k_{hi}-k_{lo}} imes (hi - lo) $。
用这个式子代替原来的 $ mid=lo + (hi-lo)/2 $ 即可。
不难看出这种方法对于分布相对均匀的数组比较有利,相对于二分查找而言迭代次数会少很多。
但如果数组分布不够均匀,也可能表现出不如二分查找的性能。
实验结果也证实了这一判断,就随机数组而言,插值查找相对于二分查找只有 1% 左右的性能提升。

代码
SearchCompare 在书中没有出现,但可以简单的实现为调用 FrequencyCounter 并计时的方法:
public static long Time<TKey>(IST<TKey, int> st, TKey[] keys)
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyKey(st, keys);
sw.Stop();
return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
由于这里需要使用数字而非字符串作为键值,需要对官方给出的 FrequencyCounter 做一些修改:
public static TKey MostFrequentlyKey<TKey> (IST<TKey, int> st, TKey[] keys)
{
foreach (TKey s in keys)
{
if (st.Contains(s))
st.Put(s, st.Get(s) + 1);
else
st.Put(s, 1);
}
TKey max = keys[0];
foreach (TKey s in st.Keys())
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
max = s;
return max;
}
另请参阅
3.1.25
解答
英文原文指的是 most recently accessed key,因此指的是最近访问的键。
实现比较简单,先在类中定义一个新的成员 cache 作为缓存,
然后修改 Get 方法,在实际查找之前先检查缓存,如果缓存未命中则在查找之后更新它。
要注意的是缓存指向内容的有效性,在数组中指的是下标是否有效,在链表中指的是结点是否为空。
利用《双城记》测试的结果:

代码
BinarySearchST
cache 是一个 int 类型的变量,代表下标。
在二分查找前先检查缓存,要注意cache超出数组大小的情况。
如果缓存未命中,则进行二分查找,并在返回结果前更新缓存。
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Get() is null");
if (IsEmpty())
return default(TValue);
if (this.cache < this.n && this.keys[this.cache].Equals(key)) // 缓存检查
return this.values[this.cache];
int rank = Rank(key);
if (rank < this.n && this.keys[rank].Equals(key))
{
this.cache = rank; // 更新缓存
return this.values[rank];
}
return default(TValue);
}
SequentialSearchST
cache 是一个结点类型的变量,代表一个键值对。
类似的,在顺序查找前先检查缓存,如果缓存未命中则更新缓存。
要注意的是如果缓存的结点被删除,需要将缓存置为 null。
Get() 方法
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
if (this.cache != null && this.cache.Key.Equals(key)) // 检查缓存
return this.cache.Value;
for (Node pointer = this.first; pointer != null; pointer = pointer.Next)
{
if (pointer.Key.Equals(key))
{
this.cache = pointer; // 更新缓存
return pointer.Value;
}
}
return default(TValue);
}
Delete() 方法
public void Delete(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
Node before = null, target = this.first;
while (target != null && !target.Key.Equals(key))
{
before = target;
target = target.Next;
}
if (target == this.cache) // 删除缓存
this.cache = null;
if (target != null)
Delete(before, target);
}
另请参阅
3.1.26
解答
字典文件:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/web2.txt
《双城记》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
浏览器可能会直接打开 txt,此时右键链接-目标另存为即可下载。
FrequencyCounter 的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
我们利用 BinarySearchST 会自动对键排序的性质来实现字典序排序。
首先将字典存到一个符号表中,按照 “单词-序号” 的形式保存。
然后读入文件,如果读入的单词存在于字典中,
则将其以 “序号-单词” 的形式存到 BinarySearchST 中去。
读入完毕后,遍历 BinarySearchST 即可获得字典序的单词列表。
对于按频率排序,我们基于已有的实现修改。
在每次取得最大值之后,输出并删除最大值,如此循环即可获得频率排序的单词序列。
也可以将单词-频率序列全部读出来存放到数组之中,然后用第二章的排序算法排序。
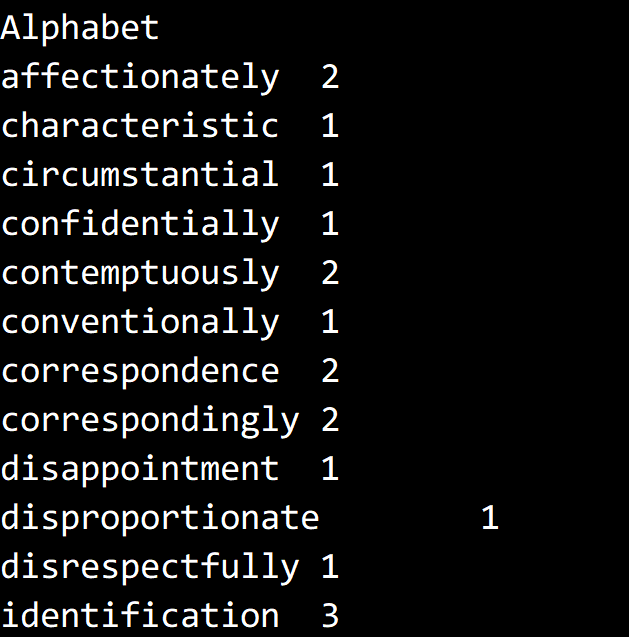
测试结果,取 minLength = 13,只截取了部分。
代码
public static void LookUpDictionary(string filename, string dictionaryFile, int minLength)
{
// 初始化字典
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(dictionaryFile));
string[] words = sr.ReadToEnd().Split(new char[] { ' ', '
', '
' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
BinarySearchST<string, int> dictionary = new BinarySearchST<string, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.Length; i++)
{
if (words[i].Length > minLength)
dictionary.Put(words[i], i);
}
sr.Close();
// 读入单词
StreamReader srFile = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(filename));
string[] inputs = srFile.ReadToEnd().Split(new char[] { ' ', '
', '
' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
srFile.Close();
BinarySearchST<int, string> stDictionary = new BinarySearchST<int, string>();
BinarySearchST<string, int> stFrequency = new BinarySearchST<string, int>();
foreach (string s in inputs)
{
if (stFrequency.Contains(s))
stFrequency.Put(s, stFrequency.Get(s) + 1);
else if (dictionary.Contains(s))
{
stFrequency.Put(s, 1);
stDictionary.Put(dictionary.Get(s), s);
}
}
// 输出字典序
Console.WriteLine("Alphabet");
foreach (int i in stDictionary.Keys())
{
string s = stDictionary.Get(i);
Console.WriteLine(s + " " + stFrequency.Get(s));
}
// 频率序
Console.WriteLine("Frequency");
int n = stFrequency.Size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string max = "";
stFrequency.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in stFrequency.Keys())
if (stFrequency.Get(s) > stFrequency.Get(max))
max = s;
Console.WriteLine(max + " " + stFrequency.Get(max));
stFrequency.Delete(max);
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.27
解答
事实上就是说,先构造一个包含 N 个不重复键的符号表,然后进行 S 次查找。
给出 S 的增长数量级,使得构造符号表的成本和查找的成本相同。
这里假设一次数组交换和一次比较的成本是相同的。
先考虑构造符号表的成本,一次 Put() 需要调用一次 Rank() 和一次插入操作。
2.1 节插入排序的命题 B 给出了每次插入平均需要移动一半的数组元素的结论。
于是构造符号表所需的成本约为:$nlg n + frac{1}{2}sum_{k=1}^{n} k=nlg n + frac{n(n-1)}{4} $ 。
这里查找的成本是这么计算的:$ lg0+lg1+cdots+lg n < nlg n $
查找所需的成本比较简单,一次二分查找的比较次数约为 $ lg n $,总成本就是 $ Slg n $ 。
令两边相等,解方程即可得到 $ S=n+frac{n(n-1)}{4lg n} $ 。
如果用大 O 记法,也可以记为 $ O(n^2 / lg n) $,如果要选择一个比较常用的上界则可以选择 $ O(n^2) $。
实验结果,两边的成本是很接近的:

另请参阅
3.1.28
解答
将重新分配数组空间的代码提前,然后添加判断语句即可。
BinarySearchSTOrderedInsertion:
/* 省略 */
if (this.n == this.keys.Length)
Resize(this.n * 2);
// 如果插入的键比所有键都大则直接插入末尾。
if (this.n == 0 || this.keys[this.n - 1].CompareTo(key) < 0)
{
this.keys[this.n] = key;
this.values[this.n] = value;
this.n++;
return;
}
int i = Rank(key);
/* 省略 */
另请参阅
3.1.29
解答
官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/TestBinarySearchST.java.html
官方实现中有几处错误,需要做一些修改。
/* 省略 */
Console.WriteLine("Testing Select()");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < st.Size(); i++) // 循环条件不能有 '='
Console.WriteLine(i + " " + st.Select(i));
Console.WriteLine();
/* 省略 */
while (!st.IsEmpty())
st.Delete(st.Select(st.Size() / 2));
Console.WriteLine("After deleting the remaining keys");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
// 异常处理
try
{
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
Console.WriteLine(s + " " + st.Get(s));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: " + ex.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine();
/* 省略 */
结果如下:
size = 10
min = A
max = X
Testing Keys()
-----------------------------------
A 8
C 4
E 12
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7
Testing Select()
-----------------------------------
0 A
1 C
2 E
3 H
4 L
5 M
6 P
7 R
8 S
9 X
key Rank Floor Ceil
-----------------------------------
A 0 A A
B 1 A C
C 1 C C
D 2 C E
E 2 E E
F 3 E H
G 3 E H
H 3 H H
I 4 H L
J 4 H L
K 4 H L
L 4 L L
M 5 M M
N 6 M P
O 6 M P
P 6 P P
Q 7 P R
R 7 R R
S 8 S S
T 9 S X
U 9 S X
V 9 S X
W 9 S X
X 9 X X
Y 10 X
Z 10 X
After deleting the smallest 3 keys
-----------------------------------
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7
After deleting the remaining keys
-----------------------------------
Exception: called Min() with empty table
After adding back N keys
-----------------------------------
A 8
C 4
E 12
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7
另请参阅
3.1.30
解答
官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html。
首先在 BinarySearchST 中添加如下方法。
/// <summary> 检查符号表结构是否有效。 </summary>
private bool Check() => IsSorted() && RankCheck();
/// <summary> 检查 <see cref="keys"/> 数组是否有序。 </summary>
private bool IsSorted()
{
for (int i = 1; i < Size(); i++)
if (this.keys[i].CompareTo(this.keys[i - 1]) < 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/// <summary> 检查 Rank(Select(i)) = i 是否成立。 </summary>
private bool RankCheck()
{
for (int i = 0; i < Size(); i++)
if (i != Rank(Select(i)))
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < Size(); i++)
if (keys[i].CompareTo(Select(Rank(this.keys[i]))) != 0)
return false;
return true;
}
然后在 Put() 和 Delete() 方法的末尾添加:Debug.Assert(Check()); 即可。
另请参阅
3.1.31
解答
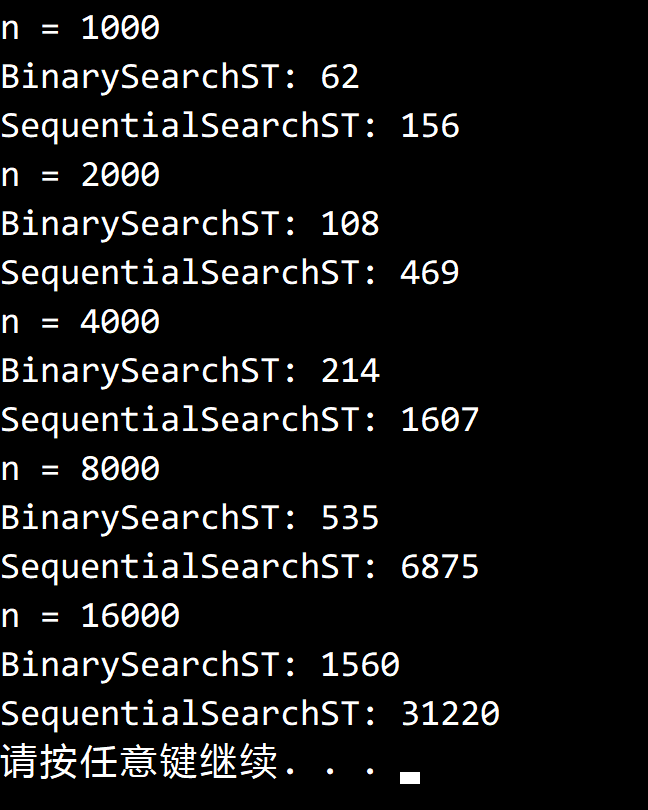
性能测试方法构造如下:
先编写一个随机字符串方法,生成一个长度大于 50 的字符串(作为未命中访问)。
然后随机生成符合要求的字符串数组,将它们全部放入符号表中。
然后遍历 10 次生成的字符串数组,对于数组中的每个元素都进行一次命中查询。
同时在每次命中查询的同时都进行一次未命中查询即可。
测试结果:
代码
按照要求编写代码,在 SearchCompare 类里添加一个 Random random 成员,并添加如下方法:
随机字符串发生器:
public static string GetRandomString(int minLength, int maxLength)
{
int length = random.Next(minLength, maxLength);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
double choice = random.NextDouble();
if (choice < 0.333)
sb.Append((char)random.Next('A', 'Z'));
else if (choice < 0.666)
sb.Append((char)random.Next('a', 'z'));
else
sb.Append((char)random.Next('0', '9'));
}
return sb.ToString();
}
生成随机字符串数组:
public static string[] GetRandomArrayString(int n, int minLength, int maxLength)
{
string[] result = new string[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
result[i] = GetRandomString(minLength, maxLength);
}
return result;
}
测试方法:
public static long Performance(IST<string, int> st, int n, int averageHit)
{
string[] keys = GetRandomArrayString(n, 2, 50);
string keyNotExist = GetRandomString(51, 52);
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
// 构建
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
st.Put(keys[i], i);
// 查询
for (int i = 0; i < averageHit; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
st.Get(keys[j]);
st.Get(keyNotExist);
}
}
sw.Stop();
return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
另请参阅
3.1.32
解答
编码实现即可,实验结果如下:
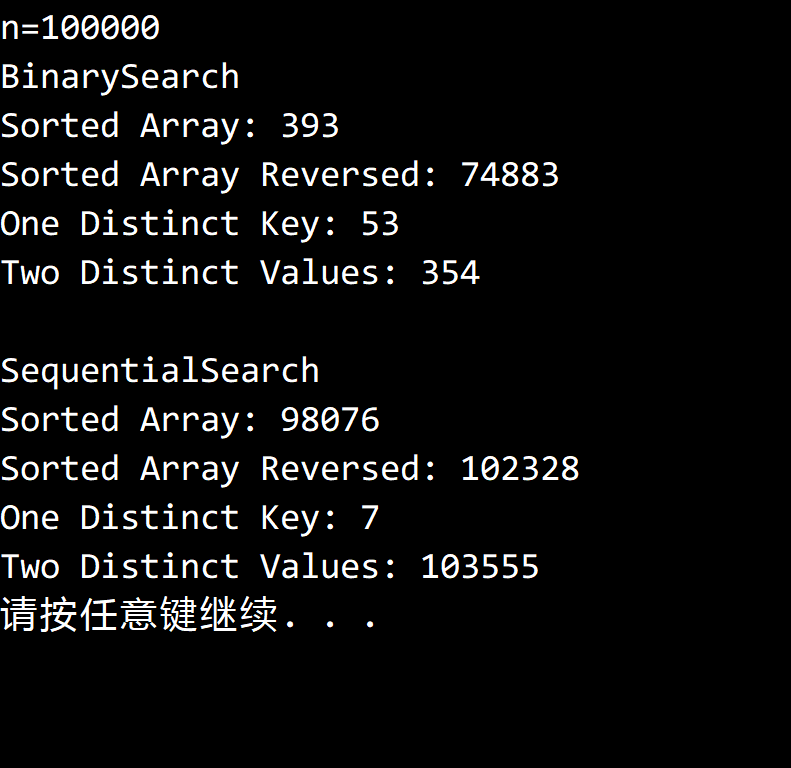
对于保持键有序的 BinarySearchST 来说,逆序输入是最坏情况,顺序输入则是最好情况。
而对于键无序的 SequentialSearchST 来说,输入顺序对于性能的影响不大。
只有一种键的时候,每次 Put 都只需要比较一次,值一直在被替换。
只有两种值对性能的影响不大,性能主要由输入的键决定。
代码
测试方法,IST 代表一个符号表。
static void Test(IST<string, int>[] sts, int n)
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
string[] data = SearchCompare.GetRandomArrayString(n, 3, 10);
string item1 = "item1";
Array.Sort(data);
// 有序的数组
Console.Write("Sorted Array: ");
sw.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sts[0].Put(data[i], i);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
// 逆序的数组
Console.Write("Sorted Array Reversed: ");
sw.Restart();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
sts[1].Put(data[i], i);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
// 只有一种键
Console.Write("One Distinct Key: ");
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sts[2].Put(item1, i);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
// 只有两种值
Console.Write("Two Distinct Values: ");
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sts[3].Put(data[i], i % 2);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
}
另请参阅
3.1.33
解答
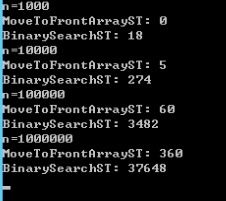
概率分布的实现方式:
假设存有键的数组为 keys,对 keys 排序。
然后再建立一个长度为 10N 的数组 querys,
前 1/2 置为 keys[0],1/2 到 3/4 置为 keys[1],以此类推,直到数组填满。
然后遍历 query 数组,对符号表进行 Get() 操作。
实验结果如下:
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 1000;
int multiplyBy10 = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < multiplyBy10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("n=" + n);
// 构造表
BinarySearchST<string, int> bst = new BinarySearchST<string, int>(n);
MoveToFrontArrayST<string, int> mst = new MoveToFrontArrayST<string, int>(n);
string[] keys = SearchCompare.GetRandomArrayString(n, 3, 20);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
bst.Put(keys[j], j);
mst.Put(keys[j], j);
}
// 构造查询
Array.Sort(keys);
string[] querys = new string[10 * n];
int queryIndex = 0, keyIndex = 0;
while (queryIndex < querys.Length)
{
int searchTimes = (int)Math.Ceiling((Math.Pow(0.5, keyIndex + 1) * querys.Length));
for (int j = 0; j < searchTimes && queryIndex < querys.Length; j++)
{
querys[queryIndex++] = keys[keyIndex];
}
keyIndex++;
}
Shuffle(querys);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
// 测试 MoveToFrontArrayST
sw.Start();
for (int j = 0; j < querys.Length; j++)
{
mst.Get(querys[j]);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("MoveToFrontArrayST: " + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
// 测试 BinarySearchST
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < querys.Length; j++)
{
bst.Get(querys[j]);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("BinarySearchST: " + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
n *= 10;
}
}
static void Shuffle<T>(T[] data)
{
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
int r = i + random.Next(data.Length - i);
T temp = data[r];
data[r] = data[i];
data[i] = temp;
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.34
解答
在上一题的基础上进行修改即可,链接:{% post_link 3.1.33 %}。
调和级数 $ H_n = 1+frac{1}{2}+frac{1}{3} + cdots+frac{1}{n} $ 。
查询数组变为前 1/2 为 key[0],随后的 1/3 为 key[1],以此类推。
和上一题中的序列进行比较即可,注意删除最后的打乱步骤。
实验结果如下:
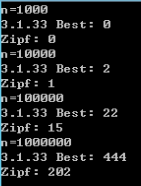
代码
首先建立一个数组计算调和级数,就像这样:
// 调和级数
double[] harmonicNumber = new double[1000 * (int)Math.Pow(10, 4)];
harmonicNumber[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < harmonicNumber.Length; i++)
{
harmonicNumber[i] = harmonicNumber[i - 1] + 1 / (i + 1);
}
然后修改构造查询的代码:
// 构造查询
Array.Sort(keys);
string[] queryZipf = new string[10 * n];
int queryIndex = 0, keyIndex = 0;
while (queryIndex < queryZipf.Length)
{
int searchTimes = (int)Math.Ceiling(queryZipf.Length / (harmonicNumber[keyIndex + 1] * (i + 1)));
for (int j = 0; j < searchTimes && queryIndex < queryZipf.Length; j++)
{
queryZipf[queryIndex++] = keys[keyIndex];
}
keyIndex++;
}
另请参阅
3.1.35
解答
实验结果:
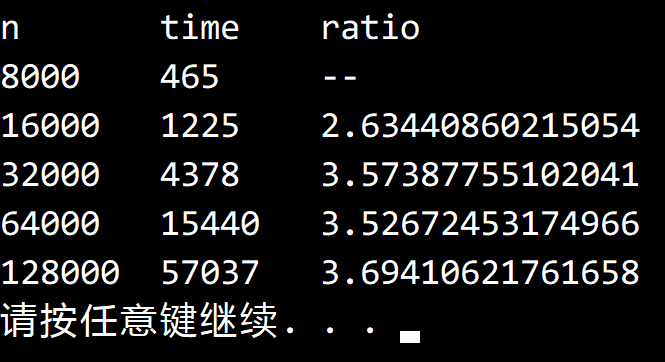
由于包含重复单词,因此结果会比 4 略低一些。
需要对 FrequencyCounter 做一些修改,令其只取前 n 个单词。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 8000;
int multiplyBy2 = 5;
int repeatTimes = 5;
double lastTime = -1;
Console.WriteLine("n time ratio");
for (int i = 0; i < multiplyBy2; i++)
{
Console.Write(n + " ");
long timeSum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < repeatTimes; j++)
{
SequentialSearchST<string, int> st = new SequentialSearchST<string, int>();
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyWord("tale.txt", n, 0, st);
sw.Stop();
timeSum += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
timeSum /= repeatTimes;
Console.Write(timeSum + " ");
if (lastTime < 0)
Console.WriteLine("--");
else
Console.WriteLine(timeSum / lastTime);
lastTime = timeSum;
n *= 2;
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.36
解答
实验结果如下,增长级为 O(N) ,但速度很快。

其实只要列出《双城记》不同长度的单词数目,原因就一目了然了。
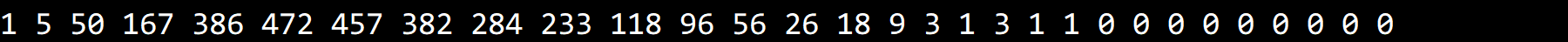
大部分单词都集中在中间长度,因此大部分访问也集中在数组中部。
二分查找在访问数组中部的元素时速度很快,因此结果好于预期。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 8000;
int multiplyBy2 = 5;
int repeatTimes = 5;
double lastTime = -1;
Console.WriteLine("n time ratio");
for (int i = 0; i < multiplyBy2; i++)
{
Console.Write(n + " ");
long timeSum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < repeatTimes; j++)
{
BinarySearchST<string, int> st = new BinarySearchST<string, int>();
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyWord("tale.txt", n, 0, st);
sw.Stop();
timeSum += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
timeSum /= repeatTimes;
Console.Write(timeSum + " ");
if (lastTime < 0)
Console.WriteLine("--");
else
Console.WriteLine(timeSum / lastTime);
lastTime = timeSum;
n *= 2;
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.37
解答
实验结果如下:
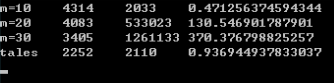
M=10 的时候随机的数字集中在 1024 到 2048 之间,重复值较多,因此 Put 耗时较少。
随着重复值的减少 Put 的耗时会大幅度提高,和实验结果显示的一样。
M=20 的时候数字在 1048576~2097152 之间随机,基本上没有重复值了。
M=30 的时候和 M=20 的情况类似,都是重复值几乎没有的情况。
随机数可以通过如下的方式产生:
result[i] = min + (long)(random.NextDouble() * (max - min));
代码
这里构造了 BinarySearchSTAnalysis 类,在类中声明了两个 Stopwatch 对象,
一个在 Put 方法的开始和结束部分进行计时,
另一个在 Get 方法的开始和结束部分进行计时。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 1000000;
int m = 10;
int addBy10 = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < addBy10; i++)
{
BinarySearchSTAnalysis<long, int> bst = new BinarySearchSTAnalysis<long, int>(n);
long[] data = SearchCompare.GetRandomArrayLong(n, (long)Math.Pow(2, m), (long)Math.Pow(2, m + 1));
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyKey(bst, data);
Console.WriteLine("m=" + m + " " + bst.GetTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds + " " + bst.PutTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds + " " + bst.PutTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds / (double)bst.GetTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds);
m += 10;
}
BinarySearchSTAnalysis<string, int> st = new BinarySearchSTAnalysis<string, int>();
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyWord("tale.txt", 0, st);
Console.WriteLine("tales " + st.GetTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds + " " + st.PutTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds + " " + st.PutTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds / (double)st.GetTimer.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.ReadLine();
}
另请参阅
3.1.38
解答
实验结果如下:
BinarySearchST
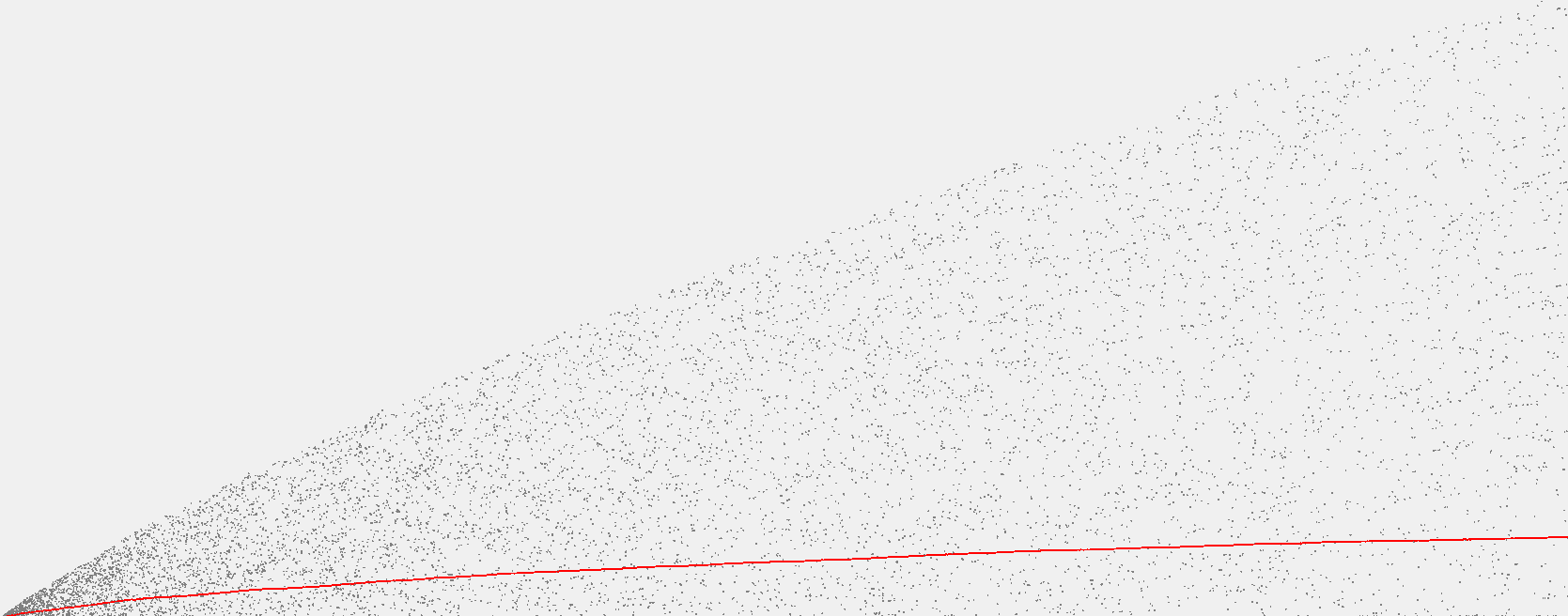
SequentialSearchST
对于 BinarySearchST ,每次比较之后以及移动元素时令 Cost 增加。
对于 SequentialSearchST,统计每次的查找次数即可。
然后绘制成散点图即可。
代码
有关绘图的函数,传入的参数为第 i 次 Put() 的开销。
public void Draw(int[] data)
{
Graphics panel = this.CreateGraphics();
float unitX = (float)this.ClientRectangle.Width / data.Length;
float unitY = (float)this.ClientRectangle.Height / data.Max();
int accumulation = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
// Gray
panel.FillEllipse(Brushes.Gray, (i + 1) * unitX, this.ClientRectangle.Bottom - data[i] * unitY, 2, 2);
// Red
panel.FillEllipse(Brushes.Red, (i + 1) * unitX, this.ClientRectangle.Bottom - accumulation / (i + 1) * unitY, 2, 2);
accumulation += data[i];
}
}
另请参阅
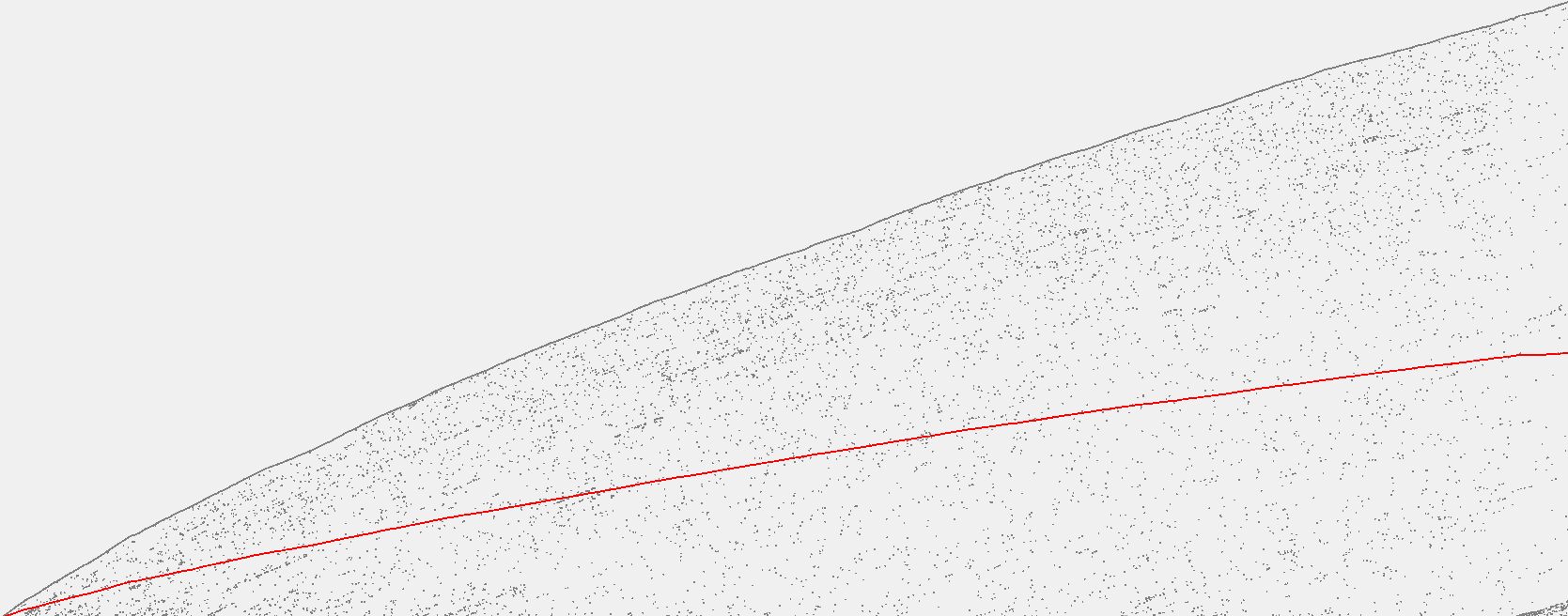
3.1.39
解答
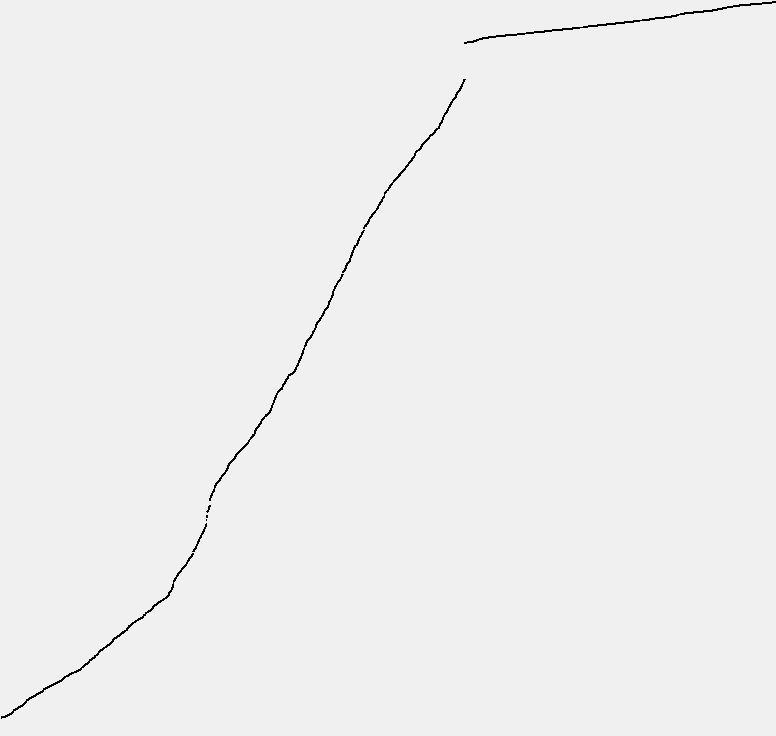
实验结果如下:
BinarySearchST

SequentialSearchST

图像分为两段,分别代表不断向符号表中加入单词和寻找频率最大的单词两个部分。
第一段两个图像的形状类似(注意它们的 y 轴比例不同)。
第二段中 BinarySearchST 的表现要比 SequentialSearchST 稳定的多。
代码
绘图部分代码:
public void Draw(int[] x, long[] y)
{
Graphics panel = this.CreateGraphics();
float unitX = (float)this.ClientRectangle.Width / x.Max();
float unitY = (float)this.ClientRectangle.Height / y.Max();
for (int i = 0; i < x.Length; i++)
{
panel.FillEllipse(
Brushes.Black,
x[i] * unitX,
this.ClientRectangle.Height - y[i] * unitY,
2, 2);
}
}
另请参阅
3.1.40
解答
顺序查找平均需要进行 $ N/2 $ 次比较,二分查找则是 $ lg N $ 次。
列出方程可以解出 N 的大小
这个方程是一个超越方程,最后的结果中出现了朗伯 W 函数。
同理可以求得 10000 倍的 N=369939。
实验结果如下:
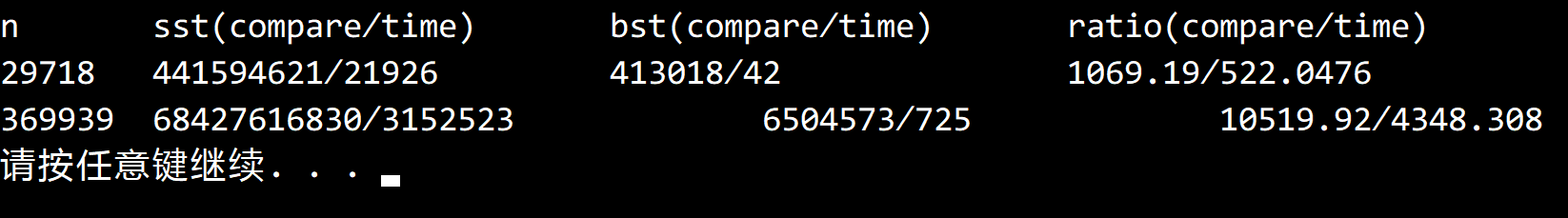
由于存在缓存优化,每次比较的耗时并不相同。
因此实际耗时并未达到预期,但比较次数是符合预期的。
另请参阅
3.1.41
解答
英文版描述为 1, 2, and 10 times faster。
即一样快,快一倍和快十倍(一个例子)。
和上题类似,也是解超越方程。
插值查找的平均查找次数为 $ lg(lg(N)) $。
可以解得 N = 1, 4, 58。
实验结果如下:
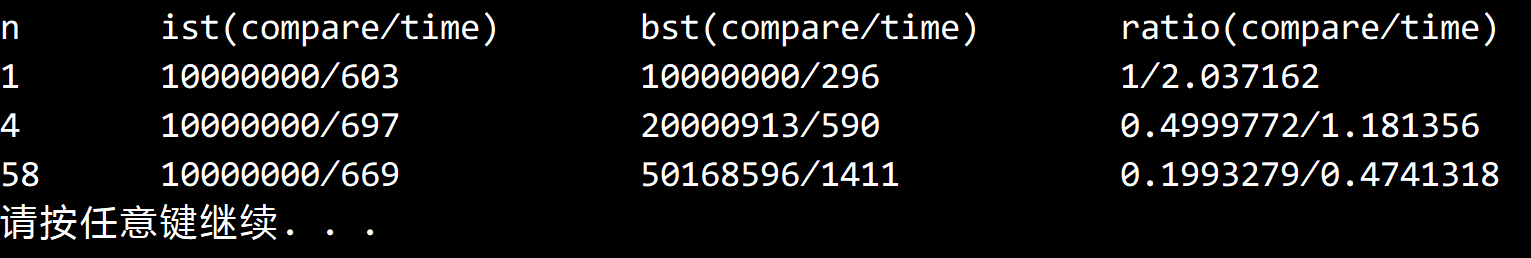
由于 N 太小,可以看到插值查找的运行时间几乎没有变化。