[抄题]:
We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation:
The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5)
have values 7, 4, and 1.
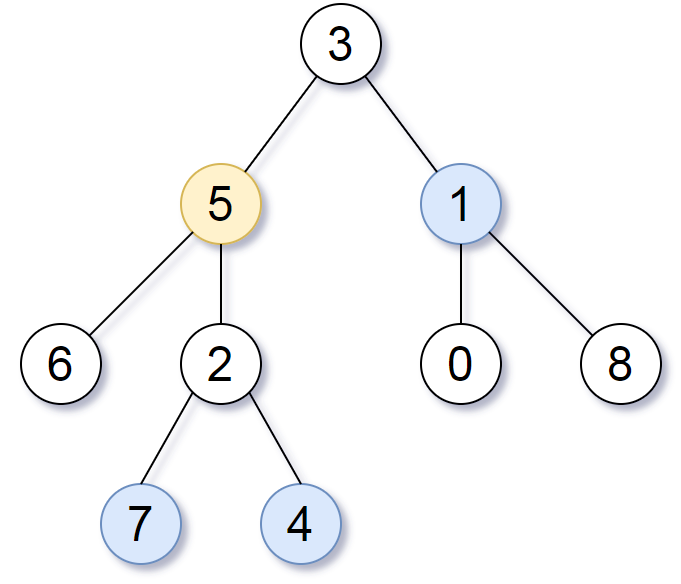 Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note:
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values
0 <= node.val <= 500. - The
targetnode is a node in the tree. 0 <= K <= 1000.
[暴力解法]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[优化后]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[奇葩输出条件]:
[奇葩corner case]:
[思维问题]:
没啥思路,以为是dfs就可以了。但是其实分为两步:
存储:把root,左右长度存在map中
取出来:length每次加一,递增为k
[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
[一句话思路]:
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:
[一刷]:
- map中存的距离是找出left之后,left+1
- 在map中找root之前要先判断是否有这个key
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
[总结]:
先在左边右边用dfs生成长度,存map。再用dfs的length+1找出所有节点
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O(n) Space complexity: O(n)
[算法思想:迭代/递归/分治/贪心]:
[关键模板化代码]:
int left = find(root.left, target, K); if (left >= 0) { map.put(root, left + 1); return left + 1; }
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
[代码风格] :
[是否头一次写此类driver funcion的代码] :
[潜台词] :

class Solution { //initialization: hashmap HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>(); public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); find(root, target, K); dfs(root, 0, target, K, result); return result; } //find and store length public int find(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { //corner case: root == null if (root == null) return -1; //root.val == target if (target == root) { map.put(root, 0); return 0; } //define left, right and add int left = find(root.left, target, K); if (left >= 0) { map.put(root, left + 1); return left + 1; } int right = find(root.right, target, K); if (right >= 0) { map.put(root, right + 1); return right + 1; } return -1; } //add the points to res public void dfs(TreeNode root, int length, TreeNode target, int K, List<Integer> res) { //corner case if (root == null) return ; //get length if there is key if (map.containsKey(root)) { length = map.get(root); } //add to res if (length == K) res.add(root.val); //dfs in left and right dfs(root.left, length + 1, target, K, res); dfs(root.right, length + 1, target, K, res); } }
