上一篇文章介绍了shiro在spring-boot中通过filter实现authentication流程(通过设置filterMaps也可以达到authorization的目的);这篇文章主要介绍spring通过AOP的方式实现shiro的authorization的流程。
ShiroAnnotationProcessorAutoConfiguration
shiro-spring-boot-web-starter除了自身在META-INF中定义了ShiroWebAutoConfiguration和ShiroWebFilterConfiguration外,还在pom文件中引用了shiro-spring-boot-stater。而后者在自己的META-INF文件中又定义了三个配置类:
ShiroAutoConfiguration:主要将shiro中重要的组件声明成bean。大部分配置被ShiroWebAutoConfiguration中的bean取代。ShiroBeanAutoConfiguration:主要设置了EventBus(便于监听各种事件)和LifecycleBeanPostProcessor(生命周期管理,对象的初始化和销毁)。ShiroAnnotationProcessorAutoConfiguration:顾名思义,shiro注解处理相关的bean都在这个类中配置。
@SuppressWarnings("SpringFacetCodeInspection")
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "shiro.annotations.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class ShiroAnnotationProcessorAutoConfiguration extends AbstractShiroAnnotationProcessorConfiguration {
//负责创建代理类的对象
@Bean
@DependsOn("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Override
public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() {
return super.defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator();
}
//声明了Adviosr,Advisor声明了Pointcut和Advice,即规定了在哪些地方做哪些事
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Override
public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(SecurityManager securityManager) {
return super.authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(securityManager);
}
}
所以shiro通过声明了Advisor,以AOP的方式在执行某些方法前先进行权限校验。
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator和创建代理的流程
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是spring框架提供的用来创建代理的类。可以通过这个类理清spring创建代理的流程。先了解DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的类继承关系。图中删除了部分继承关系,只保留了最主要的内容:
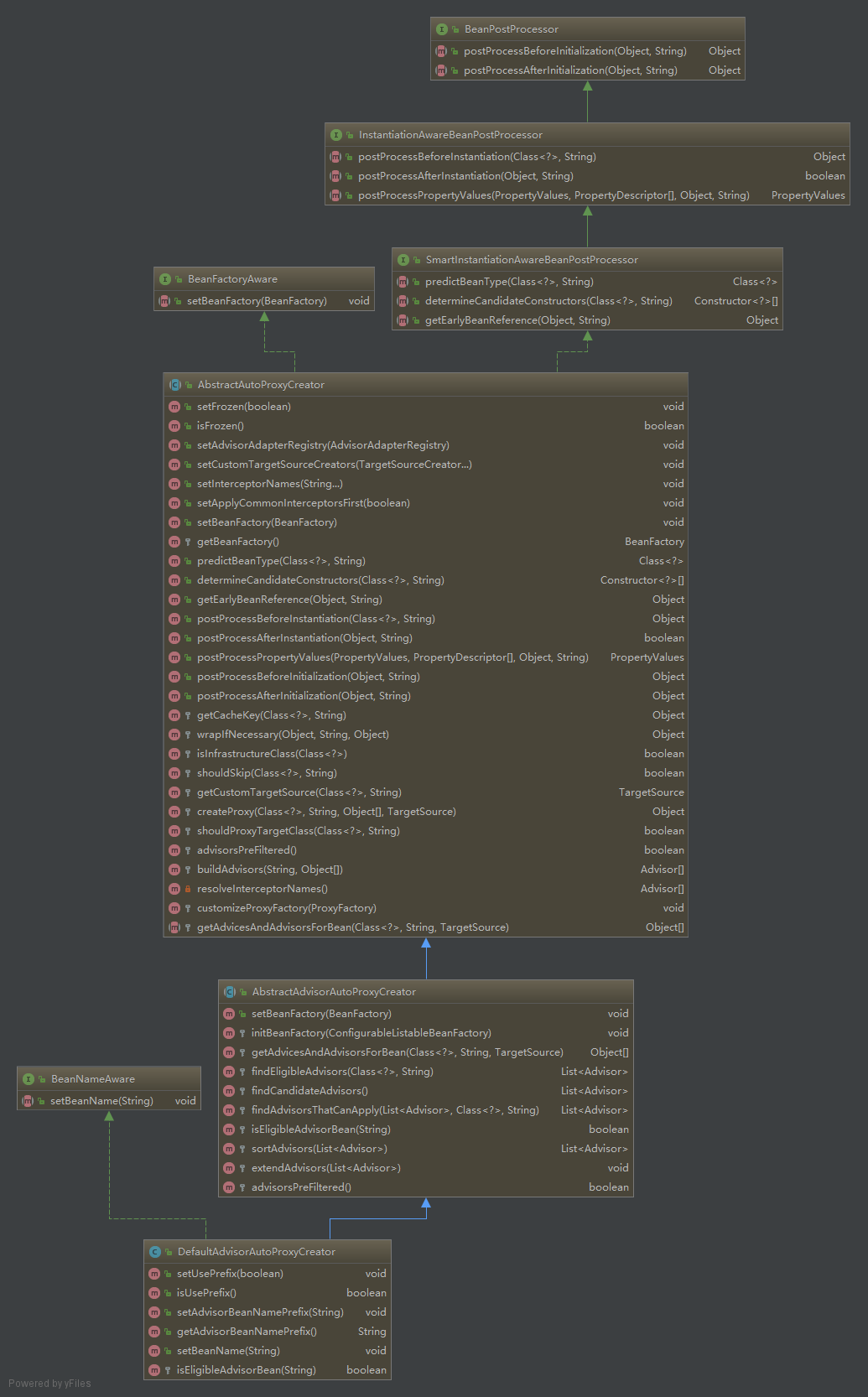
从接口的继承关系中可以看到,该类的处理可能处于类的实例化前后(Instantiation)和初始化前后(Initialization)。
下面的分析将以Bean的创建流程为顺序。
- Bean实例化前:
实例化前的操作主要是在postProcessBeforeInstantiation()中。
//实例化前置处理(该方法会在bean实例化前调用,且如果该方法返回不会空,则不会在创建bean的实例)
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
//
if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
//是否已经被代理过
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
//AOP相关的系统类 和 需要跳过的类(交由子类根据具体需求拓展) 不需要代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
//如果定义了符合该Bean的TargetSource,那么使用TargetSource为该Bean创建代理
//TargetSource可以让用户自定义代理的过程
if (beanName != null) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
- 创建Bean实例:
如果在postProcessBeanBeforeInstantication中已经创建了Bean的代理对象,则会跳过createBean的过程。 - 实例化后置处理
postProcessAfterInstantication():
该方法返回boolean型的值,决定是否继续执行是剩下的InstantationAwareBeanPostProcessor。 - 初始化前置处理
postProcessBeforeInitialization():这里不对bean做任务处理直接返回。
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
- bean初始化,这个阶段可能会设置bean的属性
- 初始化后置处理
postProcessAfterInitialization()。这一步是spring创建代理的过程。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
//获取缓存的key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
//获取是否在之前已经对其代理过
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
//如果需要代理,则对其进行包装
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
其中的wrapIfNecessary就是为bean创建代理的过程。先判断该bean是否需要创建代理,如果需要则创建代理封装该bean。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
//判断是否已经由TargetSource产生过代理
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//判断是否已经解析过该bean,且结果是不需要代理
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
//判断是否是AOP相关类 或是 不需要代理的类
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
//获取该Bean相关的Advice
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
//如果不等于空,则说明需要代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
决定这个bean是否要代理的一个重要过程是getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean()。这个方法会返回需要应用在该bean上的advice或是advisor。如果返回为空,则说明不需要代理。这个方法的具体实现是在AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。
//获取可以应用在该bean上的advise或advisor
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
//具体查找方法交给findEligibleAdvisors实现
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
//如果没找到,则返回特定对象 表示不需要代理
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
//否则转成数组返回
return advisors.toArray();
}
//查询核实的advisor方法
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//找出所有的advisor做候选
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//再在候选的advisor筛选出适用的
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
//拓展Advisor
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
//排序
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
//查找候选advisor的方法委托给BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
//获取适用的Advisor,主要委托给AopUtil
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
/**
* Return whether the Advisor bean with the given name is eligible
* for proxying in the first place.
* @param beanName the name of the Advisor bean
* @return whether the bean is eligible
*/
protected boolean isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName) {
return true;
}
//对Advisor排序
protected List<Advisor> sortAdvisors(List<Advisor> advisors) {
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(advisors);
return advisors;
}
BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans()大概过程就是先通过在beanFactory中查询类型为Advisor.class或其子类的的bean的name。然后根据beanName,再从beanFactory中根据beanName获取对应的Advisor的bean。
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// 如果已经缓存过,则直接使用缓存的结果
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
//没缓存 则在BeanFactory中搜索一次
if (advisorNames == null) {
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the auto-proxy creator apply to them!
//根据Advisor类型查询
//这里只是获取bean的name,并未进行实例化
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<Advisor>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<Advisor>();
//根据beanName获取对应的Advisor的bean
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
}
else {
try {
//实例化advisor的bean advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bce.getBeanName())) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
再来看决定Advisors是否适用的过程:AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply()。
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
主要是将Advisor根据不同的类型分成两类:IntroducationAdvisor和PointcutAdvisor。两种Advisor因为类型不同,所以判断方式也不一样。IntroductionAdvisor因为是类级别的拦截,它描述的”切点“是针对类,所以是通过ClassFilter来判断。而PointcutAdvisor可以针对方法,通过Pointcut描述切点。这点可以从canApply()中看出。
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
//IntroductionAdvisor直接通过classFilter匹配
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
//PointcutAdvisor则是通过pointcut,在调用canApply的重载方法实现
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
找到Advisor之后,剩下的就是创建代理的过程。回到wrapIfNecessary,创建代理的过程在createProxy()中。
//创建代理对象
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建代理工厂类,并且拷贝需要的配置
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//将拦截器封装成advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
//设置拦截器和TargetSource
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
//留给子类根据需要拓展
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//创建代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
上述方法中主要是创建了ProxyFactory对象,并设置属性,在通过ProxyFactory对象创建代理对象。
最后返回的代理对象便取代了原始的bean对象保存在spring容器中待取用。
如果对上述流程图还有不清楚的地方,可以参考我画的流程图。
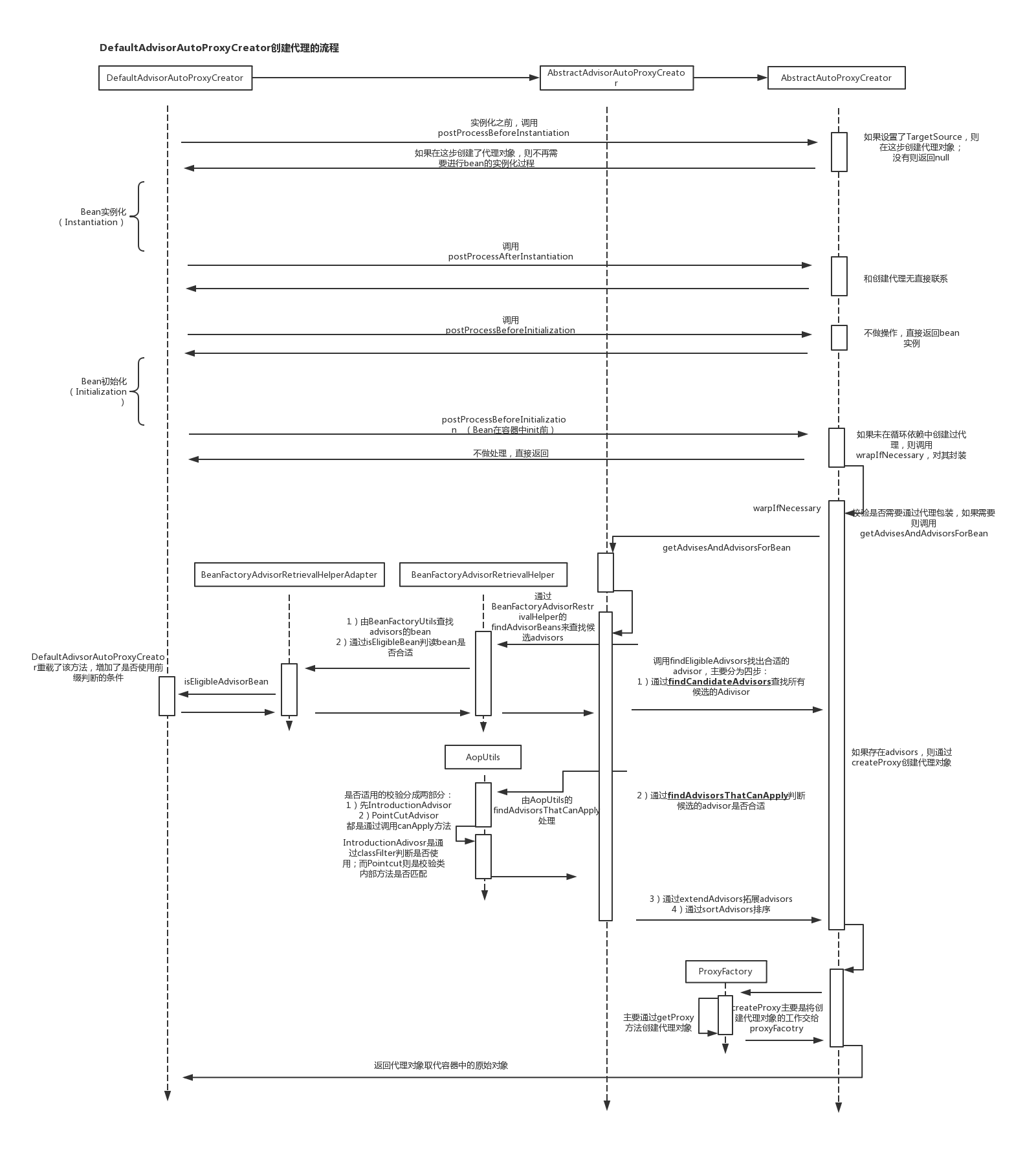
shiro生命的Advisor:AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor
通过上述流程我们了解了spring如何根据advisor创建代理。现在我们要了解的是shiro的advisor:AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor。
类的关系图:
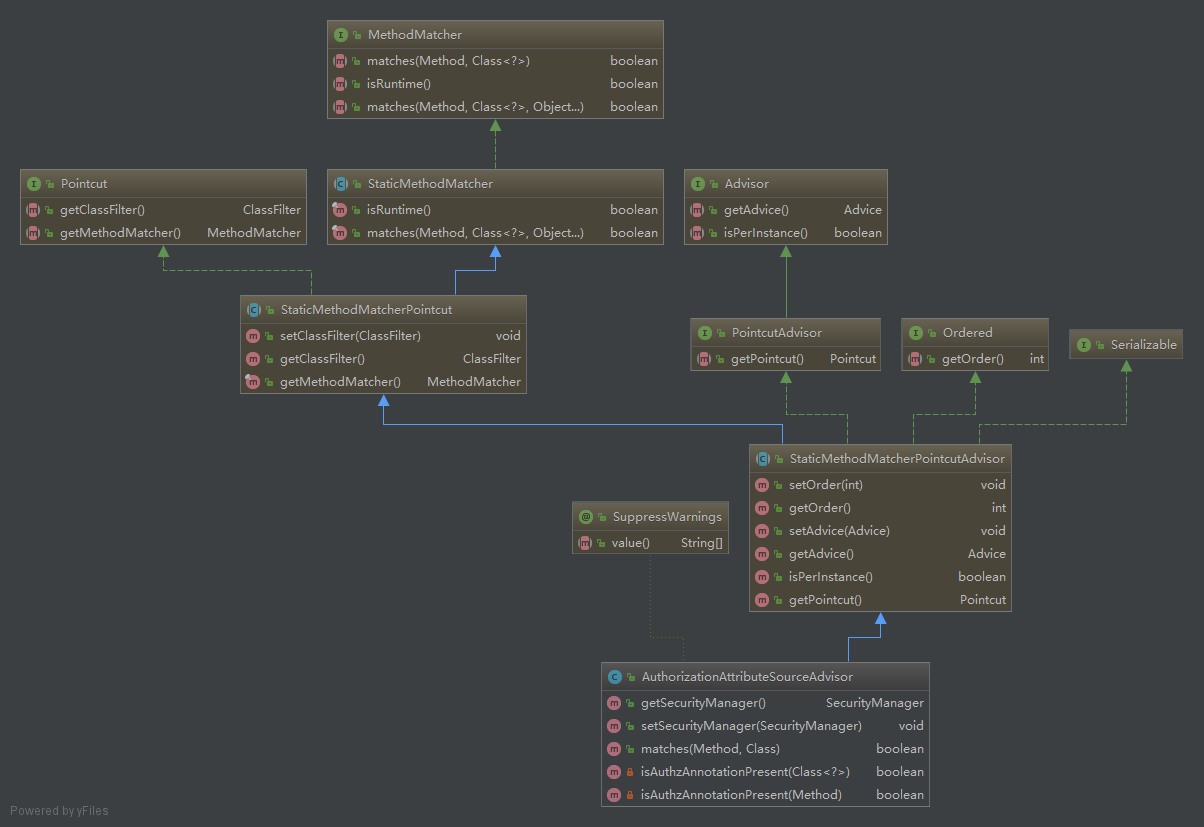
从图中我们可以了解到AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor是一个PointcutAdvisor。如果看代码的话你会发现Pointcut设置的ClassFilter是TureClassFilter,也就是说它对任何类判断都会是通过,只校验方法是否正确。因此AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor中最重要的方法就是matches:
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
public class AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
private static final Class<? extends Annotation>[] AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES =
new Class[] {
RequiresPermissions.class, RequiresRoles.class,
RequiresUser.class, RequiresGuest.class, RequiresAuthentication.class
};
protected SecurityManager securityManager = null;
/**
* Create a new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.
*/
public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor() {
//设置通知
setAdvice(new AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor());
}
public SecurityManager getSecurityManager() {
return securityManager;
}
//设置SecurityManager
public void setSecurityManager(org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager) {
this.securityManager = securityManager;
}
public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) {
Method m = method;
if ( isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) ) {
return true;
}
//The 'method' parameter could be from an interface that doesn't have the annotation.
//Check to see if the implementation has it.
if ( targetClass != null) {
try {
m = targetClass.getMethod(m.getName(), m.getParameterTypes());
//判断方法或是类上是否有shiro关注的注解
return isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) || isAuthzAnnotationPresent(targetClass);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) {
//default return value is false. If we can't find the method, then obviously
//there is no annotation, so just use the default return value.
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean isAuthzAnnotationPresent(Class<?> targetClazz) {
for( Class<? extends Annotation> annClass : AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES ) {
Annotation a = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(targetClazz, annClass);
if ( a != null ) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean isAuthzAnnotationPresent(Method method) {
for( Class<? extends Annotation> annClass : AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES ) {
Annotation a = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, annClass);
if ( a != null ) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
除了Advisor的matches方法外,还需要关注到的是Advisor设置的advise对象:AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor。
个人的理解是AopAllianceAnnotattionsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor是将shiro框架中的MethodInterceptor和aopalliance框架中的MethodInterceptor做了适配,让shiro的处理过程转变成aopalliance的MethodIntercetor的处理过程。而后者是我们所熟悉的spring的拦截器。
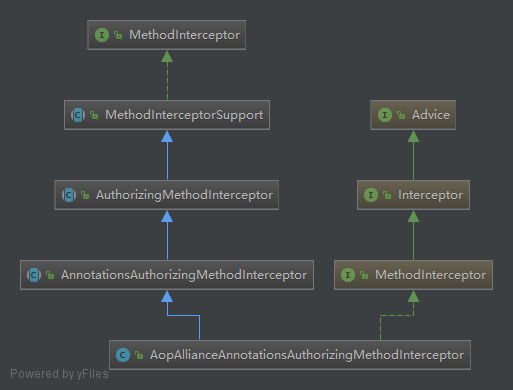
上图可以看到同时实现了两个MethodInterceptor接口。
AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor代码相对简单。
public class AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor
extends AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
public AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor() {
List<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> interceptors =
new ArrayList<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor>(5);
//配置shiro拦截器
AnnotationResolver resolver = new SpringAnnotationResolver();
//we can re-use the same resolver instance - it does not retain state:
interceptors.add(new RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver));
interceptors.add(new PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver));
interceptors.add(new AuthenticatedAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver));
interceptors.add(new UserAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver));
interceptors.add(new GuestAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver));
setMethodInterceptors(interceptors);
}
/**
* Creates a {@link MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} that wraps an
* {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} instance,
* enabling Shiro Annotations in <a href="http://aopalliance.sourceforge.net/">AOP Alliance</a> environments
* (Spring, etc).
*
* @param implSpecificMethodInvocation AOP Alliance {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation MethodInvocation}
* @return a Shiro {@link MethodInvocation MethodInvocation} instance that wraps the AOP Alliance instance.
*/
protected org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation createMethodInvocation(Object implSpecificMethodInvocation) {
final MethodInvocation mi = (MethodInvocation) implSpecificMethodInvocation;
return new org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation() {
public Method getMethod() {
return mi.getMethod();
}
public Object[] getArguments() {
return mi.getArguments();
}
public String toString() {
return "Method invocation [" + mi.getMethod() + "]";
}
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
return mi.proceed();
}
public Object getThis() {
return mi.getThis();
}
};
}
/**
* Simply casts the method argument to an
* {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation} and then
* calls <code>methodInvocation.{@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation#proceed proceed}()</code>
*
* @param aopAllianceMethodInvocation the {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation}
* @return the {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation#proceed() org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation.proceed()} method call result.
* @throws Throwable if the underlying AOP Alliance <code>proceed()</code> call throws a <code>Throwable</code>.
*/
protected Object continueInvocation(Object aopAllianceMethodInvocation) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation mi = (MethodInvocation) aopAllianceMethodInvocation;
return mi.proceed();
}
//通过spring中的拦截器机制发起拦截,并将处理转换成shiro的拦截器处理过程,是一个适配的过程
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
//将spring的MethodInvocation转换成shiro的MethodInvocation对象
org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInvocation mi = createMethodInvocation(methodInvocation);
//调用AuthorizingMethodInterceptor的invoke方法
return super.invoke(mi);
}
}
AuthorizingMethodInterceptor的invoke则会调用asserAuthorized方法。
public abstract class AuthorizingMethodInterceptor extends MethodInterceptorSupport {
//拦截器方法被调用
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
assertAuthorized(methodInvocation);
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
//授权判断,交给子类实现
protected abstract void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws AuthorizationException;
}
AnnotationAuthorizingMethodInterceptor方法实现了assertAuthorized方法,遍历其配置的AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor对象,如果匹配则进行验证。
public abstract class AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor extends AuthorizingMethodInterceptor {
/**
* The method interceptors to execute for the annotated method.
*/
protected Collection<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> methodInterceptors;
public AnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor() {
//配置默认的权限认证拦截器
methodInterceptors = new ArrayList<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor>(5);
methodInterceptors.add(new RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new AuthenticatedAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new UserAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
methodInterceptors.add(new GuestAnnotationMethodInterceptor());
}
public Collection<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> getMethodInterceptors() {
return methodInterceptors;
}
public void setMethodInterceptors(Collection<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> methodInterceptors) {
this.methodInterceptors = methodInterceptors;
}
//遍历所有权限认证拦截器,如果拦截器支持,则使用拦截器认证
protected void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws AuthorizationException {
//default implementation just ensures no deny votes are cast:
Collection<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> aamis = getMethodInterceptors();
if (aamis != null && !aamis.isEmpty()) {
for (AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor aami : aamis) {
if (aami.supports(methodInvocation)) {
aami.assertAuthorized(methodInvocation);
}
}
}
}
}
而权限认证拦截器则是将具体认证过程委托给内部的Handler对象处理。因此拦截器处理的过程大致如下:
AopAllianceAnnotationAuthorizingMethodInterceptor的invoke方法被调用- 调用
assertAuthorized() - 获取内部配置的认证拦截器,逐个调用
assertAuthorized方法 - 内部认证拦截器将认证委托给内部的
AuthorizingAnnotationHandler处理 - 以
RoleAnnotationHandler为例,它会在自己的assertAuthorized方法中校验Subject对象的Role和@RequiredRole中要求的是否一致,不一致则会抛出异常,拦截器不在往下走,因为也无法进入到被拦截的方法里。
总结
Shiro权限认证的过程是通过AOP动态代理实现的。相当于在Spring中配置了一个用于权限认证的拦截器,拦截拥有指定注解(@RequiresAuthentication,@RequiresUser,@RequiresGuest,@RequiresRoles,@RequiresPermissions)的方法。