链表 List
链表实现了内存零碎片的有效组织。
静态链表
链表中有两个成员,数据域和指针域
数据域:我们存储的数据。
指针域:指针指向下一个具体的节点,代表了下一个节点的类型是链表类型。
所谓的指针的指向谁,就是保存了谁的地址
typedef struct node{
int data;//数据域
struct node * next;//指针域的类型表示指向自身
}Node;
int main() {
Node a,b,c,d,e;//声明数据域
Node *head;//链表的表头
head = &a;//头部指针---步骤一
a.data = 1;//赋值内容---步骤二
b.data = 2;
c.data = 3;
d.data = 4;
e.data = 5;
a.next = &b;//链接 改变指针指向 步骤三
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
e.next = NULL;//结尾 步
//访问:利用遍历,当前指针指向第一个元素,并且不为空,打印第一个元素的值,同时能得到第二个元素的地址,第二个元素的地址赋值给当前指针。
Node * pHead = head;//游标,这个指针最后指向链表的末尾的未知空间,如果直接使用链表的头部就会使得链表缺少头部。
while(pHead != NULL) {
printf("%d
",pHead->data);
pHead = pHead->next;
}
return 0;
}
静态链表的封装:
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node;
void linkList(Node *head) {
while(head) {//这里直接用的head相当于链表中另外的一个head,并非实际链表中的head
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
动态链表
他与静态链表的区别是,只有头节点放在栈空间中,其它的成员都放在堆内存中。
尾插法:在尾节点插入元素,每次插入一个元素即成此链表的尾节点
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//头节点为空的链表,头节点中什么也不放
Node * createList() {//空链表
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));//动态的生成空的链表(堆中)类型的节点
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
//尾插法
Node *t = head,*cur;//t指向头指针
int nodeData;
scanf("%d",&nodeData);
while(nodeData) {//输入的数据存在进行创建节点
cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//赋值操作
t->next = cur;//创建的节点插入到链表的末尾
t = cur;//t指向当前的节点
scanf("%d",&nodeData);
}
t->next = NULL;//最后末尾节点置空
return head;
}
//输出并且遍历节点,指向头节点不断地指向下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;//头节点
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;//节点之间的指向变化,节点循环时不断地指向下一个
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
头插法:在头节点后面插入元素,每插入元素就为首节点。
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//头节点中什么也不放
Node * createList() {//空链表
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
//头插法,让新来的节点先有所指向,避免打断原有的指向。
Node *cur;
int nodeData;
scanf("%d",&nodeData);
while(nodeData) {
cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//新节点指向头节点的后一个节点。
head->next = cur;//把待插入的节点指向头节点的后一个节点
scanf("%d",&nodeData);
}
return head;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
插入操作:
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
*/
链表的长度
本质是遍历
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//遍历链表设置一个变量++操作,返回变量
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
list of length:10
*/
查找
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {//节点类型的指针,是由main函数中变量确定的。
head = head->next;//只要是有链表的操作就有头节点指向下一个节点
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//只要是有遍历,就有链表指针的偏移指向的改变
}
return head;
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!");
}else{
printf("find your's list item!");
}
return 0;
}
删除
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}//head->next = pfind
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);//释放节点
pfind = NULL;
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
//在这里可以修改
//pfind->data = 100;
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
list of length:10
find your's list item!
9
8
7
6
4
3
2
1
0
找到并且删除了5
*/
删除的优化
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
/*Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
if(pfind->next == NULL) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}else {
Node *t = pfind->next;//待删除节点的后继
pfind->data = pfind->next->data;//把待删除的元素的后继元素数据赋值给待删除的元素,用待删除元素的后继元素数据覆盖待删除的元素数据
pfind->next = pfind->next->next;//改变指向,待删除元素的后继的后继赋值给待删除元素的后继
free(t);
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
//在这里可以修改
//pfind->data = 100;
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
list of length:10
find your's list item!
9
8
7
6
4
3
2
1
0
*/
链表的冒泡排序
/*
N个数比较N-1次(外层循环)
内层循环的下标每次都是从头开始,比较下一个,内层循环的次数是N-1-i;
*/
int main() {
int arr[5] = {3,4,6,2,1};
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < 4-i;j++) {
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
arr[j] ^=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] ^=arr[j];
arr[j] ^=arr[j+1];
}
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++) {
printf("arr[i] = %d
",arr[i]);
}
}
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
/*Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
if(pfind->next == NULL) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}else {
Node *t = pfind->next;
pfind->data = pfind->next->data;//把待删除的元素的后继元素数据赋值给待删除的元素,用待删除元素的后继元素数据覆盖待删除的元素数据
pfind->next = pfind->next->next;//改变指向,待删除元素的后继的后继赋值给待删除元素的指向赋值给待删除元素的后继
free(t);
}
}
//链表的排序
void popSortList(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
head = head->next;//必须有的
Node *p,*q;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
p = head; //每次内层循环从头开始,每次内层循环遍历结束要重新指向头节点
q = p->next;//q总是指向p的下一个节点,依旧是被比较的节点
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
p->data ^= q->data;
q->data ^= p->data;
p->data ^= q->data;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;//遍历中必须有的改变指针指向
}
}//数据搬运量很大,如果改变指向,不改变数据的移动效能更好
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
popSortList(head);
printf("排序后的链表:");
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
list of length:10
find your's list item!
9
8
7
6
4
3
2
1
0
排序后的链表:0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
*/
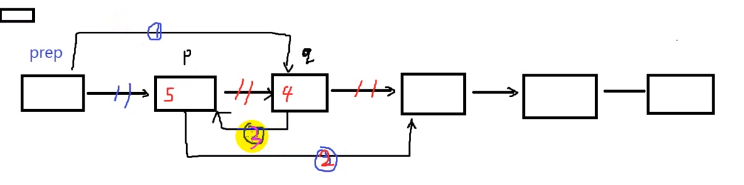
链表冒泡排序的改进:如果数据之间搬运量很大,上述数据交换的方法执行效率不是很高,如果改变指向,不改变数据的移动效能更好
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
/*Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
if(pfind->next == NULL) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}else {
Node *t = pfind->next;
pfind->data = pfind->next->data;//把待删除的元素的后继元素数据赋值给待删除的元素,用待删除元素的后继元素数据覆盖待删除的元素数据
pfind->next = pfind->next->next;//改变指向,待删除元素的后继的后继赋值给待删除元素的指向赋值给待删除元素的后继
free(t);
}
}
//链表的排序
void popSortList(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
head = head->next;
Node * p,*q;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
p = head;//每次内层循环从头开始
q = p->next;//q总是指向p的下一个节点,依旧是被比较的节点
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
p->data ^= q->data;
q->data ^= p->data;
p->data ^= q->data;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}//数据交换,如果数据之间搬运量很大,效率不是很高,如果改变指向,不改变数据的移动效能更好
}
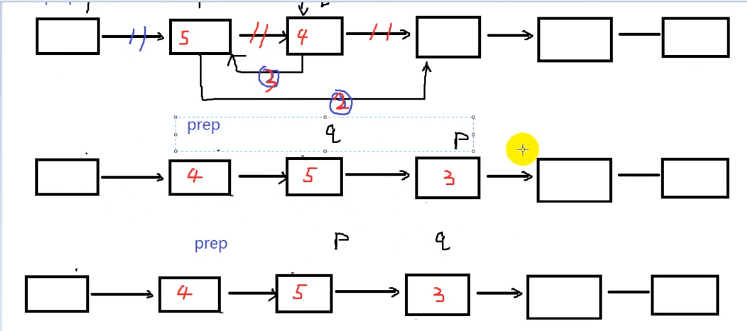
//改进:
void popSortList2(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
Node *prep,*p,*q,*t;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
prep = head;
p = head->next;
q = p->next;
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
prep->next = q;
p->next = q->next;
q->next = p;//有严格的顺序
//eg 1-->4-->3-->5,第一步1-->3,第二步4-->5,第三步3-->4
t = p;
p = q;
q = t;//p要保证在q的前面,保证下次执行是顺序
}//即使不交换指针也要整体指向下一个
prep = prep->next;
p = p->next;
q = p->next;
}
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
popSortList(head);
printf("排序后的链表:");
traverseList(head);
return 0;
}
链表的逆秩
基本思想还是头插法,对一个链表,现申请一个空的链表成员Node *cur,赋值于head->next,之后割裂链表,判断下一个是否存在,存在则赋值给t,把t用头插法插入到链表中,依次循环,待到空为止。
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
/*Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
if(pfind->next == NULL) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}else {
Node *t = pfind->next;
pfind->data = pfind->next->data;//把待删除的元素的后继元素数据赋值给待删除的元素,用待删除元素的后继元素数据覆盖待删除的元素数据
pfind->next = pfind->next->next;//改变指向,待删除元素的后继的后继赋值给待删除元素的指向赋值给待删除元素的后继
free(t);
}
}
//链表的排序
void popSortList(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
head = head->next;
Node * p,*q;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
p = head;//每次内层循环从头开始
q = p->next;//q总是指向p的下一个节点,依旧是被比较的节点
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
p->data ^= q->data;
q->data ^= p->data;
p->data ^= q->data;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}//数据搬运量很大,如果改变指向,不改变数据的移动效能更好
}
//改进:
void popSortList2(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
Node *prep,*p,*q,*t;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
pre = head;
p = head->next;
q = p->next;
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
prep->next = q;
p->next = q->next;
q->next = p;//有严格的顺序
//eg 1--4--3--5,第一步1--3,第二步4--5,第三步3--4
t = p;
p = q;
q = t;//保证下次执行是顺序
}
prep = prep->next;
p = p->next;
q = p->next;
}
}
}
//链表的逆秩
void reverseList(Node *head) {
Node *cur = head->next;
head->next = NULL;//割裂链表,以便后面重新头插
Node * t;
while(cur) {
t = cur;
cur = cur->next;
//头插法
t->next = head->next;
head->next = t;
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
popSortList(head);
printf("排序后的链表:
");
traverseList(head);
printf("逆秩后的链表
");
reverseList(head);
return 0;
}
/*
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
list of length:10
find your's list item!
9
8
7
6
4
3
2
1
0
排序后的链表:
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
逆秩后的链表
9
8
7
6
4
3
2
1
0
*/
链表的销毁
有多少malloc就有多少free
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node * next;//类型表示自身
}Node,*NodePtr;
//创建空的列表
Node * createList() {
Node * head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//插入操作
void insertList(Node *head,int nodeData) {
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL == head) {
exit(-1);
}
cur->data = nodeData;//储存数据
cur->next = head->next;//插入到头节点处
head->next = cur;
}
//指向头节点的下一个节点
void traverseList(Node *head) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
printf("%d
",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
}
int lenList(Node * head) {
int len = 0;
head = head->next;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//查找
Node *searchList(Node *head,int findData) {
head = head->next;
while(head) {
if(head->data == findData) {
break;//找到跳出循环
}
head = head->next;//循环
}
return head;
}
//删除,先找到前驱
/*
int i = 0;
while(i != 100) {
i++;
printf("%d
",i);//i = 100;
}
*/
/*Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}*/
Node *deleteNodeOfList(Node *head,Node *pfind) {
if(pfind->next == NULL) {
while(head->next != pfind) {
head = head->next;//找到pfind前驱
}
head->next = pfind->next;//pfind的前驱指向pfind的后继
free(pfind);
pfind = NULL;
}else {
Node *t = pfind->next;
pfind->data = pfind->next->data;//把待删除的元素的后继元素数据赋值给待删除的元素,用待删除元素的后继元素数据覆盖待删除的元素数据
pfind->next = pfind->next->next;//改变指向,待删除元素的后继的后继赋值给待删除元素的指向赋值给待删除元素的后继
free(t);
}
}
//链表的排序
void popSortList(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
head = head->next;
Node * p,*q;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
p = head; //每次内层循环从头开始
q = p->next;//q总是指向p的下一个节点,依旧是被比较的节点
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
p->data ^= q->data;
q->data ^= p->data;
p->data ^= q->data;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}//数据搬运量很大,如果改变指向,不改变数据的移动效能更好
}
//改进:
void popSortList2(Node *head) {
int len = lenList(head);
Node *prep,*p,*q,*t;
for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++) {
pre = head;
p = head->next;
q = p->next;
for(int j = 0;j < len-1-i;j++) {
if(p->data > q->data) {
prep->next = q;
p->next = q->next;
q->next = p;//有严格的顺序
//eg 1--4--3--5,第一步1--3,第二步4--5,第三步3--4
t = p;
p = q;
q = t;//保证下次执行是顺序
}
prep = prep->next;
p = p->next;
q = p->next;
}
}
}
//链表的逆秩
void reverseList(Node *head) {
Node * cur = head->next;
head->next = NULL;//割裂链表,以便后面重新头插
Node * t;
while(cur) {
t = cur;
cur = cur->next;
//头插法
t->next = head->next;
head->next = t;
}
}
//链表的销毁
//循环链表,不为空时把之前的释放掉。
void destoryList(Node *head) {
Node * t;
while(head) {
t = head;
head = head->next;
free(t);
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = createList();//通过该函数返回一个链表
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
insertList(head,i);
}
traverseList(head);
printf("list of length:%d
",lenList(head));
Node *pfind = searchList(head,5);
if(pfind == NULL) {
printf("not find!
");
}else{
printf("find your's list item!
");
deleteNodeOfList(head,pfind);
}
traverseList(head);
popSortList(head);
printf("排序后的链表:
");
traverseList(head);
printf("逆秩后的链表
");
reverseList(head);
return 0;
}
加入头节点的目的是对于链表的所有操作不需要跟新头指针,头指针在栈上,更新很复杂