Question
Suppose a sorted array is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 might become 4 5 6 7 0 1 2).
You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return -1.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Solution
This problem is solved by binary search in O(log n) time.
Example
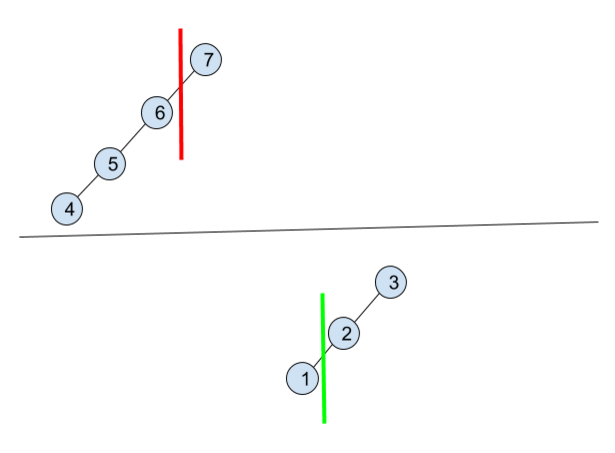
Above is an illustration of rotated sorted array. There are 2 possibilities for median position and 4 sub-situations of possible position of target:
1. red line (start < median)
1.1 target < median && target >= start -> [ start --- mid ]
1.2 else -> [ mid --- end ]
2. green line (start > median)
2.1 target > median && target <= end -> [ mid --- end ]
2.2 else -> [ start -- mid ]
1 public class Solution { 2 public int search(int[] nums, int target) { 3 if (nums == null || nums.length < 1) 4 return -1; 5 int start = 0, end = nums.length - 1, mid; 6 while (start + 1 < end) { 7 mid = (end - start) / 2 + start; 8 if (nums[mid] == target) 9 return mid; 10 if (nums[mid] > nums[start]) { 11 // Red line situation 12 if (nums[start] <= target && target < nums[mid]) { 13 end = mid; 14 } else { 15 start = mid; 16 } 17 } else { 18 // Green line situation 19 if (nums[end] >= target && target > nums[mid]) { 20 start = mid; 21 } else { 22 end = mid; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 if (nums[start] == target) 27 return start; 28 if (nums[end] == target) 29 return end; 30 return -1; 31 } 32 }
Follow-up
What if duplicates are allowed?
Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
Solution
If an array contains duplicate elements, we can't apply binary search.
For example, nums = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, we find that start = mid = end. Under this circumstance, we cannot decide which next step should take.
So we can just use linear traverse to get result, time complexity O(n).