Referrence: Oracle Java Doc
Two levels
top level: public, or package-private (no explicit modifier)
member level: public, private, protected, package-private (no explicit modifier)
Three Modifiers & Four Access Control Types
1. public
A class/ member may be declared with the modifier public, in which case that class is visible to all classes everywhere.
2. package-private (no explicit modifier)
If a class/ member has no modifier (the default, also known as package-private), it is visible only within its own package.
3. private
The private modifier specifies that the member can only be accessed in its own class.
4. protected
The protected modifier specifies that the member can only be accessed within its own package (as with package-private) and, in addition, by a subclass of its class in another package.
Access Levels Chart
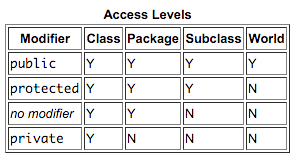
1st col: Whether the class itself has access to the member defined by the access level.
2nd col: Whether classes in the same package as the class (regardless of their parentage) have access to the member.
3rd col: Whether subclasses of the class declared outside this package have access to the member.
4th col: Whether all classes have access to the member.